Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 4th January 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- FSSAI new Trans Fat levels
- National Metrology Conclave
- .International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO)
- Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline
- Scottish independence referendum
- India approved two COVID-19 vaccines for Emergency Use
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS) scheme:
- Gibraltar
- Wooden satellites
- Other important current affairs:
1.FSSAI new Trans Fat levels:

The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has capped the number of trans fatty acids (TFA) in oils and fats to 3% for 2021 and 2% by 2022 from the current permissible limit of 5% through an amendment to the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restriction on Sales) Regulations.
- The revised regulation applies to edible refined oils, vanaspati (partially hydrogenated oils), margarine, bakery shortenings and other mediums of cooking such as vegetable fat spreads and mixed fat spreads.
- Transfats are associated with an increased risk of heart attacks and death from coronary heart disease.
- According to the World Health Organization, approximately 5.4 lakh deaths take place each year globally because of the intake of industrially-produced trans-fatty acids.
- The WHO has also called for the global elimination of transfats by 2023.
Trans fats:
- Trans fatty acids (TFAs) or Trans fats are the most harmful type of fats which can have much more adverse effects on our body than any other dietary constituent.
- These fats are largely produced artificially but a small amount also occurs naturally.
- Thus in our diet, these may be present as Artificial TFAs and/ or Natural TFAs.
- Artificial TFAs are formed when hydrogen is made to react with the oil to produce fats resembling pure ghee/butter.
- In our diet, the major sources of artificial TFAs are partially hydrogenated vegetable oils (PHVO)/vanaspati/ margarine while the natural TFAs are present in meats and dairy products, though in small amounts.
2.National Metrology Conclave:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi is to deliver an inaugural address at the National Metrology Conclave on January 4, 2021.
The conclave will strengthen the role of Precision measurement in various segments that has direct implication in the economic growth of India. It will mainly focus on establishing and developing primary standards, accreditation, quality systems and standardization, regulations and Legal Metrology, conformity assessment.
The theme of National Metrology Conclave 2021: Metrology for the Inclusive Growth of the Nation.
- The National Metrology Conclave is organised by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Physical Laboratory (CSIR-NPL).
- National Metrology Conclave held in New Delhi
- It is held on the 75th foundation day of CSIR, January 4, 2021.
- Key events of the 2021 National Metrology conclave:
- The National Atomic Time Scale is to be dedicated to the nation.
- Bhartiya Nirdeshak Dravya is to be dedicated to the nation.
- Foundation stone of National Environmental Standards Labs to be laid.
- The National Atomic Timescale will create the Indian Standard Time with 2.8 nanoseconds of accuracy. The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is called the Timekeeper of India.
- The time scale is maintained with the help of five caesium atomic clocks.
- Time scale is the time standard.
- Bhartiya Nirdeshak Dravya is a laboratory to support, test, and calibrate Quality Assurance. Currently the Government of India is focusing to support nanotechnology, material science, Ayush, Food and Agriculture and biologics through Bhartiya Nirdeshak Dravyas.
- National Environmental Standards lab will focus on self-Reliance in the certification of ambient air and industrial emission monitoring equipment.
- The Global market value of an air pollution monitoring system is to reach 7000 million USD by 2025.
- The Ministry of environment, forest and climate change has designated the CSIR-NPL the for verifying and certifying the emission and ambient air pollution monitoring equipment.
- Thus, CSIR-NPL is launching the dedicated National Environmental Standards Laboratory.
3.International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO):

The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has become an Associate Member of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO).
IFSC in India:
- The first International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) in the country has been set up at the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT) in Gandhinagar.
- To regulate such institutions, the government established IFSCA on April 27 last year with its head office in Gandhinagar.
- In December 2019, Parliament passed a bill to set up a unified authority for regulating all financial activities at IFSCs in the country.
About IOSCO:
- It is the international body that brings together the world’s securities regulators and is recognized as the global standard-setter for the securities sector.
- IOSCO develops, implements and promotes adherence to internationally recognized standards for securities regulation.
- It works intensively with the G20 and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) on the global regulatory reform agenda.
Members:
- IOSCO was established in 1983. Its membership regulates more than 95% of the world’s securities markets in more than 115 jurisdictions; securities regulators in emerging markets account for 75% of its ordinary membership.
4.Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi is to dedicate the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline to India on January 5, 2021.
Key Highlights of the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline:
- The pipeline is 444 kilometres long.
- The pipeline is to carry natural gas from the Liquefied Natural Gas regasification terminal at Kochi to Mangaluru.
- In its way, it will pass through Ernakulam, Palakkad, Thrissur, Malappuram, Kannur, Kozhikode and Kasaragod districts. Around 8 districts are to benefit from the pipeline project.
- The main junction of the pipeline is at Koottanad. At the junction, the pipeline bifurcates towards Bengaluru and Mangaluru.
- The pipeline is expected to fulfil the gas demand of 80 to 90 million cubic metres of gas per annum.
- The average cost of the project is Rs 5,750 crores.
- Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline project launched was launched in 2009.
- The pipeline is expected to bring in tax revenue of thousand crores of Rupees.
- GAIL will built the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline
- The transportation capacity of the Kochi-Mangaluru Natural Gas Pipeline is 12 million metric standard cubic meters per day.
5.Scottish independence referendum:

Boris Johnson has suggested Scotland should not hold another independence referendum until at least the 2050s, shrugging off claims that Brexit has strengthened the case for a new vote.
- The referendum for Scottish independence was held in 2014, Scotland had voted to remain in the UK.
- The Act of Union between Scotland and England was signed on Jan. 16, 1707.
- It came into effect on May 1 of that year, creating the United Kingdom of Britain.
- The Scottish Parliament was dissolved, and a single Parliament was created at Westminster in London.
- Scotland and England have a complicated history, but the short answer is that Scotland needed an economic boost.
- The country’s finances were a mess after a failed attempt to establish a trading colony in Panama. This unsuccessful scheme was conclusive evidence that Scotland’s future prosperity was best served by union.
- Those who support independence believe Scotland “would be richer” if it breaks from England.
- Proponents of independence want Scotland to make its own decisions about how resources are controlled and money is invested.
- Rather than investing billions of pounds in nuclear weapons, for example, they would focus on things like childcare or programs to retain talent and encourage young Scots to stay.
6.India approved two COVID-19 vaccines for Emergency Use:
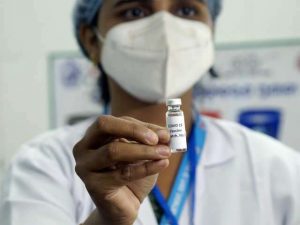
The Drug Controller General of India recently announced that it has authorised two COVID-19 vaccines for restricted Emergency Use in India.
- In a significant development, the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has formally approved Serum Institute and Bharat Biotech vaccines for restricted emergency use against COVID-19 in India.
- Neither Covishield nor Covaxin has completed the crucial Phase-3 trial, under which a vaccine candidate is administered to volunteers at multiple locations across the country.
- The approval was based on a recommendation by a Subject Expert Committee which deliberated for two days on granting approvals to the vaccines.
About Covishield:
- Covishield has been developed by Oxford University in collaboration with Astrazeneca.
- Pune-based Serum Institute of India is their manufacturing and trial partner.
- It uses a replication-deficient chimpanzee viral vector based on a weakened version of a common cold virus.
- This virus causes infections in chimpanzees and contains the genetic material of the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein.
About Covaxin:
- Covaxin is developed by Bharat Biotech and it is India’s first indigenous vaccine against Covid-19.
- Bharat Biotech has developed this vaccine in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research and the National Institute of Virology.
- It is an inactivated vaccine that is developed by inactivating (killing) the live microorganisms that cause the disease.
- This destroys the ability of the pathogen to replicate but keeps it intact so that the immune system can still recognize it and produce an immune response.
Emergency use authorization in India:
- Experts and activists say India’s drug regulations do not have provisions for a EUA, and the process for receiving one is not clearly defined or consistent.
- Despite this, CDSCO has been granting emergency or restricted emergency approvals to Covid-19 drugs during this pandemic for remdesivir and favipiravir.
7.“Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)” scheme:

The scheme was recently reviewed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- ACROSS scheme pertains to the atmospheric science programs of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It addresses different aspects of weather and climate services, which includes warnings for cyclone, storm surges, heat waves, thunderstorms etc.
- Each of these aspects is incorporated as nine sub-schemes under the umbrella scheme “ACROSS” and is implemented in an integrated.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- The scheme will provide improved weather, climate and ocean forecast and services, thereby ensuring transfer of commensurate benefits to the various services.
- It will also provide a sizable number of scientific and technical staff along with requisite administrative support, thereby generating employment.
- To ensure last-mile connectivity of the weather based services to the end -user, a large number of agencies like the Krishi Vigyana Kendras of ICAR, Universities and local municipalities are roped in thus generating employment opportunities to many people.
8.Gibraltar:

Hours before the Brexit transition period ended on New Year’s Eve, Spain announced it had struck a deal with the UK to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar. Officially remaining a British Overseas Territory,
- Gibraltar will now be part of the Schengen zone and follow EU rules, thus ensuring that a hard border does not separate it from the rest of Europe.
- Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory.
- Under the Gibraltar constitution of 2006, Gibraltar is self-governing, with some responsibilities, such as defence and foreign relations, remaining with the British government.
- In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces captured Gibraltar from Spain during the War of the Spanish Succession. The territory was ceded to Great Britain in perpetuity under the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713.
- It remains strategically important, with half the world’s seaborne trade passing through the strait. It is also an important Tourist and cargo ship refuelling centre.
- It is located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula.
- Gibraltar’s territory covers 6.7 square kilometres and shares a 1.2-kilometre land border with Spain. It shares a maritime border with Morocco.
- Gibraltar’s terrain consists of the 426-metre-high Rock of Gibraltar made of Jurassic limestone, and the narrow coastal lowland surrounding it.
- Gibraltar is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea and has “No Contact With The Atlantic Ocean”.
9.Wooden satellites:

In order to solve the problem of space debris, Japanese researchers are to launch wooden satellites by 2023.
- These satellites are made of wood.
- They will burn up without releasing harmful substances into the atmosphere when they plunge back to the earth.
- With this, the satellite will not leave out any waste in space after it completes its service or when it becomes de functional.
- The wooden satellites are being designed by the Sumitomo Forestry and Kyoto University.
- Sumitomo Forestry is a 400-year-old woodworking company of Japan.
- Both entities will research tree growth and the use of wood materials in space.
- They will experiment with different types of wood in extreme environments on earth.
- All the satellites that re-enter the earth atmosphere burn and create tiny Alumina particles.
- These particles float in the upper atmosphere for many years.
- According to NASA, 95% of man-made objects in orbit were space junk. These objects are dangerous to functioning live satellite.
Space debris:
- According to the European space agency, there are 128 million pieces of debris in the orbit.
- Out of these only 34000 objects are larger than 10.
- However, when these larger objects collide, they produce smaller ones.
- The smaller particles can travel more than 20000 miles per hour that collide with other particles to make even smaller particles.
According to the World Economic Forum, there is more than 6000 satellite circling the earth.
- Out of these 60% of them are de-functional. It is estimated that a thousand satellites will be launched every year this decade.
- With this, there will be 15000 satellite by 2028.
- Therefore, potential damages to living satellites will increase.
- In 2006 a very tiny piece of space debris collided with the International Space Station and took out a chip of the heavily reinforced window.
- This costed severe damages.
- Therefore, it is essential to develop solutions like wooden satellites to completely remove space debris.
Other important current affairs:
1. China’s National Defence Law has been amended.
- Key changes:
- Gives the Central Military Commission (CMC) greater power in mobilizing resources to protect a new and broader definition of what constitutes the national interest.
- Experts say the phrase “development interests” included the protection of China’s economic activities and assets overseas, such as those under the Belt and Road Initiative, as a reason for defence mobilisation.
- The amendment broadened the scope of key security fields beyond land borders, maritime and air defence, to include outer space and electromagnetic networks.
- The amendment also said China “will participate in global security governance, join multilateral security talks and push for and set up a set of international rules that is widely accepted, fair and reasonable”.
- The change comes amid a push for closer civil-military fusion, with a target to make the PLA a “world-class” military, or on par with the United States military, by 2049, when the People’s Republic of China turns 100.
2.Scientists at the CSIR-National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (NIIST) at Pappanamcode here in Kerala have come up with a new product, banana grit or granules, developed from raw Nendran bananas.
- The product resembles to ‘rava’ and broken wheat. Billed as an ideal ingredient for a healthy diet, banana grit can be used for making a wide range of dishes, according to the NIIST.
- The granules can be used for making upma, or it can be mixed with banana powder for porridge, with milk or coconut milk for use as a health drink.
- The concept was introduced to utilise the presence of resistant starch in bananas, which is reported to improve gut health.
- Hence, the dishes prepared with banana grit and its by-product, banana powder, incline to the new focus on gut health, which the scientific community is widely discussing now to maintain health and well-being.
- Changalikodan Nendran Banana or famously known as Changalikodan is a banana variety originated and cultivated in Chengazhikodu village of Thrissur District in Kerala
- Changalikodan, now are cultivated on the banks of the Bharathapuzha river.
- Changalikodan got Geographical indication registration from the Geographical Indications Registry, Chennai.
- Generally consumed ripe, Nendran banana also finds use in typical Kerala dishes such as avial and thoran.
3.The Karnataka government has allowed all shops and commercial establishments to operate round the clock all days of the week for the next three years under provisions of the Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishments Act (1961).
- The revision of rules by the Labour Department is expected to help businesses recover from financial difficulties they faced during the coronavirus-induced lockdown which led to a decline in economic activity.
- The rules permits only shops and commercial establishments employing ten or more persons to operate 24×7. The period of this extension of timings will be in force till January 2, 2024.
- While the permitted time allowed for each employee to work in a week is fixed at 48 hours per week (eight hours a day), employers can ask them to work overtime.
- However, the period of work including overtime should not exceed 10 hours a day.
- The employees are also entitled to get overtime wages, which the employer is directed to credit to their savings bank account as prescribed under the Payments of Wages Act (1963).
4.The UK began 2021 by abolishing a 5 percent Value Added Tax (VAT) on women’s sanitary products, often referred to as the “tampon tax” and which many activists had described as sexist.
- It now joins the list of countries that have already eliminated this tax, which includes India, Australia, and Canada.
- The measure is part of a wider UK government effort called ‘End Period Poverty’.
- Scotland, which is a part of the UK, made history in November 2020 by becoming the first country in the world to make period products free of cost to those who need them.
- Until December 31, the UK was a part of the EU, where period products such as sanitary napkins and tampons are classified as non-essential, and member states are required to levy a 5 per cent tax on them.
- Now that the UK is out of the 27-member bloc, it is not bound by its directives, under which sanitary products had been subjected to five different VAT rates since 1973– with the lowest 5 per cent slab being applicable since 2001.
5.The Nation’s first indigenously developed DNA vaccine candidate against COVID-19, ZyCoV-D, by M/s Zydus Cadila has been approved by Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI), for conduct of the Phase III clinical trials.
- The candidate has been supported by the National Biopharma Mission (NBM) under the aegis of BIRAC and the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India.
- Zydus Cadila completed Phase-I/II clinical trials of this DNA Vaccine candidate, in India, in more than 1,000 participants and interim data indicated that the vaccine is safe and immunogenic when three doses were administered intradermally.
- Based on the recommendations of the Subject Expert Committee, which reviewed the interim data, the DCGI has accorded permission for conducting Phase-III clinical trial in 26,000 Indian participants.
6.The United States recently passed the Malala Yousafzai Act for Pakistani Women.
- The Act requires the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to award at least 50% of scholarship to Pakistani women between 2020 and 2022.
- It requires the USAID to leverage investments by the Pakistani private sector in the United States.
- This is being done to improve and expand access to education programs in Pakistan.
- The act makes it mandatory for the USAID to brief the US Congress about the number of scholarships provided under the program.
- This includes a percentage of recipients who are involuntarily pushed out of the program for their failure to meet program requirements as well.
- The USAID has so far awarded more than 6000 scholarships to the young women of Pakistan since 2010.
- These scholarships help Pakistani women to receive Higher Education in Pakistan.
- The Malala Yousafzai Scholarship Act aims to expand this program.
- Malala Yousafzai is a Pakistani activist for female education.
- She is also the youngest Nobel Prize Laureate. She fought against the Taliban for women’s education.
- The Taliban had banned girls from attending schools.
7.Every year, World Braille Day is celebrated on January 4 by United Nations and several other international organizations. The day is celebrated to create awareness of the importance of Braille as a means of communication in the realization of human rights for the blind.
- It is celebrated on January 4 because the day marks the birthday of Louis Braille, the creator of this writing system.
- He was born in France in 1809.
- Braille is the representation of alphabetic and numerical symbols using six dots.
- The dots represent the letters and numbers and mathematical, musical and scientific symbols as well.
- Braille was invented by Louis Braille in the 19th century in France.
- India adopted the uniform Braille codes for different languages in 1951.
- India established the first-ever Braille plant called Central Braille Plant in Dehradun. In 1954, the Central Braille press was established to manufacture Braille appliances.
- The press produces simple equipment such as Braille slate, stylus, and arithmetic Braille




