Today Current Affairs: 15th April 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Waterways Conclave 2022:

The Waterways Conclave 2022 was organized by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) on 11th and 12th April 2022 in Dibrugarh, Assam.
- The aim of this conclave was to focus on harnessing the potential of the international and domestic waterway ecosystem in the country’s North-eastern region.
- The industry partner of this conclave was the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI).
- The conclave was launched by Sarbananda Sonowal, Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways and AYUSH.
- The conclave was attended by various stakeholders in the sector of the waterway ecosystem like Senior Government Officials, Policy Planners, Sector Experts, Domestic and International Investors, Infrastructure players, Cruise Tourism industry, Vessel Owners and Operators, Representatives of Major Ports, Cargo Passengers, and representatives from the Governments of Maritime States in India.
- The aim of this conclave is to fast-track the Multimodal projects for the development of the country’s Northeast region so that business opportunities, economic activities, and employment generation can be enhanced.
Two Full-Time Degree Programmes : UGC

The students of the country have been allowed to pursue two degrees simultaneously by the University Grants Commission.
- From the academic session of 2022-23, the students can start applying for these dual degree programmes.
- Both the degrees can be pursued either from different universities or from the same university.
- Students of the country will be allowed to choose two master’s programmes, a diploma and a UG programme, or two bachelor’s programmes.
- The students can also apply for a PG and a UG programme.
- It must be ensured that there is no clash in the timings of the classes that are being pursued by the students.
- The programmes must be pursued in only those institutes that are recognised by the Statutory Council or UGC or Govt. of India.
- A student can pursue both the programmes with one being in physical mode and the other in Online or Open and Distance Learning mode.
- Also, the students can take up two Online or Open and Distance Learning programmes simultaneously.
- The guidelines have been made applicable to all academic programs except PhD.
- Both the degrees can be pursued in physical mode, provided that the class timings do not clash.
Amrit Samagam : Conference Of Tourism And Culture Ministers

The Amrit Samagam, a summit of the country’s cultural and tourism ministers was launched by Union Minister of Home Affairs, Amit Shah. This summit was launched in New Delhi.
- This is a two-day conference that was hosted by the Ministry of Culture on 12th and 13th April 2022, as part of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav (AKAM).
- The conference’s goal is to discuss the progress of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The topics of discussion at this conference included landmark initiatives of AKAM like Swatantra Swar, Har Ghar Jhanda, Digital District Repository, and Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar.
- Also, in this conference, the Ministry of Tourism focused on the significant contributions made by the organization to the AKAM campaign.
- The Utsav Portal website was launched by G. Kishan Reddy, Union Minister for Tourism, Culture, and DONER during this conference.
- It is a Ministry of Tourism’s digital initiative that will be used to showcase all festivals, events, and live darshans across the country with the aim of promoting different regions of India as popular tourist destinations across the world.
- Har Ghar Jhanda:This initiative was implemented by the National Implementation Committee from 11th to 15th August 2022 with the aim of encouraging citizens of India, institutions, and organizations to hoist the country’s National Flag on their premises.
- The purpose of this initiative was to create a repository of data and store them in one place.
- The Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav mobile App was launched by the Ministry of Culture so that the users can access all information that is related to India’s 75th independence anniversary celebrations.
- Swatantra Swar: This initiative highlighted all the writings that were banned during the British Raj. Under this initiative, the banned writings were recited by prominent personalities in different languages like Bengali, Hindi, Gujarati, Marathi, Odia, Kannada, Sindhi, Punjabi, Telugu, Tamil, and Urdu.
- Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar: This initiative was launched by the Ministry of Culture partnering with the Common Services Centres (CSC). Under this initiative, the cultural identity of the country’s villages is being promoted.
National Conference On Cooperation Policy:

The National Conference on Cooperation Policy concluded in New Delhi.
Highlights of the Conference:
- The conference was structured into six important themes covering not only the whole life cycle of cooperatives but also touching upon all the facets of their business and governance.
- The panel discussions have been held on following themes:
- Present legal framework, identification of Regulatory policy, Operational barriers and measures required for their removal leading to Ease of Doing Business and providing a level playing field to cooperatives and other economic entities.
- Reforms for strengthening governance including cooperative principles, democratic member control, increasing member participation, transparency, regular elections, Human Resource Policy, leveraging International & National best practices, account keeping & auditing.
- Multi Cooperative Vibrant economic entities by strengthening infrastructure, strengthening equity base, access to capital, diversification of activities, promoting entrepreneurship, promoting branding, marketing, business plan development, innovation, technology adoption and exports
- Training, Education, knowledge sharing and Awareness Building including mainstreaming cooperatives, linking training with entrepreneurship, inclusion of Women, Youth & Weaker Sections.
- Promoting new cooperatives, revitalising defunct ones, promoting cooperation among cooperatives, increasing membership, formalising collectives, developing cooperatives for sustainable growth, mitigating regional imbalances & exploring new sectors.
- Promoting social cooperative and role of cooperatives in social security.
- The ministry is planning a series of such conferences with different stakeholders, besides, shortly, another workshop with all cooperative federations to invite their views.
- These efforts will culminate in the formulation of a new robust National Cooperation Policy, giving impetus to strengthen the cooperative based economic model in the country to realise the vision and mantra of Sahkar Se Samaridhi.
Birth Anniversary Of B R Ambedkar:

The nation celebrated the 131st birth anniversary of B R Ambedkar on 14th April 2022.
- Dr. Ambedkar was a social reformer, jurist, economist, author, polyglot (knowing or using several languages) orator, a scholar, and thinker of comparative religions.
- Babasaheb Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar was born in 1891 in Mhow, Central Province (now Madhya Pradesh).
- He is known as the Father of the Indian Constitution and was India’s first Law Minister.
- He was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee for the new Constitution.
- He was a well-known statesman who fought for the rights of the Dalits and other socially backward classes.
- He led the Mahad Satyagraha in March 1927 against Hindus who were opposing the decision of the Municipal Board.
- In 1926, the Municipal Board of Mahad (Maharashtra) passed an order to throw open the tank to all communities. Earlier, the untouchables were not allowed to use water from the Mahad tank.
- He participated in all three Round Table Conferences.
- In 1932, Dr. Ambedkar signed the Poona pact with Mahatma Gandhi, which abandoned the idea of separate electorates for the depressed classes (Communal Award).
- However, the seats reserved for the depressed classes were increased from 71 to 147 in provincial legislatures and to 18% of the total in the Central Legislature.
- His ideas before the Hilton Young Commission served as the foundation of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- In 1936, he was elected to the Bombay Legislative Assembly as a legislator (MLA).
- He was appointed to the Executive Council of Viceroy as a Labour member in 1942.
- In 1947, Dr. Ambedkar accepted PM Nehru’s invitation to become Minister of Law in the first Cabinet of independent India.
- He resigned from the cabinet in 1951, over differences on the Hindu Code Bill.
- He converted to Buddhism. He died on 6th December 1956 (Mahaparinirvan Diwas).
- Chaitya Bhoomi is a memorial to B R Ambedkar, located in Mumbai.
- He was awarded India’s highest civilian honour the Bharat Ratna in 1990.
Important Works:
Journals:
- Mooknayak (1920)
- Bahishkrit Bharat (1927)
- Samatha (1929)
- Janata (1930)
Books:
- Annihilation of Caste
- Buddha or Karl Marx
- The Untouchable: Who are They and Why They Have Become Untouchables
- Buddha and His Dhamma
- The Rise and Fall of Hindu Women
Organisations:
- Bahishkrit Hitkarini Sabha (1923)
- Independent Labor Party (1936)
- Scheduled Castes Federation (1942)
Mahavir Jayanti:

The Prime Minister has greeted people on Mahavir Jayanti, recalling the noble teachings of Bhagwan Mahavir, especially the emphasis on peace, compassion and brotherhood
- Mahavir Jayanti is one of the most auspicious festivals in the Jain community.
- This day marks the birth of Vardhamana Mahavira, who was the 24th and the last Tirthankara who succeeded the 23rd Tirthankara, Parshvanatha.
- According to Jain texts, Lord Mahavira was born on the 13th day of the bright half of the moon in the month of Chaitra.
- As per the Gregorian calendar, Mahavir Jayanti is usually celebrated during the month of March or April.
- A procession is called with the idol of Lord Mahavira called the Rath Yatra.
- Reciting stavans or Jain prayers, statues of the lord are given a ceremonial bath called abhisheka.
Lord Mahavira:
- Mahavir was born to King Siddhartha of Kundagrama and Queen Trishala, a Lichchhavi princess in the year 540 BC in the Vajji kingdom, identical with modern day Vaishali in Bihar.
- Mahavira belonged to the Ikshvaku dynasty.
- There are several historians who believe that he was born in a place called Ahalya bhumi and the land has not been plowed for hundreds of years by the family that owns it.
- Lord Mahavir was named Vardhamana, which means “one who grows”.
- He abandoned worldly life at the age of 30 and attained ‘kaivalya’ or omniscience at the age of 42.
- Mahavira taught ahimsa (non-violence), Satya (truth), asteya (non-stealing), brahmacharya (chastity) and aparigraha (non-attachment) to his disciples and his teachings were called Jain Agamas.
- Ordinary people were able to understand the teachings of Mahavira and his followers because they used Prakrit.
- It is believed that the Mahavira passed away and attained moksha (liberation from the cycle of birth and death) at the age of 72 in 468 BC at a place called Pavapuri near modern Rajgir in Bihar.
What Is Colour Blindness?
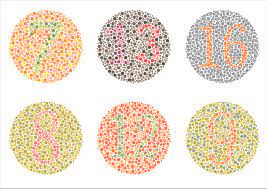
The Supreme Court has directed the Film and Television Institute of India (FTII) not to exclude candidates suffering from colour blindness from its courses on film making and editing and asked it to make changes to its curriculum instead.
- Colour blindness is the inability to see colours in the normal way. Colour blind individuals often cannot distinguish between certain colours usually greens and reds, and sometimes blues as well.
- It is also known as colour deficiency.
- Two types of cells in the retina detect light:
- Rods: These help in distinguishing between light and dark.
- Cones: These help in detecting colour.
- There are three types of cones that see colour red, green, and blue and our brains use the information from these cells to perceive colour.
- Colour blindness can be the result of the absence of one or more of these cone cells, or their failure to work properly.
- Colour blindness may be of different kinds and degrees.
- In a situation where all three cone cells are present but one of them is malfunctioning, mild colour blindness may occur.
- Mildly colour blind people often see all colours properly only when the light is good.
- In the most severe kind of colour blindness, vision is black-and-white, that is, everything appears as a shade of grey. This is not very common.
- Causes:
- Congenital Colour Blindness: Most colour blind people are born with the condition (congenital colour blindness).
- Congenital colour vision deficiencies are usually passed on genetically.
- This type of Colour blindness generally affects both eyes, and the condition remains roughly the same for as long as the individual is alive.
- Medical Conditions: A problem with colour vision that arises later in life could be the result of disease, trauma, or ingested toxins.
- If colour blindness arises out of disease, one eye may be affected differently from the other, and the difficulty could worsen over time.
- Medical conditions that may increase the risk of getting colour blindness include glaucoma, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, alcoholism, leukaemia, and sickle-cell anaemia.
- Treatment: Colour blindness cannot as yet be treated or reversed
Book On The Life Of Tribal Freedom Fighter Birsa Munda:

Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan recently released a book on the life of tribal freedom fighter Birsa Munda.
- The book titled ‘Birsa Munda – Janjatiya Nayak’ is written by Prof Alok Chakrawal, Vice-Chancellor of Guru Ghasidas Vishwavidyalaya, Bilaspur.
- The book is a comprehensive attempt to bring to the fore the struggle of Bhagwan Birsa Munda and the contribution of forest dwellers in the freedom movement.
- Bisra Munda was a folk hero and a tribal freedom fighter hailing from the Munda tribe.
- He was a spearhead behind the Millenarian movement that arose in the Bihar and Jharkhand belt in the 19th century under British colonisation.
- He is also known as ‘Dharti Abba’ or the Earth Father.
- Born on 15th November 1875.
- Bisra wanted to reform the tribal society and so, he urged them to let go of beliefs in witchcraft and instead, stressed on the importance of prayer, staying away from alcohol, having faith in God and observing a code of conduct. Based on these, he started the faith of ‘Birsait’.
- Bisra started a movement called ‘Ulgulan’, or ‘The Great Tumult’.
- His struggle against the exploitation and discrimination against tribals led to a big hit against the British government in the form of the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act being passed in 1908.
- The act restricted the passing on of land from the tribal people to non-tribals.
Munda Rebellion:
It is one of the most important tribal movements.
It was led by Birsa Munda in the south of Ranchi in 1899-1900.
The movement identified following forces as the cause of the misery the Mundas were suffering:
The land policies of the British were destroying their traditional land system.
Hindu landlords and moneylenders were taking over their land.
Missionaries were criticising their traditional culture.
InTranSE -II Program:
The government has launched Indigenous Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) Solutions for Indian Traffic Scenario under Intelligent Transportation System Endeavor for Indian Cities Phase-II Program.
- InTranSE -II is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It incorporates vehicle-borne sensors for monitoring driver propensity and vehicle surroundings to deliver acoustic and visual alerts for driver assistance.
- It is an operational strategy that modifies normal traffic signal operations to better accommodate in-service public buses at signal-controlled intersections.
- CoSMiC provides a Dashboard page showing IoT units, products, applications, and its live data in a Geographical Information System (GIS) map.
InTranSe:
- Intelligent Transportation System Endeavour (InTranSe) for Indian IndianCities” is a National level Collaborative Research and Development Program.
- Funded by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, Government of India.
- InTranSe aims at Development, Demonstration, Deployment, Technology Transfer and Commercialization of products and technologies relevant to Intelligent Transportation System (ITS).
- Overall objective of the program is to provide the country with the capability to become a significant player in the area of Intelligent Transportation System (ITS).
Malcolm Adiseshiah Award 2022:

Renowned Indian economist and political commentator Prabhat Patnaik has been named the recipient of the Malcolm Adiseshiah Award this year.
- The award is annually given by the Malcolm and Elizabeth Adiseshiah Trust to an outstanding social scientist for Distinguished Contributions to Development Studies.
- Patnaik has taught at the Centre for Economic Studies and Planning in the School of Social Sciences at Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Delhi, and has served as Vice-Chairman of the Kerala State Planning Board.
- Malcolm Sathiyanathan Adiseshiah (1910 – 1994), was an Indian development economist and educator.
- In 1976 he was awarded the Padma Bhushan.
International Gandhi Award For Leprosy, 2021:

M. Venkaiah Naidu, the Vice President on 13th April 2022 has conferred the International Gandhi Award for Leprosy, 2021 to Sahyog Kushtha Yagna Trust, Gujarat, and Dr. Bhushan Kumar of Chandigarh in New Delhi.
- It is an annual award that is instituted by the Gandhi Memorial Leprosy Foundation.
- The Vice President also urged the people of the country and the various organizations to join the eradicating leprosy campaign.
- There should be social mobilization to support the eradication of this disease.
- The Gram Sabhas were also urged to help in the fight against leprosy.
- The country’s fight against leprosy was also highlighted as India’s leprosy count decreased to less than one case per ten thousand population.
- Award given: Sahyog Kushtha Yagna Trust and Dr. Bhushan Kumar have been working round the clock to raise awareness regarding leprosy and the care that can be provided to those afflicted with this disease. They have also been working to remove the social stigmas that are associated with this disease.
- Leprosy or Hansen’s disease is a chronic granulomatous disease that is caused due to the bacteria named Mycobacterium Leprae.
- This disease mostly affects the nerves, skin, respiratory system, and eyes
Tree City Of The World Tag 2021:

The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (UN-FAO) along with Arbor Day Foundation has recognized Hyderabad and Mumbai jointly as the ‘2021 Tree City of the World.’
- The recognition has been won by the two Indian cities due to their commitment to maintaining and growing greenery and urban trees so as to build resilient, healthy, and happy cities.
- This is the first time Mumbai has made it to the list.
- Hyderabad has been featured on this list for the second consecutive year.
‘Tree Cities of the World’ tag:
- The programme was started by the UN-FAO and Arbor Day Foundation, an American non-profit organisation.
- The aim of starting this programme was to recognise towns and cities across the world that are committed to ensuring that their trees and urban forests are sustainably managed, properly maintained, and duly celebrated.
- Under this programme assistance, direction, and worldwide recognition is provided to those communities that are showing dedication to their urban forest.
- The programme also provides a framework for a sustainable and healthy urban forestry programme in a city or a town.
- To be recognized as a ‘Tree City,’ a city needs to meet five core standards that show its commitment to caring for its forests and trees.
- For a city to be recognized as a Tree City, it must delegate responsibility for the caring of trees within the municipal boundary to a city department, a staff member, or a group of citizens known as a Tree Board.
- Also, a law or an official policy must be in place in the city to govern the management of trees and forests.
- The city must also have an updated assessment or inventory of the local tree resources so that it can establish an effective long-term plan for caring for, planting, and removing city trees.
- The city must also have a dedicated annual budget for implementing a tree management plan.
Pradhan Mantri Sangrahalaya:

The Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in New Delhi. The contribution of India’s prime ministers will be showcased in the Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya.
- The first person to buy a ticket to the museum was PM Modi.
- The museum has been inaugurated on Ambedkar Jayanti.
- The tickets have been priced at Rs 100 if it is bought online, and Rs 110 if bought in the offline mode. For foreigners, the ticket has been priced at Rs 750.
- The children who will be visiting the museum aged between 5 to 12 years will be given a 50 per cent discount per ticket.
- The school and college students will receive a 25 per cent discount if the bookings are made by the colleges and the schools
- The sangrahalaya is being built adjacent to the Nehru Memorial Museum Library in Teen Murti Bhavan on a 10,000-square metre piece of land.
- The museum will be housing exhibits related to the former prime ministers of the country.
- The museum will have 43 galleries.
- The design of the museum has incorporated energy conservation practices that are sustainable. To build this museum no trees have been transplanted or felled.
- The logo of this museum represents the hands of the Indian people holding the Dharma Chakra which symbolizes democracy and the nation.
- All the information for the museum has been collected with the help of the institutions like Doordarshan, Prasar Bharati, Sansad TV, Films Division, Media Houses (Indian and foreign), and Ministry of Defence, Foreign News Agencies, etc.
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved continuation of the revamped Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA) for implementation during the period from 1st April 2022 to 31st March 2026 .
- The scheme is now co-terminus with the 15th Finance Commission period.
- The scheme is aimed to develop governance capabilities of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA):
- The scheme was first approved by the Cabinet in 2018 for implementation from 2018-19 to 2021-22.
- Implementing Agency: Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- The main Central Components were Incentivisation of Panchayats and Mission Mode Project on e-Panchayat including other activities at Central level.
- The State component primarily includes Capacity Building & Training (CB&T) activities, institutional mechanisms for CB&T along with other activities at a limited scale.
- It envisaged developing governance capabilities of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) to deliver on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The key principles of SDGs, i.e. leaving no one behind, reaching the farthest first and universal coverage, along with gender equality will be embedded in the design of all capacity building interventions including training, training modules and materials.
- The revamped RGSA will comprise Central and State components.
- The Central Components of the scheme will be fully funded by the Government of India.
- The funding pattern for State Components will be in the ratio of 60:40 among Centre and States respectively, except NE, Hilly States and Union Territory (UT) of J&K where Central and State share will be 90:10.
- However, for other UTs, Central share will be 100%.
- It is an effort in the direction of achieving “Sabka Sath, Sabka Gaon, Sabka Vikas”
Policy For Use Of Land Acquired Under CBA Act, 1957:

The Union Cabinet has approved the policy for use of land acquired under the Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition & Development) Act, 1957 [CBA Act].
- The policy provides for utilisation of such land for the purpose of development and setting up of infrastructure relating to coal and energy.
The CBA Act, 1957:
- The Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957 provides for the acquisition of land containing or likely to contain coal deposits and for matters connected therewith.
- Under the provisions of this Act, the land is acquired for Government Companies only for coal mining and activities strictly incidental to mining purposes.
- For other requirements, like permanent infrastructure, offices, residence etc. the land is acquired under Land Acquisition Act, 1894.
- Mining rights and surface rights of a single patch of land may not be acquired under different Acts.
Provisions of the Proposed Policy:
- The policy provides clear policy framework for utilisation of following types of lands acquired under the CBA Act:
- Lands no longer suitable or economically viable for coal mining activities; or
- Lands from which coal has been mined out / de-coaled and such land has been reclaimed.
- Coal India Ltd. (CIL) will Remain Owner of the Land:
- The Government coal companies, such as Coal India Ltd. (CIL) and its subsidiaries shall remain owners of these lands acquired under the CBA Act.
- Leasing of Land for Specified Period:
- The Government company which owns the land would lease such land for a specific period given under the policy.
- The entities for leasing shall be selected through a transparent, fair and competitive bid process and mechanism in order to achieve optimal value.
- The lands will be considered for activities such as setting up washeries, coal gasification and coal-to-chemical plants and to set up or provide for energy-related infrastructure.




