Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 13th June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Sahakar Mitra scheme launched:
- .Inclusion of Reservation Laws in Ninth Schedule:
- 40th Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council meeting :
- Per Drop More Crop’ component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY- PDMC)
- Small Farmers’ Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC):
- Discussion Paper on ‘Governance in Commercial Banks in India’ for public comments.
- Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) road:
- Other important current affairs
1. Sahakar Mitra scheme launched:

Union Agriculture Minister launched Sahakar Mitra: Scheme on Internship Programme (SIP).
- Objective: To help cooperative institutions access innovative ideas of young professionals while the interns will gain experience of working in the field to be self-reliant.
- The scheme is an initiative by the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), the cooperative sector development finance organization.
- Eligibility under the scheme: Professional graduates in disciplines such as Agriculture and allied areas, IT, etc. will be eligible for an internship. Professionals who are pursuing or have completed their MBA degrees in Agri-business, Cooperation, Finance, International Trade, Forestry, Rural Development, Project Management, etc. will also be eligible.
- Each intern will get financial support over a 4 months internship period.
2.Inclusion of Reservation Laws in Ninth Schedule:
Recently, a Union Minister emphasized the need to include all reservation-related laws in the Ninth Schedule of Constitution so that they are shielded from judicial review.
- The minister argued that reservation is not confined just to Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) and is available to Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and poor sections of the upper castes as well and have been attached to Fundamental Rights.
- SC/ST Reservation:
- Both the Centre and the states are permitted to make any special provision for the advancement of SCs and STs.
- The quota in government jobs and educational institutions for SCs and STs is 15% and 7.5% respectively (total 22.5%).
- Other Backward Class (OBC) Reservation:
- Both the Centre and the states are empowered to make provision for the advancement of OBCs regarding their admission to educational institutions and government jobs.
- The quota limit for OBCs is 27%.
- However, various state governments have different quota limits for OBCs in their state like Tamil Nadu has a 50% reservation for OBCs.
- In the Indra Sawhney & Others vs Union of India, 1992 judgment, the Supreme Court fixed the upper limit for the combined reservation quota i.e. should not exceed 50% of seats.
- Economically Weaker Section (EWS) Reservation:
- The 103rd Constitution Amendment Act, 2019 empowers both Centre and the states to provide 10% reservation to the EWS category of society in government jobs and educational institutions.
This demand comes after the Supreme Court’s recent observation that the Right to Reservation is not a Fundamental Right.
- Earlier, SC ruled that reservation in the matter of promotions in public posts was not a fundamental right and that a state cannot be compelled to offer quota if it chooses not to.
- Apart from that, there have been repeated challenges to the Scheduled Castes and Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 and its amendments.
Ninth Schedule
- The Schedule contains a list of central and state laws which cannot be challenged in courts and was added by the Constitution (First Amendment) Act, 1951.
- The first Amendment added 13 laws to the Schedule. Subsequent amendments in various years have taken the number of protected laws to 284 currently.
- It was created by the new Article 31B, which along with Article 31A was brought in by the government to protect laws related to agrarian reform and for abolishing the Zamindari system.
- While Article 31A extends protection to ‘classes’ of laws, Article 31B shields specific laws or enactments.
- While most of the laws protected under the Schedule concern agriculture/land issues, the list includes other subjects.
- Article 31B also has a retrospective operation which means that if laws are inserted in the Ninth Schedule after they are declared unconstitutional, they are considered to have been in the Schedule since their commencement, and thus valid.
.
3. 40th Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council meeting :

Key Points
- GST Collections:
- In the first two months of the current financial year, 2020-21, the cumulative GST revenues of states and the Centre has been only 45% of the monthly target.
- In 2020-21, the combined monthly GST revenue target is estimated at Rs. 1.21 lakh crore taking into account the budget estimate and states’ protected revenue.
- Market Borrowing:
- As revenue has fallen for both the Centre and states, the GST Council has decided to hold a single-point agenda meeting in July 2020 which will discuss market borrowing by the Council itself as one of the ways to raise money and compensate states for GST revenue losses.
- The GST Act, 2017 extends a guarantee to states that any loss in revenues in the first five years (2017-2022) of GST implementation will be compensated through a cess that accrues to the Compensation Fund.
- The shortfall is calculated assuming a 14% annual growth in GST collections by states over the base year of 2015-16.
- Tax Rationalisation:
- The Council discussed correction of inverted duty structure for footwear, fertilizers and textiles.
- Inverted duty structure is a situation where the rate of tax on inputs used is higher than the rate of tax on the finished good.
- Compliance-related Relief:
- The GST Council also provided compliance-related relief to small taxpayers with turnover up to Rs. 5 crores.
- It reduced the interest by half on delayed filing of GST returns for February, March, and April 2020 to 9%, provided the returns are filed by September 2020.
- For May-July, 2020 the deadline for filing GST returns has been extended till 30 September 2020 without any penalty.
GST Council
- It is a constitutional body under Article 279A.
- It makes recommendations to the Union and State Government on issues related to Goods and Service Tax and was introduced by the Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016.
- The GST Council is chaired by the Union Finance Minister and other members are the Union State Minister of Revenue or Finance and Ministers in-charge of Finance or Taxation of all the States.
- It is considered as a federal body where both the center and the states get due representation.
4.‘Per Drop More Crop’ component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY- PDMC) :

Annual allotment of Rs. 4000 crore made to State Governments under ‘Per Drop More Crop’ component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY- PDMC) for the year 2020-21.
About ”Per Drop More Crop” component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY-PDMC):
- The Department of Agriculture Cooperation and Farmers’ Welfare is implementing the ”Per Drop More Crop” component of PMKSY-PDMC.
- It is operational in the country from 2015-16.
- It focuses on enhancing water efficiency at the farm level through micro-irrigation technologies such as ”drip and sprinkler” irrigation.
- Micro Irrigation Fund corpus of Rs. 5000 crore has been created with NABARD.
- The objective of the fund is to facilitate the states in mobilizing the resources for expanding coverage of Micro Irrigation by taking up special and innovative projects and also for incentivizing micro irrigation beyond the provisions available under PMKSY-PDMC to encourage farmers to install micro-irrigation systems.
- The Government provides financial assistance at 55% for small and marginal farmers and @ 45% for other farmers for installation of Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation Systems.
- In addition, some states provide additional incentives/top-up subsidy for encouraging farmers to adopt Micro Irrigation.
5. Small Farmers’ Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC):

Recently the Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare highlighted the role of Small Farmers’ Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC) in increasing incomes of small and marginal farmers through aggregation and development of agribusiness.
- Established: SFAC was established in 1994 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 as an autonomous body promoted by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
- Objectives: Promoting agribusiness by encouraging institutional and private sector investments and linkages to ensure the empowerment of all farmers in the country.
- Organizing small and marginal farmers as Farmer Interest Groups, Farmer Producer Organisations, and Farmer Producer Company for endowing them with bargaining power and economies of scale.
- Few Important Schemes Implemented by SFAC: Equity Grant & Credit Guarantee Fund (EGCGF) Scheme, Venture Capital Assistance (VCA) Scheme, Farmer Producer Organization (FPO) Scheme, National Agriculture Market (NAM) Scheme, etc.
- Recent Initiatives/Developments: SFAC launched the Kisan Rath app with the help of officials of the Ministry of Agriculture which lessened the problem of transport of farm produce during the lockdown.
- It signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) to bring in better synergy in the agricultural activities.
6.Discussion Paper on ‘Governance in Commercial Banks in India’ for public comments:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released a Discussion Paper on ‘Governance in Commercial Banks in India’ for public comments.
- The objective of the discussion paper is to align the current regulatory framework with global best practices while being mindful of the context of the domestic financial system.
- Based on the feedback, fresh guidelines will be issued. The new norms will come into effect within six months after being placed on the RBI’s website or April 1, 2021, whichever is later.
- The norms will be applicable to private, foreign, and public sector banks.
Major highlights of the paper are as follows:
- Board members should not be a member of any other bank’s board or the RBI and should not be either a Member of Parliament or State Legislature or Municipality or other local bodies.
- Board of directors of a bank should not be less than six and not more than 15, with a majority being independent directors.
- The board shall meet at least six times a year and at least once every 60 days.
- A director on the board of an entity other than a bank may be considered for appointment as a director on a bank’s board, if the person is not an owner of an NBFC or a full-time employee and that the NBFC does not enjoy a financial accommodation from the bank.
- Appointment, re-appointment, and termination of whole-time directors (WTDs) and chief executive officers CEOs) should be with the previous approval of RBI.
- The upper age limit for CEO and WTDs of banks is suggested at 70 years. Banks will be free to set a lower age for such appointments.
7. Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) road:
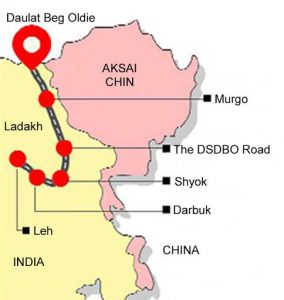
In the reporting on the Line of Actual Control (LAC) stand-off, the Darbuk-Shyok-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) road has often appeared. The Chinese build-up along the Galwan River valley region overlooks and hence poses a direct threat to the DSDBO road.
- Darbuk-Shyokh-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) is the 255-km long all-weather road built by India’s Border Roads Organisation (BRO) in eastern Ladakh.
- It runs almost parallel to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) at Aksai Chin, the eastern ear of erstwhile Jammu and Kashmir state that China occupied in the 1950s, leading to the 1962 war in which India came off worse.
- In October 2019, Defence Minister Singh inaugurated a 500-m-long Bailey Bridge on the road.
- The bridge is named after Colonel Chewang Rinchen, an Indian Army hero from Ladakh. Located at 14,650 ft, it is believed to be the world’s highest such bridge.
Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO):
- DSDBO connects Leh to Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO), the northernmost corner of Indian territory in Ladakh. DBO itself is less than 10 km west of the LAC at Aksai Chin.
- DBO has the world’s highest airstrip.
Other important current affairs:
1. Indian-American soil scientist Rattan Lal has been named this year’s recipient of the World Food Prize for developing and mainstreaming a soil-centric approach to increasing food production that conserves natural resources and mitigates climate change.
- The World Food Prize recognizes the achievements of individuals who have advanced human development by improving the quality, quantity, or availability of food in the world.
- It recognizes contributions in any field involved in the world food supply such as plant, animal and soil science; nutrition; rural development; marketing; food processing and packaging; water and the environment; physical infrastructure; policy analysis, etc.
- The prize is open to every individual without regard to race, religion, nationality, or political beliefs.
- Presented by: World Food Prize Foundation, with various sponsor companies.
- The prize was conceived by Dr. Norman E. Borlaug, winner of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in global agriculture. The Prize was created in 1986 and was first awarded in 1987 with M. S. Swaminathan of India being the first recipient.
2. Adani Green Energy Ltd has bagged the world’s largest solar bid entailing building a photovoltaic (PV) power plant of 8 GW and setting up a domestic solar panel manufacturing capacity of 2 GW, envisaging total investment of roughly $6 billion.
- The State-run renewable energy agency SECI (formerly Solar Energy Corporation of India) has awarded Adani Group’s renewable energy arm a project to build an 8 GW solar power plant and 2 GW of additional solar cell and module manufacturing capacity over the next five years.
- The project, which Adani Green Energy Ltd (AGEL) claims is the “largest of its type”, will entail a single investment of $6 billion and is expected to create 4,00,000 direct and indirect jobs.
- The development also helps AGEL overtake ReNew Power as the largest renewable player, as it will be managing a renewable portfolio with a 15 GW capacity compared with ReNew’s 8.65 GW renewable assets. Azure Power will become the third-largest player.
- The projects will include a variety of locations, including a 2 GW single-site generation project that is tied for the rank of the largest single-site project announced globally.
- The solar cell and module manufacturing capacity of 2 GW will be established by 2022 and along with the existing 1.3 GW of capacity will further consolidate the Group’s position as India’s largest solar manufacturing facility.
3. On June 7, astronaut and oceanographer Kathy Sullivan, who was the first American woman to walk in space in 1984, became the first woman and the fifth person in history to descend to the Challenger Deep. Sullivan is now the only human who has walked in space and reached the deepest point in the ocean.
- The Challenger Deep is the deepest known point in the Earth’s oceans, with a depth of 10,902 to 10,929 m.
- It is located in the Western Pacific Ocean, at the southern end of the Mariana Trench near the Mariana Islands group.
- This location is in the ocean territory of the Federated States of Micronesia.
- The depression is named after the British ship HMS Challenger, whose expedition of 1872–1876 made the first recordings of its depth.
4. International Albinism Awareness Day 2020 is being observed on June 13 under the theme “Made to Shine” to celebrate the achievements of persons with albinism worldwide.
- Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized in humans by the complete or partial absence of pigmentation (melanin) in the skin, hair, and eyes. It is non-contagious.
- Albinism is associated with a number of vision defects, such as photophobia, nystagmus, and amblyopia. Lack of skin pigmentation increases vulnerability to the sun and bright light. As a result, almost all people with albinism are visually impaired and are prone to developing skin cancer.
- Albinism results from the inheritance of recessive gene alleles. In almost all types of albinism, both parents must carry the gene for it to be passed on, even if they do not have albinism themselves.




