Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 12th August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Vaccine “Sputnik V,”:
- Mount Sinabung:
- Depsang Plains:
- Hindu women’s inheritance rights::
- Naga framework agreement::
- Student Entrepreneurship Programme 2.0: AIM:
- SpaceX’s SN5 Starship prototype
- Other important current affairs.
1. Vaccine “Sputnik V,”:
President Vladimir Putin announced that Russia had become the first country in the world to grant regulatory approval to a Covid-19 vaccine ‘Sputnik V’.
- Russia named the newly approved vaccine “Sputnik V,” in reference to Sputnik 1, the world’s first artificial satellite, launched in 1957 during the space race.
- Russia’s vaccine candidate is an adenovirus-based viral vector vaccine which is combined with the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to induce an immune response in the body.
- The vaccine still has to complete final trials, raising concerns among some experts at the speed of its approval, but the Russian business conglomerate Sistema has said it expects to put it into mass production by the end of the year.
- Phase III or what we call a final-stage study usually involves tens of thousands of people, which is the only way to prove if an experimental vaccine is safe and really works.
Use in India:
- Russia has claimed that around 20 countries have shown interest in the Sputnik V vaccine, including India.
- India has also partnered with the USA for the development of the Covid-19 vaccine.
- The approval for a vaccine is given by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, CDSCO is responsible for the approval of Drugs, Conduct of Clinical Trials, laying down the standards for Drugs, control over the quality of imported drugs in the country and coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations by providing expert advice.
- CDSCO can ask Russia to conduct late-phase human trials, usually both phase-2 and phase-3, on an Indian population.
- This is the usual requirement for all vaccines developed outside of India.
- CDSCO can also give emergency authorisation without late-phase trials, considering the extraordinary situation.
- Pune-based Serum Institute of India, the world’s largest manufacturer of vaccines by volume, has already entered into tie-ups with developers to mass-produce their vaccines. Other Indian companies have also done similar agreements but there is none with Russia.
Clinical development is a three-phase process:
- Clinical trials in humans are classified into three phases: phase I, phase II, and phase III, and in certain countries formal regulatory approval is required to undertake any of these studies.
- The phase I clinical studies carry out initial testing of a vaccine in small numbers (e.g. 20) of healthy adults, to test the properties of a vaccine, its tolerability, and, if appropriate, clinical laboratory and pharmacological parameters. Phase I studies are primarily concerned with safety.
- Phase II studies involve larger numbers of subjects and are intended to provide preliminary information about a vaccine’s ability to produce its desired effect (usually immunogenicity) in the target population and its general safety.
- Extensive phase III trials are required to fully assess the protective efficacy and safety of a vaccine. The phase III clinical trial is the pivotal study on which the decision on whether to grant the license is based and sufficient data have to be obtained to demonstrate that a new product is safe and effective for the purpose intended.
- Many vaccines undergo Phase IV formal ongoing studies after the vaccine is approved and licensed.
2.Mount Sinabung:

Indonesia’s Mount Sinabung volcano erupted, sending a column of ash and smoke more than 16,000 feet into the air. The volcano, which is situated in North Sumatra, has been active since 2010.
- Indonesia is home to many active volcanoes, due to its position on the “Ring of Fire”, or the Circum-Pacific Belt, which is an area along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
- The Ring of Fire is home to about 75 percent of the world’s volcanoes and about 90 percent of its earthquakes.
Why Do volcanoes erupt?
- A volcano can be active, dormant or extinct.
- An eruption takes place when magma (a thick flowing substance), formed when the earth’s mantle melts, rises to the surface.
- Because magma is lighter than solid rock, it is able to rise through vents and fissures on the surface of the earth. After it has erupted, it is called lava.
- Not all volcanic eruptions are explosive since explosivity depends on the composition of the magma.
- When the magma is runny and thin, gases can easily escape it, in which case, the magma will flow out towards the surface.
- On the other hand, if the magma is thick and dense, gases cannot escape it, which builds up pressure inside until the gases escape in a violent explosion.
3.Depsang Plains:
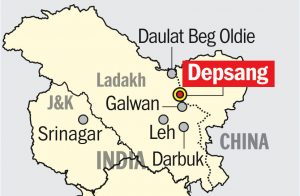
Recently, India and China have held talks at the Major General-level to discuss issues concerning the strategic Depsang Plains.
- The talks were held at Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO) and were limited to Depsang to discuss issues of varying claims and also blocking patrols by each other.
About the Meeting:
- This was the first high-level talks post-Galwan clash of 15th June 2020.
- Military talks since then have been limited to Corps Commander level.
- The meeting only discussed routine patrolling patterns by both sides as part of border management leaving aside disengagement or de-escalation.
Depsang Plains:
- The Depsang Plains along with Pangong Tso are the two major areas of concern in the ongoing standoff along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in eastern Ladakh.
- Despite the strategic importance of the Depsang Plains, the series of military talks held so far have focussed on the standoff areas at Galwan, Gogra Hotsprings and Finger area of Pangong Tso.
- Depsang is one of the few places on the LAC where tank maneuvers are possible.
- During the 1962 war, Chinese troops occupied the Plains. In 2013, Chinese troops came 19 km inside and pitched tents resulting in a 21-day standoff.
Issues:
- There is a heavy Chinese presence at a crucial area called the Bulge, in the Depsang Plains.
- Chinese troops have blocked the Indian Army patrols from reaching the various patrolling points.
- There has also been a build-up of tanks and armored vehicles on the Chinese side very close to the LAC.
- It threatens Indian positions at Burtse and Raki Nala inside Indian territory and further DBO by bringing Chinese troops closer to the 255 km long crucial Darbuk-Shyok-DBO road.
- Depsang is also close to the Karakoram Pass, overlooking the very strategic Saltoro Ridge and Siachen glacier.
4.Hindu women’s inheritance rights::

Supreme Court has expanded on a Hindu woman’s right to be a joint legal heir and inherit ancestral property on terms equal to male heirs.
- A Hindu woman’s right to be a joint heir to the ancestral property is by birth and does not depend on whether her father was alive or not when the law was enacted in 2005.
- The ruling now overrules the verdicts from 2015 and April 2018.
- While the 2005 law granted equal rights to women, questions were raised in multiple cases on whether the law applied retrospectively, and if the rights of women depended on the living status of the father through whom they would inherit.
Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005:
- It gave Hindu women the right to be coparceners or joint legal heirs in the same way a male heir does.
- The amended act made a daughter of a coparcener also a coparcener by birth “in her own right in the same manner as the son”.
- The law also gave the daughter the same rights and liabilities “in the coparcenary property as she would have had if she had been a son”.
- Applicability of the law: It applies to ancestral property and to intestate succession in personal property — where succession happens as per law and not through a will.
5.Naga framework agreement:

The National Socialist Council of Nagaland-IM has for the first time released the details of the 2015 framework agreement.
- It has also accused interlocutor R.N. Ravi of deleting a keyword from the original document and sharing the modified version with other Naga groups.
- The agreement released by the NSCN-IM stated “sharing the sovereign power” and provide for an “enduring inclusive new relationship of peaceful co-existence of the two entities”.
- However, it is alleged that Mr. Ravi, also Nagaland Governor, “craftily deleted the word new from the original” and circulated to the other Naga groups including the Naga National Political Groups (NNPGs).
- The NSCN claimed that the word ‘new’ is politically sensitive as it goes to define the meaning of peaceful co-existence of the two entities (two sovereign powers) and it strongly indicates outside the purview of the Constitution.
- It has demanded that the Centre should come out with an undertaking that the framework agreement is still alive in its original form and “to be handled by somebody other than RN Ravi” who is sensitive enough to understand and respect what has been achieved during the past 23 years.
- Naga talks have hit rough weather as the NSCN-IM has demanded that the present interlocutor be removed from the position.
- The NSCN-IM has been fighting for ‘Greater Nagaland’ or Nagalim — it wants to extend Nagaland’s borders by including Naga-dominated areas in neighboring Assam, Manipur and Arunachal Pradesh, to unite 1.2 million Nagas.
- The Centre has said there will be no disintegration of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Manipur to merge the Naga inhabited areas with Nagaland.
6.Student Entrepreneurship Programme 2.0:

Atal Innovation Mission (AIM – an initiative by the NITI Aayog) in collaboration with Dell Technologies has launched the second edition of its Student Entrepreneurship Programme (SEP 2.0) for student innovators of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs).
- SEP 1.0 was launched in January 2019.
SEP 2.0:
- Objective: It will allow student innovators to work closely with Dell volunteers. They will receive mentor support; prototyping and testing support; end-user feedback; intellectual property registration and patenting of ideas, processes, and products; manufacturing support; as well as the launch support of the product in the market.
- As many as 1500 innovations were submitted in the last season of ATL Marathon (2019). ATL Marathon is a nationwide contest where students identify community challenges and create grassroots innovations and solutions within their ATLs.
- 50 teams were selected and mentored by Atal Incubation Centres via the Student Innovator Programme 2.0.
Student Innovator Programme provides training on business and entrepreneurship skills to students. - The top 8 will take their prototypes to the product through SEP 2.0.
SEP 1.0:
- SEP 1.0 was a 10-month-long program through which the top 6 teams of ATL Marathon 2017 got a chance to transform their innovative prototypes into fully functioning products, which are now available in the market.
ATLs: - Vision: AIM is establishing ATLs in schools across India with a vision to cultivate one million children in India as neoteric (modern) innovators.
- It is aimed at disrupting the Indian education system, creating a paradigm shift where children as young as 12 years of age are being introduced to the world of technology innovation.
- Objectives: To foster curiosity, creativity and imagination in young minds; and inculcate skills such as design mindset, computational thinking, adaptive learning, physical computing etc.
- Eligibility: Schools (minimum Grade VI – X) managed by Government, local body or private trusts/society.
- Financial Support: AIM provides grant-in-aid of Rs. 20 Lakh to each school that includes a one-time establishment cost of Rs. 10 lakh and operational expenses of Rs. 10 lakh for a maximum period of 5 years to each ATL.
- Features:ATL is a workspace where young minds can give shape to their ideas through hands-on do-it-yourself mode, and learn innovation skills.
- Young children get a chance to work with tools and equipment to understand the concepts of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math).
- CollabCAD was launched in ATL schools to provide students with experience in creating and modifying 3D designs.
- In order to foster inventiveness among students, ATL conducts different activities ranging from regional and national level competitions, exhibitions, workshops on problem-solving, designing and fabrication of products, lecture series, etc. at periodic intervals.
7. SpaceX’s SN5 Starship prototype:

It is a prototype of SpaceX’s uncrewed “Mars ship”. It is a stainless steel test.
- It is a part of the Starship spacecraft.
- The prototype recently completed its first test flight. It successfully flew to an altitude of over 500 feet for a little less than 60 seconds.
- Starship: Designed by SpaceX, Starship is a spacecraft and super-heavy booster rocket meant to act as a reusable transportation system for crew and cargo to the Earth’s orbit, Moon and Mars.
- SpaceX has described Starship as “the world’s most powerful launch vehicle” with an ability to carry over 100 metric tonnes to the Earth’s orbit.
- Once functional, the Starship spacecraft will enter Mars’ atmosphere at a speed of 7.5 km per second and will be designed to withstand multiple entries.
- Starship can deliver satellites further and at lower marginal costs than SpaceX’s Falcon vehicles and it can ferry both cargo and crew to the International Space Station (ISS).
- Once developed, Starship is also expected to help carry large amounts of cargo to the Moon, for human spaceflight development and research.
- Beyond the Moon, the spacecraft is being designed for carrying crew and cargo for interplanetary missions as well.
Other important current affairs:
1.The ambassadors of India and Nepal are likely to meet in Kathmandu (Nepal) to review projects funded by the Indian government.
- The meeting is likely to take place via videoconference in view of the Covid-19 pandemic situation.
- This meeting will be a part of India- Nepal Joint Oversight Mechanism.
- The mechanism was established in 2016 to review ongoing bilateral economic and development projects.
- The government of India has allocated Rs. 800 crore in budget 2020-21 for projects in Nepal.
- These projects include building roads in the Terai region, helping Nepal in its post-earthquake (2015) reconstruction work, building railway lines, a police training academy, a polytechnic college, an oil pipeline and border check posts.
- Recently, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between India and Nepal for the construction of a sanitation facility at the Pashupatinath Temple, Kathmandu.
- This meeting is important in light of recent tensions between India and Nepal.
2.New tick-borne virus
- This new virus is rapidly spreading in China.
- It causes a disease called Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS).
- While the disease is transferred to humans through tick bites, Chinese virologists have warned that human-to-human transmission of the virus cannot be ruled out.
- The current case fatality rate rests between approximately 16 and 30 percent.
- Due to the rate at which it spreads and its high fatality rate, SFTS has been listed among the top 10 priority diseases blueprint by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- Unlike SARS-CoV-2 however, this is not the first time the SFTS virus has infected people. The recent spate of cases merely marks a re-emergence of the disease.
- Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) belongs to the Bunyavirus family and is transmitted to humans through tick bites.
- The virus was first identified by a team of researchers in China over a decade ago.
3.India and Maldives signed a contract for the development of five eco-tourism zones in Addu atoll of the island nation.
- These eco-tourism zones are part of grant projects being implemented under the High-Impact Community Development project (HICDP) scheme which involves total grant assistance of 5 million US dollars to the Maldives.
- Currently, there are 9 such high-impact projects being implemented in the Maldives. Developing high-impact assets, building capacities within the local councils, and supporting the local island economy are most important objectives of these projects.
- Addu Atoll: Addu Atoll, also known as Seenu Atoll, is the southernmost atoll of the Maldives.
- Addu Atoll, together with Fuvahmulah, located 40 km north of Addu Atoll, extend the Maldives into the Southern Hemisphere.
- Unlike other atolls of the Maldives, Addu Atoll has a lagoon that is a natural anchorage, accessible through four natural channels. This results in a natural harbor that is very calm and safe for sea vessels.
5. The World Health Organisation (WHO) has renewed its invite to countries to join its COVAX facility, an international alliance aimed at accelerating the development and manufacture of novel Coronavirus vaccines and ensuring equitable access to all.
- The COVAX facility, launched in April 2020, is stitching together agreements with developers and manufacturers of vaccine candidates it thinks are most likely to succeed.
- The facility is trying to raise funds to support the rapid development of promising candidates, and the quick expansion of manufacturing capacities, so that the vaccines once approved, could be produced on mass scale.
- The facility aims to procure at least two billion doses of a novel Coronavirus vaccine by the end of next year, for deployment and distribution mainly in the low and middle-income countries.
- The countries that join the initiative are also assured supply of vaccines whenever they become successful. The countries will get assured supplies to protect at least 20 percent of their populations.
6. International Youth Day 2020 is being observed on 12 August with the theme “Youth Engagement for Global Action.”
- In 1999, the UN General Assembly endorsed the recommendation made by the World Conference of Ministers Responsible for Youth (Lisbon, 8-12 August 1998) that 12 August be declared International Youth Day.
- The first IYD was observed in 2000.
- Objective: The day celebrates young peoples’ initiatives, as well as their meaningful engagement.
7. A special committee set up by the Supreme Court of India has recommended the restoration of 4G internet services in Jammu & Kashmir (J&K).
- The committee is of the view that the threat perception on the security front in J&K continues to be high.
- However, it has recommended restoring 4G internet services after 15th August 2020 on a trial basis in a careful manner in specified areas to assess the impact on the security situation.
- The internet could be restored in one district each of the Jammu region and Kashmir region which are away from the international border or line of control and has a low intensity of terrorist activities.
- Telecom operators in the districts which are allowed to have 4G services on a trial basis may also have to submit reports of data usage volume and which apps are being used the most.
- The committee is also of the view that internet speed related restrictions are not posing any hindrance to COVID control measures, access to education programs, or carrying out business activities.
- According to it, there is adequate access to the internet through broadband services available over landline to business and healthcare institutions.




