Today Current Affairs: 10th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Giant Pandas :IUCN Status:

Giant pandas are no longer classified as endangered but are still vulnerable, Chinese officials say.
- The classification was downgraded as their number in the wild has reached 1,800.
- The new classification comes years after the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) had already removed the animal from its endangered species list and re-labelled it as vulnerable in 2016.
- At the time, however, Chinese officials had disputed the decision, saying that it could mislead people into believing that conservation efforts could be relaxed.
- This week’s announcement by China’s environmental ministry is the first time the animal’s status was changed on its own endangered species list, which uses similar standards as the Swiss-based IUCN.
- Experts have said that the success is largely due to Chinese efforts to recreate and repopulate bamboo forests. Bamboo makes up some 99 per cent of their diet, without which they are likely to starve.
BRICS Innovation Cooperation Action Plan (2021-24):

All BRICS countries have agreed to the STI-led BRICS Innovation Cooperation Action Plan (2021-24) proposed by India during 12th Meeting of BRICS S&T Steering Committee.
- Indian had proposed the plan to facilitate sharing of experiences of each other’s innovation ecosystem and networking of innovators and entrepreneurs.
- The Details of the Action Plan would be worked out by BRICS Science, Technology Innovation Entrepreneurship partnership (STIEP) Working Group.
- It was agreed that the proposal may be forwarded to BRICS STIEP working group through the respective country’s STI focal point.
- Department of Science and Technology (DST), India, hosted the 12th Meeting of BRICS S&T Steering Committee on 8th July, 2021. Scientific ministries and agencies of all BRICS countries participated in it.
India And The United Kingdom (UK) : Meeting

India and the United Kingdom (UK) held the inaugural meeting of the India-UK Financial Markets Dialogue (‘the Dialogue’) virtually.
- The Dialogue was established at the 10th Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD) in October 2020 to deepen bilateral ties in the financial sector.
- The Dialogue was led by senior officials from the Indian side by the Ministry of Finance and from UK, Her Majesty’s Treasury, with participation from Indian and UK independent regulatory agencies, including the RBI, SEBI, Bank of England, and the Financial Conduct Authority.
Discussions during the Dialogue were focused on four themes:
- GIFT (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) City, India’s flagship international financial centre,
- banking and payments,
- insurance, and
- capital markets
India-Nepal Rail Services Agreement (RSA):

India and Nepal have signed a Letter of Exchange (LoE) to the India-Nepal Rail Services Agreement (RSA) 2004.
- It will allow all authorized cargo train operators to utilize the Indian railway network to carry Nepal’s container and other freight – both bilateral between Indian and Nepal or third country from Indian ports to Nepal.
- The authorized cargo train operators include public and private container trains Operators, automobile freight train operators, special freight train operators or any other operator authorized by Indian Railways.
About Rail Services Agreement (RSA), 2004:
- The Rail Services Agreement was executed in 2004 between the Ministry of Railways, Government of India and the Ministry of Commerce, the Govt. of Nepal for introduction of freight train services between these two countries to and from Birgunj (Nepal) via Raxaul (India).
- The agreement guides movement between India and Nepal by rail.
- The Agreement shall be reviewed every five years and may be modified (through Letters of Exchange) by the Contracting Parties by mutual consent.
- In the past, there have been amendments to RSA through LoE on three occasions.
- First such amendment was in 2004.
- Second LoE was signed in 2008 at the time of introduction of bilateral cargo between the two countries which required introduction of new customs procedures.
- Third LoE was signed in 2016 enabling rail transit traffic to/from Visakhapatnam Port in addition to existing provision of rail transportation through Kolkata/Haldia Port.
Benefits of the Latest Agreement:
- Allow Market Forces to Operate: This liberalization will allow market forces (such as consumers and buyers) to come up in the rail freight segment in Nepal, and is likely to increase efficiency and cost- competitiveness, eventually benefiting the Nepalese consumer.
- Reduce Transportation Cost: The liberalisation will particularly reduce transportation costs for automobiles and certain other products whose carriage takes place in special wagons and will boost rail cargo movement between the two countries.
- Enhance Regional Connectivity: Wagons owned by Nepal Railway Company will also be authorized to carry Nepal-bound freight (inbound and outbound on Kolkata/Haldia to Biratnagar/Birganj routes) over the Indian Railways network as per IR standards and procedures.
- The signing of this LoE marks another milestone in India’s efforts to enhance regional connectivity under the “Neighbourhood First” policy.
Joint Communication For Tribal Communities:

A joint communication was signed by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change which is aimed at giving more power to the tribal communities in managing the forest resources.
Joint Communication:
- It pertains to more effective implementation of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 and for harnessing the potential for livelihood improvement of the Forest Dwelling Scheduled Tribes (FDSTs) and other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFDs).
- State forest departments will carry out verification of claims for forest rights, mapping of forest lands involved and provision of necessary evidence as required, authentication of records, joint field inspections, awareness generation etc.
- The lack of recognition of forest rights has left tribal and forest dwelling communities across the country insecure of tenure and fear of eviction from their lands.
- State forest departments are to undertake projects for value chain addition including capacity building of primary collectors, new harvesting methods, storage, processing and marketing of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFP).
- A nodal agency to be designated for specific non-timber forest products as supply chain platforms in collaboration with TRIFED, Ministry of Ayush, MFP (Minor Forest Produce) Federations, Van Dhan Kendras etc.
Kappa Variant: Covid-19:
Two cases of the Kappa variant of Covid-19 have been recorded in Uttar Pradesh (UP).
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), Kappa is one of the two Covid-19 variants, the other being Delta, first identified in India.
- Earlier a new variant Lambda was reported from Peru.
- As India raised objection over the B.1.617.1 mutant of the novel coronavirus being termed an “Indian Variant”, the WHO had named this variant ‘Kappa’ and B.1.617.2 ‘Delta’ just as it named various variants of the coronavirus using Greek alphabets.
- The Delta and Kappa variants are actually siblings, the direct descendants of a variant that earlier used to be referred to as the double mutant, or B.1.617.
- It is still listed among ‘variants of interest’ and not ‘variants of concern’ by the WHO.
Variants of Interest:
- They are SARS-CoV-2 variants with genetic changes that are predicted or known to affect virus characteristics such as transmissibility, disease severity, immune escape, diagnostic or therapeutic escape.
- Examples: Lambda, Iota, Eta and Kappa variants.
Variant of Concern:
- A variant for which there is evidence of an increase in transmissibility, more severe disease (e.g., increased hospitalizations or deaths), significant reduction in neutralization by antibodies generated during previous infection or vaccination, reduced effectiveness of treatments or vaccines, or diagnostic detection failures.
- Examples: Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants.
Jammu And Kashmir Delimitation Commission:
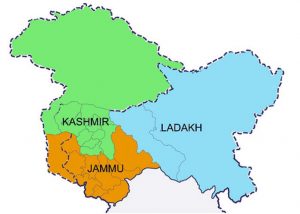
The Jammu and Kashmir Delimitation Commission has said that it will base its final report on the 2011 Census and will also take into account the topography, difficult terrain, means of communication and convenience available for the ongoing delimitation exercise.
Delimitation exercise in J&K:
- The first delimitation exercise, carving out 25 assembly constituencies in the then state, was carried out by a Delimitation Committee in 1951.
- The first full-fledged Delimitation Commission was formed in 1981 and it submitted its recommendations in 1995 on the basis of 1981 Census. Since then, there has been no delimitation.
- In 2020, the Delimitation Commission was constituted to carry out the exercise on the basis of 2011 Census, with a mandate to add seven more seats to the Union Territory’ and grant reservations to SC and ST communities.
- Now, the total number of seats in Jammu and Kashmir will be raised to 90 from the previous 83. This is apart from 24 seats which have been reserved for areas of PoK and have to be kept vacant in the Assembly.
- The Delimitation Commission for Jammu and Kashmir was constituted by the Centre on March 6 last year to redraw Lok Sabha and assembly constituencies of the union territory in accordance with the provisions of the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which bifurcated the state into union territories of J&K and Ladakh.
What is Delimitation?
- Delimitation literally means the process of fixing limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies in a state that has a legislative body.
Who carries out the exercise?
- Delimitation is undertaken by a highly powerful commission. They are formally known as Delimitation Commission or Boundary Commission.
- These bodies are so powerful that its orders have the force of law and they cannot be challenged before any court.
Composition of the Commission:
- According to the Delimitation Commission Act, 2002, the Delimitation Commission will have three members:
- a serving or retired judge of the Supreme Court as the chairperson,
- Chief Election Commissioner or Election Commissioner nominated by the CEC
- State Election Commissioner as ex-officio members.
WHO Pre-qualification, Or Emergency Use Listing (EUL):
A WHO pre-qualification, or Emergency Use Listing (EUL), is necessary for a vaccine company to supply vaccines to global facilities such as COVAX or international procurement.
- So far, eight vaccines have got an EUL from the WHO.
- WHO will also take a decision on including Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin in its list shortly.
About WHO’s Emergency Use List (EUL):
- The WHO Emergency Use Listing Procedure (EUL) is a risk-based procedure for assessing and listing unlicensed vaccines, therapeutics and in vitro diagnostics with the ultimate aim of expediting the availability of these products to people affected by a public health emergency.
- To be eligible, the following criteria must be met:
- The disease for which the product is intended is serious or immediately life threatening, has the potential of causing an outbreak, epidemic or pandemic and it is reasonable to consider the product for an EUL assessment, e.g., there are no licensed products for the indication or for a critical subpopulation (e.g., children).
- Existing products have not been successful in eradicating the disease or preventing outbreaks (in the case of vaccines and medicines).
- The product is manufactured in compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in the case of medicines and vaccines and under a functional Quality Management System (QMS) in the case of IVDs.
- The applicant undertakes to complete the development of the product (validation and verification of the product in the case of IVDs) and apply for WHO prequalification once the product is licensed.
Himalayan Yaks:

The National Research Centre on Yak (NRCY) at Dirang in West Kameng district, Arunachal Pradesh, has tied up with the National Insurance Company Ltd. for insuring their livestock.
- The insurance policy would shield the yak owners against the risks posed by weather calamities, diseases, in-transit mishaps, surgical operations and strikes or riots.
- According to the policy, the owners would have to get their yaks ear-tagged and provide a proper description in order to get their animals insured.
About Himalayan Yaks:
- Yak is accustomed to very cold temperatures and can up to minus 40 degrees.
- Two other prominent nomadic communities engaged in yak rearing are Changpas and Dokpas in Ladakh, Sikkim and Himachal Pradesh.
- Currently considered to be Vulnerable by the IUCN.
- The number of yaks across the country declined by almost 24.7% between 2012 and 2019.
- Yak population in India is found in Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal and Uttarakhand.
- IUCN Red list status: Vulnerable
- Listed under Appendix I of CITES
- Indian WildLife (Protection) Act of 1972: Schedule II
India Industrial Land Bank (IILB):

It is a GIS-based portal with all industrial infrastructure-related information such as connectivity, infra, natural resources and terrain, plot-level information on vacant plots, line of activity, and contact details.
- It acts as a one-stop repository of all industrial infrastructure-related information.
- It serves as a decision support system for investors scouting for land remotely.
- It has around 4,000 industrial parks mapped across an area of 5.5 lakh hectare of land and is expected to achieve pan-India integration by December 2021.
- It is under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).




