Today Current Affairs: 11th October 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Air India:

After 68 years, Air India is all set to return to the Tata fold. Tata Sons subsidiary Talace Pvt. Ltd. emerged as the winning bidder for the debt-laden national carrier after quoting an enterprise value of ₹18,000 crore. The government will take a hit of ₹28,844 crore.
- The Tatas will own a 100% stake in Air India, as also 100% in its international low-cost arm Air India Express and 50% in the ground handling joint venture, Air India SATS.
- Apart from 141 aircraft and access to a network of 173 destinations, including 55 international ones, Tatas will also have the ownership of iconic brands such as Air India, Indian Airlines and the Maharajah.
- The Group of Ministers led by Home Minister Amit Shah approved the winning bidder in its meeting on October 4. The government aims to complete the transaction by December 2021, when it will transfer its shares and hand over the airline to the new buyer.
- Talace quoted an enterprise value of ₹18,000 crore. Of this, ₹15,300 crore is the debt component of Air India to be taken on by the winner, and the remaining ₹2,700 crore will be cash paid to the government
- It will provide a very strong market opportunity to the Tata Group’s presence in the aviation industry. Tata Sons owns 84% share in Air Asia, which has a market share of 5.2%, and 51% stake in Vistara, which has a market share of 8.3%.
- Together with Air India’s market share of 13.2%, Tatas could be in control of 26.7% market share, and be the second biggest player after IndiGo.
Nobel Prize For Peace:

In an age marked by authoritarian regimes around the world, misinformation and hate speech, the Nobel Prize for Peace was awarded to two journalists who have been running independent news organisations in their countries, often under the threat of detention and even death.
- Maria Ressa of the Philippines and Dmitry Muratov of Russia received the Prize “for their courageous fight for freedom of expression”.
- An investigative journalist, Ressa in 2012 co-founded Rappler, a digital media platform for investigative journalism, which she continues to head. Rappler has “focused critical attention” on President Rodrigo Duterte regime’s controversial, murderous anti-drug campaign.
- In the RSF’s 2021 World Press Freedom Index, the Philippines ranked 138 of 180 nations (India was ranked lower, at 142).
- Dmitry Muratov “has for decades defended freedom of speech in Russia under increasingly challenging conditions”. During the Vladimir Putin regime, Russia has ranked 150 in the RSF’s 2021 World Freedom Index.
- Five years after Muratov left the popular daily Komsomolskaya Pravda, he along with around 50 colleagues started Novaja Gazeta in 1993, as one of its founders. He has served as the newspaper’s editor-in-chief since 1995
G-Sec Acquisition Programme (GSAP):

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is halting its bond buying under the G-Sec Acquisition Programme (GSAP) for now.
- It said that the measure had succeeded in ensuring adequate liquidity and stabilising financial markets.
- Coupled with other liquidity measures, it facilitated congenial and orderly financing conditions and a conducive environment for the recovery.
Government Security Acquisition Programme (G-SAP):
- The G-Sec Acquisition Programme (G-SAP) is basically an unconditional and a structured Open Market Operation (OMO), of a much larger scale and size.
- RBI has called the G-SAP as an OMO with a ‘distinct character’.
- The word ‘unconditional’ here connotes that RBI has committed upfront that it will buy G-Secs irrespective of the market sentiment.
Objective:
- To achieve a stable and orderly evolution of the yield curve along with management of liquidity in the economy.
Significance:
- The GSAP would provide more comfort to the bond market. As the borrowing of the Government increased this year, RBI has to ensure there is no disruption in the Indian market.
- The programme will help to reduce the spread between repo rate and the ten-year government bond yield.
- The G-SAP will almost serve the purpose of an OMO calendar, which had been on the bond market’s wish list for a long time.
Open market operations :
- It is the sale and purchase of government securities and treasury bills by RBI or the central bank of the country.
- The objective of OMO is to regulate the money supply in the economy.
- It is one of the quantitative monetary policy tools.
Rohingya Crisis:

Bangladesh is planning to send more than 80,000 Rohingya refugees to a remote island- Bhasan Char- in the Bay of Bengal after sealing an agreement for the United Nations to provide help.
- Some 19,000 of the Muslim refugees from Myanmar have already relocated from crowded camps on the mainland to Bhashan Char island, despite doubts raised by aid groups.
- Bhasan Char is an island specifically developed to accommodate 1,00,000 of the 1 million Rohingya who have fled from neighbouring Myanmar.
- While human rights groups have criticised the move and some are being forced to go against their will, the government has insisted that refugees moving to the island have done so voluntarily.
Who are Rohingyas?
- They are an Ethnic group, mostly Muslims.
- They were not granted full citizenship by Myanmar.
- They were classified as “resident foreigners or associate citizens”.
- Ethnically they are much closer to Indo-Aryan people of India and Bangladesh than to the Sino-Tibetans of the Country
Digital Divide:

The Supreme Court has flaggedthe consequences of growing digital divide.
- It observed, the digital divide caused by online classes will defeat the fundamental right of every child to education
- Little children whose parents are too poor to afford laptops, tablets or an “optimum” Internet package at home for online classes during the pandemic have dropped out of school and even run the danger of being drawn into child labour or worse, child trafficking.
- Even, the right to education has now hinged on who could afford “gadgets” for online classes and who could not.
- The court was hearing a petition filed by private school managements challenging a Delhi High Court order of September 2020, directing them to provide their 25% quota EWS/DG students online facilities free of cost.
- The High Court had said the schools could get reimbursement from the government.
- The Delhi government had said it had no resources to reimburse the schools for the online gadgets.
- Though the Supreme Court had stayed the High Court order in February 2021, the court said both the Centre and States such as Delhi could not bow out of their responsibilities towards children.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS):
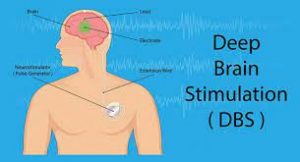
Physicians at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) have successfully treated a patient with severe depression by recognising and tapping into the brain circuits linked with depressive brain patterns.
- The physicians have tried to reset these patterns, which they have said is the equivalent of using a pacemaker for the heart. The work, which represents a landmark in the use of neuroscience to treat psychiatric disorders, has been published in the journal Nature Medicine.
- The doctors used an existing technique called deep brain stimulation (DBS), customising it for this patient’s case.
- DBS is a surgical procedure in which electrodes are implanted into certain brain areas. These electrodes, or leads, generate electrical impulses that control abnormal brain activity.
- The electrical impulses can also adjust for the chemical imbalances within the brain that cause various conditions.
A DBS system has three components
- The electrode, or lead. This is a thin, insulated wire inserted through a small opening in the skull and implanted into a specific brain area.
- The extension wire. This too is insulated, and is passed under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder, connecting the electrode to the third component of the system.
- The internal pulse generator (IPG) is the third component. It is usually implanted under the skin in the upper chest.
Market Based Economic Despatch (MBED):

Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) has released the Framework for Implementation of Market Based Economic Despatch (MBED) – Phase1 for lowering the cost of power purchase to Consumers.
- Implementing an Market Based Economic Despatch (MBED) is an essential next step in reforming electricity market operations and in moving towards “One Nation, One Grid, One Frequency, One Price” framework.
- MBED will ensure that the cheapest generating resources across the country are despatched to meet the overall system demand and will thus be a win-win for both the distribution companies and the generators and ultimately result in significant annual savings for the electricity consumers.
- The implementation of Phase 1 of MBED is planned to start with effect from 1st April 2022. Before this CERC will align their regulations and mock drill will be carried out to ensure that the system runs smoothly.
Corbett National Park : Now Ramganga National Park

Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change Ashwini Kumar Choubey proposed to change the name of Corbett National Park to Ramganga National Park.
- Jim Corbett’s name has lent itself to India’s oldest and most celebrated national parks and to the cottage industry that has grown around it.
- Corbett’s name lives on in and around the forests of Uttarakhand where the celebrated hunter-naturalist once lived and whose efforts led to the establishment of the national park.
- Name history: But the Park was not always called Corbett. Set up in 1936 as India’s — and Asia’s — first national park, it was called Hailey National Park after Sir Macolm Hailey, the governor of the United Province.
- It was renamed Ramganga National Park, named after the river that flows through it, shortly after Independence and was rechristened yet again as Corbett National Park in 1956.
- It was at the insistence of Corbett’s friend, the great freedom fighter from Kumaon and the first chief minister of Uttar Pradesh, Govind Ballabh Pant, that the park was renamed after him, to honour his conservation efforts.
- Located in the Himalayan foothills near the tourist hill station of Nainital, Corbett National Park is spread over 520 sq km and is part of the Corbett Tiger Reserve which is over 1,288 sq km.
- The national park along with the neighbouring 301-sq km-Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary together make the critical tiger habitat of the Corbett Tiger Reserve.
World Bank GDP Projection For India:

According to the World Bank, India’s economy, South Asia’s largest, is expected to grow by 8.3% in the fiscal year 2021-22.
- The South Asia economic focus report projects the region to grow by 7.1% in 2021 and 2022.
- It is a biannual economic update presenting recent economic developments and a near-term economic outlook for South Asia.
- Other Major reports of the World bank include Human Capital Index, World Development Report. Recently, it has decided to discontinue the practice of issuing ‘Doing Business reports’.
GDP Growth:
- The projected growth (8.3%) is supported by an increase in public investment to bolster domestic demand and schemes like the Production Linked Incentive (PIL) to boost manufacturing.
- India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased by 20.1% in the first quarter (April-June quarter) of financial year 2021-22 in the backdrop of “a significant base effect, limited damage to domestic demand and strong export growth”.
- In the first quarter of financial year 2020-21, GDP of India contracted by 24.4% because of nationwide coronavirus lockdown.
- The World Bank also observed that the disruption in India’s economy during the second wave of the pandemic was limited, compared to the
- Economic recovery across various sectors in India has been unequal.
- Manufacturing & construction sectors recovered steadily in 2021 but low-skilled individuals, self-employed people, women and small firms were left behind.
- The extent of recovery in the financial year 2021-’22 will depend on how fast household incomes recover and activity across informal sector & smaller firms normalises.
- India’s economic prospects will be determined by its pace of vaccination against Covid-19 and successful implementation of agriculture & labour reforms.
- Economic data such as ‘GDP growth rate’ are calculated on a year-on-year basis.
- Thus, a low growth rate in the previous year leads to a low base for the number in the current year.
Risks associated with the extent of recovery include- worsening of financial sector stress, slowdown in vaccination, higher inflation constraining monetary-policy support etc.
Monetary Policy Report: RBI

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released the Monetary Policy Report (MPR) for the month of October 2021.
- It kept the policy rate unchanged for the Eighth time in a row maintaining an accommodative stance till the recovery is durable.
Unchanged Policy Rates:
- Repo Rate – 4%.
- Reverse Repo Rate – 3.35%.
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) – 4.25%.
- Bank Rate- 4.25%.
GDP Projection:
- Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth for 2021-22 has been retained at 9.5%.
Inflation:
- RBI has revised the projection for Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation to 5.3% from 5.7% in August 2021.
India And China Patrols Face Off In Tawang:

Chinese soldiers were detained, let off later.
- Face-offs occurred because of the differing areas of perception due to the demarcated boundary, and as both sides undertook patrolling activities up to their line of perception.
- Tawang was historically part of Tibet.
- The 1914 Simla Accord defined the McMahon Line as the new boundary between British India and Tibet. By this treaty Tibet relinquished some of its territories, including Tawang, to the British. But it was not recognised by China.
- In 1950, Tibet lost its de facto independence and was incorporated into the newly established People’s Republic of China.
- Later, in 1959, when the current Dalai Lama fled Tibet, he came into India through Tawang.
- During the Sino-Indian war of 1962, Tawang fell briefly under Chinese control, but China voluntarily withdrew its troops at the end of the war.
- Tawang again came under Indian administration, but China has not relinquished its claims on most of Arunachal Pradesh including Tawang.
Stubble Burning:

The Commission for Air Quality Management has said that a reduction in the area under paddy cultivation in Haryana, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh, as well as a shift away from paddy varieties that take long to mature, could see a reduction in stubble burning this year.
Reasons for this:
- The total paddy area in Haryana, Punjab and the eight NCR (National Capital Region) districts of Uttar Pradesh has reduced by 7.72% during the current year as compared to last year.
- Total paddy straw generation from the non-basmati variety of rice is likely to be reduced by 12.42% during the current year as compared to the previous year.
- Both Central and State Governments of Haryana, Punjab and U.P. have been taking measures to diversify crops as well as to reduce the use of PUSA-44 variety of paddy.
- Crop diversification and moving away from PUSA-44 variety with short duration High Yielding Varieties are part of the framework and action plan for control of stubble burning.
Stubble Burning:
- It is a common practice followed by farmers to prepare fields for sowing of wheat in November as there is little time left between the harvesting of paddy and sowing of wheat.
- Impact: Stubble burning results in emission of harmful gases such carbon diaoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide along with particulate matter.
Palk Bay Scheme:
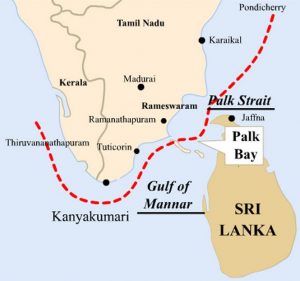
The Union Government is considering increasing the unit cost of deep-sea fishing vessels under the Palk Bay scheme to make it more attractive to fisherfolk.
Palk Bay scheme:
- Launched in July 2017 under the Blue Revolution programme.
- The scheme is financed by the Union and the State Governments with beneficiary participation.
- It had envisaged the provision of 2,000 vessels in three years to the fishermen of the State and motivate them to abandon bottom trawling.
- It was planned to have 500 boats built in the first year (2017-18). Of the unit cost of each vessel (₹80 lakh), 50% would be borne by the Centre, 20% by the State government and 10% by the beneficiary, and the remaining 20% would be met through institutional financing.
- The Deep Sea fishing plan is to remove as many trawl vessels from the Palk Bay as possible.
- Potential beneficiaries of the deep see fishing project should possess a registered, seaworthy trawl vessel of over 12m in length that must be scrapped or disposed of outside the Palk Bay.
- The disposed vessel should also have been physically verified.
- Equally important, new replacement tuna long liner boats cannot trawl or operate in the Palk Bay.
- Beneficiaries are not allowed to sell their boats within five years of obtaining them.
Significance of the scheme:
- The scheme was envisioned as the remedy to the Palk Bay fishing conflict.
- The Centre feels that deep sea fishing is the “only solution” to promote ecologically sustainable fishing and reduce “fishing pressure” around the close proximity of the the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) and the incidents of cross-border fishing.




