Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:16th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Video Conference of SAARC Leaders on COVID-19:
- Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2019 in Parliament.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) and multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).:
- Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence
- United States Reserve Bank key interest rates.
- ROPAX service:
- New Website of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
- Torreites sanchezi,
- Wasp-76b, an exoplanet:
- Ganga Amantran Abhiyan:
- one health
- other important current affairs
1.Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
Thirty-six major changes to the global indicator framework for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were approved and adopted by the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC), at its 51st session that concluded on March 6, 2020, in New York.
- The revised global framework will have 231 indicators, approximately the same number as in the original framework.
- These changes are based on the ‘2020 comprehensive review’ conducted by the UN Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators (IAEG-SDGs).
changes:
- Eight additional indicators were added across six SDG goals — 2, 3, 4, 10, 13 and 16.
- These include:
- Indicator 13.2.2 on the total greenhouse gas emissions per year for the SDG target 13.2 to integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
- Prevalence of anemia in women aged 15-49 years, by pregnancy status (percentage) under the target 2.2 to end forms of malnutrition by 2030.
- A new indicator of reducing the percentage of bloodstream infections due to selected antimicrobial-resistant organisms has been added under the Global health goal (SDG 3).
- Indicator 10.7.3 on the number of migrants killed while attempting to cross maritime, land and air borders.
- Indicator 10.7.4 on the proportion of the population who are refugees, by country of origin.
- Six indicators across six SDG goals — 1, 4, 8, 11, 13 and 17 — have been deleted.
- These include:
- Indicator 1.a.1 on the proportion of domestically-generated resources allocated by the government directly to poverty reduction programs.
- Indicator 4.2.1 on the proportion of children under five years of age who are developmentally on track in health, learning, and psychosocial well-being, by sex.
- The portion of the indicator that measures progress for children between 0 and 23 months of age, which is currently in tier III was proposed for deletion by the IAEG.
- Under the SDG goal on combating climate change, the indicator 13.3.2, quantifying the number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of capacity-building for implementing adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer, and development actions has been deleted.
2.Video Conference of SAARC Leaders on COVID-19:

The Video Conference of South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Leaders on COVID-19 was held recently.
- All the members of SAARC (India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Afghanistan, and Pakistan) attended the conference.
- The conference is considered as a step towards the revival of SAARC as the SAARC Summit has not taken place since 2014 because of India-Pakistan tensions.
Key Points
- COVID-19 Emergency Fund:
- India has proposed to create a COVID-19 Emergency Fund which could be based on a voluntary contribution from all SAARC members.
- Further, $10 million has been extended by India as a contribution to the fund.
- The fund can be used to meet the cost of immediate actions by any member and will be coordinated through foreign secretaries and embassies of the member countries.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has also constituted the COVID-19 Solidarity Response Fund with the help of corporate bodies, foundations, and the UN Foundation.
- India has also proposed a rapid response team of doctors and specialists, along with testing kits and other equipment for all the member countries.
- India has set up an Integrated Disease Surveillance Portal to better trace possible virus carriers and the people they contacted. India has offered to share it with member countries.
- Economic Issues and Measure:
- The conference also discussed the longer-term economic consequences of COVID-19.
- The member countries have also proposed to insulate the internal trade of South Asia and local value chains from its impact.
- Measures by SAARC to Manage Health Pandemics:
- It has been decided to frame and enforce the common SAARC pandemic protocols.
- The members have also decided to establish a working group of national authorities for health information, data exchange, and coordination in real-time.
- It has also proposed a SAARC health ministers’ conference and the development of regional mechanisms to share disease surveillance data in real-time.
- Country-Specific Issues:
- Afghanistan has highlighted the vulnerability as it shares a long and open border with Iran, one of the worst affected countries in the world.
- The Maldives has cited the economic downturn owing to the drop in tourists inflow from Italy, China, and Europe – the main source of tourists for the country and sought a South Asian response to the crisis.
- The tourism-dependent countries like Bhutan, Sri Lanka has also sighted issues related to the economic slowdown.
2.Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2019 in Parliament.:

The Standing Committee on Information and Technology tabled its report on the Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2019 in Parliament.
- Union government is dragging its feet on overhauling the archaic film certification and censorship mechanism, bringing only incremental changes to the Cinematograph Act that was first introduced in 1952.
- The Cinematograph Amendment Bill, 2019, is a belated measure by the government to tackle the issue of piracy.
- It seeks to introduce two Sections to the Cinematograph Act, 1952,
- one, prohibiting illegal recording in cinema halls to make a “pirate copy” of the film, and
- second, prescribing the punishment of up to three years or a fine of up to ₹10 lakh for the said offence.
- The Bill was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in February last year and referred to the Standing Committee.
- The committee has found the scope of the Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2019, limited.
- The Bill only tackles illegal recording at cinema halls.
- Also, the punishment prescribed in the Bill is too little when compared with the losses that a pirated film can lead to.
3. Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) and multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).:
Recently, a small trial was undertaken to test the safety and efficacy of a few oral drugs against the extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) and multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
- The trial showed encouraging results with a success rate of 90%.
- The favourable results held true regardless of the HIV status of the patients.
- The trial (Nix-TB) tested three oral drugs namely bedaquiline, pretomanid and linezolid in patients with XDR-TB and MDR-TB.
- The 90% treatment success in the case of hard-to-treat patients is at par with the success rate seen while treating drug-sensitive TB.
- Of the 109 patients treated, 11 had unfavorable outcomes.
- Of the 11 patients, there were seven deaths and two had a relapse during the six-month follow-up period.
- The treatment success rate was 89% for XDR-TB and 92% for MDR-TB.
- The MDR-TB patients included in the trial were either not responsive to standard treatment or had discontinued treatment due to side effects.
4. Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence has shown concern at the widening gap between projections and allocations in the defense budget.:
Recently, a Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence has shown concern at the widening gap between projections and allocations in the defense budget.
- The Committee noted that since 2015-16, none of the three Services (Army, Navy and Air Force) has been given the matching allocation as per the projection.
- There is a considerable shortage in the allocation in the Capital Head, which is 35% less than the projection.
- The Committee noted that committed liabilities constitute a significant part of the Capital Head and inadequate allocation would definitely lead to a ‘default situation’ on contractual obligations.
- Committed liabilities are payments anticipated during a financial year for contracts concluded in previous years.
- Such a situation is not conducive for the preparation of the country to modern-day warfare, where possession of capital intensive modern machines is a prerequisite for tilting the result of the war in favor and also to have a credible deterrence.
- Both the Navy and the Indian Air Force (IAF) has a situation where their committed liabilities are more than their share of the capital allocation in the Budget.
- To offset this, the Services have been forced to defer payment of committed liabilities of the Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSU) among other measures.
6. ROPAX service:

Union Minister for Shipping inaugurated ROPAX service from Bhaucha Dhakka, Mumbai to Mandwa, Alibag in Maharashtra.
- ROPAX service is a ‘Water Transport Service Project’, under Eastern Waterfront Development.
- ROPAX Vessel M2M -1 can carry 200 cars and 1000 passengers at a time and has a ramp on both sides, hence cars can move in and out of the vessel easily and reduce the turn- around time.
- The benefits of this service include a reduction in the travel time, vehicular emission and traffic on the road.
- Mumbai Port Trust has developed ROPAX jetty and terminal facilities at Bhaucha Dhakka (Ferry Wharf) at the cost of Rs 31 Crores.
- Maharashtra Maritime Board has developed Breakwater, ROPAX jetty and terminal facilities at Mandwa at the cost of Rs 135 Crores.
7.New Website of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy:

Recently, a new website of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy was launched. The Ministry website hosts KUSUM Scheme Portal, Akshay Urja Portal and India Renewable Idea Exchange (IRIX) Portal.
KUSUM Scheme
- KUSUM stands for Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan.
- It’s objective is to provide financial and water security to farmers through harnessing solar energy capacities of 25,750 MW by 2022.
- The scheme consists of three components:
- Installation of ground-mounted grid-connected renewable power plants in rural areas.
- Installation of standalone solar-powered agriculture pumps.
- Solarisation of grid-connected agriculture pumps to make farmers independent of grid supply and also enable them to sell surplus solar power generated to DISCOM.
- Benefits
- A stable and continuous source of income to the rural landowners.
- Availability of sufficient local solar/other renewable energy-based power for feeding rural load centres and agriculture pump-set loads.
- Reducing transmission losses.
- Save the expenditure incurred on diesel for running diesel pumps.
- Substantial environmental impact in terms of savings of CO2 emissions.
- India Renewable Idea Exchange (IRIX)
- IRIX is a platform that promotes the exchange of ideas among energy-conscious Indians and the Global community.
8.Torreites sanchezi, :
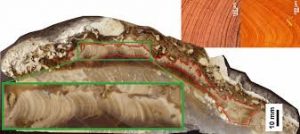
According to a new study of fossil mollusc shells from the Late Cretaceous, Earth spun 372 times a year 70 million years ago, compared to the current 365. This means the day was 23½ hours long, compared to 24 today.
- Torreites sanchezi, an extinct species of rudist clam that lived during the Cretaceous period, some 70 million years ago, grew fast, laying down daily growth rings.
- In a new study, a team of researchers used lasers to sample minute slices of Torreites sanchezi’s shell and count the growth rings.
- The rings allowed the scientists to determine the number of days in a year and more accurately calculate the length of a day 70 million years ago.
- The new measurement also informs models of how the Moon formed and how close to Earth it has been over the 4.5-billion-year history of the Earth-Moon gravitational dance.
9.Wasp-76b, an exoplanet:

Wasp-76b, an exoplanet (a planet outside the solar system), probably have iron raining on it.
- Wasp-76b orbits so close to its host star that its dayside temperatures exceed 2,400 degrees Celsius – hot enough to vaporize metals like iron.
- The planet’s nightside, on the other hand, is 1,000 degrees cooler, allowing those metals to condense and rain out.
Wasp-76b
- Wasp-76b is a huge gas planet that is twice the width of Jupiter. Its name comes from the UK-led Wasp telescope system that detected it in 2016.
- The UK Wide Angle Search for Planets (WASP) is a collaborative project involving several UK universities. The primary aim is the discovery of exoplanets.
- It is 640 light-years from the Earth and is so close to its star that it takes just 43 hours to complete one revolution.
- Another of the planet’s interesting features is that it always presents the same face to the star – a behavior scientists call being “tidally locked”. Earth’s Moon does exactly the same thing.
- Tidal locking is the name given to the situation when an object’s orbital period matches its rotational period.
- The moon takes 28 days to go around the Earth and 28 days to rotate once around its axis. This results in the same face of the Moon always facing the Earth.
10.“Ganga Amantran Abhiyan:
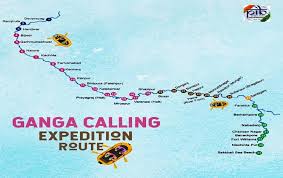
The National Mission for Clean Ganga organized “Ganga Amantran Abhiyan” (GAA). The GAA is an open-water rafting and kayaking expedition in the Ganga river.
- The expedition is conducted between Devprayag and Ganga Sagar.
- Devprayag is the place where two rivers Alakananda and Bhagirathi meet to form the mighty Ganges. Ganga Sagar is a part of Sunderbans.
- The NMCG has been organizing several environmental, economic and cultural values in India.
- This is being done to increase public participation in the mission.
- GAA is a major part of these programmes.
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga was launched in 2011. It was initially operating inder the National Ganga River Basin Authority that was dissolved in 2016. The authority was replaced with National Ganga Council.
- The mission is now being operated under the Ministry of Jal Shakti. It is registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
11.One Health’:
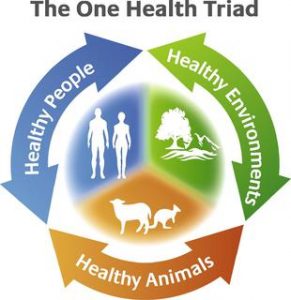
The concept of ‘One Health’, which recognizes that the health of human beings is connected to the health of animals and the environment, is gaining importance as most of the contagious diseases affecting humans are zoonotic (animal to man origin) in nature.
- The concept of One Health can be effectively implemented for reducing the incidence of emerging zoonotic threats like COVID-19.
- One Health is the collaborative efforts of multiple disciplines working locally, nationally, and globally, to attain optimal health for people, animals, and our environment, as defined by the One Health Initiative Task Force.
- One Health model facilitates an interdisciplinary approach in disease control so as to control emerging and existing zoonotic threats.
- One Health issues include zoonotic diseases, antimicrobial resistance, food safety, and food security, vector-borne diseases, environmental contamination, and other health threats shared by people, animals, and the environment.
- Even the fields of chronic disease, mental health, injury, occupational health, and noncommunicable diseases can benefit from a One Health approach involving collaboration across disciplines and sectors.
- One Health model is a globally accepted model for research on epidemiology, diagnosis, and control of zoonotic diseases.
- The WHO is very effectively addressing emerging issues of antimicrobial resistance through One Health research.
- All the developing countries are in the process of promoting One Health research for developing a sustainable disease control system.
Other important current affairs:
1. While listing the measures taken to tackle the coronavirus pandemic, US President Donald Trump announced that Google was helping the government develop a website “to determine whether a test is warranted and to facilitate testing at a nearby convenient location”.
- Trump was talking about Verily, a subsidiary of Google’s parent company Alphabet “focused on life sciences and healthcare”.
- Verily Life Sciences, also known as Verily (formerly Google Life Sciences), is Alphabet Inc.’s research organization devoted to the study of life sciences.
- It is an independent subsidiary of Alphabet Inc.
2. The Commerce Ministry reported that the gold imports for the period April to February (2019-20) has reduced by 8.86% as compared to the previous year.
- The Indian economy has been facing increased current account deficit due to the import of gold and fuel.
- The Current Account Deficit is the difference between money flowing in on exports and the money flowing out on imports.
- A country with increasing CAD means that it is becoming uncompetitive. It also means that investors are not willing to invest.
- Therefore, reducing gold and oil imports will reduce the current account deficit.
3. The Uttar Pradesh Government passed an ordinance, “Recovery of Damages to public and private property ordinance, 2020”.
- The ordinance aims to deal with violent acts and control its persistence.
- It will also provide recovery of public and private property damages.
- In December 2019, the Government of India passed the Citizenship Amendment Act.
- The act provides citizenship only to non-Muslim refugees.
- The protestors are of the opinion that the act is discriminating against Muslims in the country.
4. The famous annual Chaitra Jatra festival scheduled to be held on March 17 at Odisha’s Tara Tarini hill shrine was canceled as a precautionary measure against COVID-19 infection.
- This festival is celebrated at Tara Tarini hill shrine on Tuesdays of the Hindu month of Chaitra.
- The largest gatherings occur on the second and third Tuesdays. March 17 happens to be the second Tuesday.
- Tara Tarini hill shrine, located at Kumari hill on banks of the Rushikulya river, is a major center of Shakti worship in Odisha.
5. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development recently released a report on the effect of COVID-19 on the global economy. According to the report, India was ranked 10th.
- The report says that the slow down in the manufacturing sector of China due to the virus will affect 50 billion USD trade all over the world hitting global value chains greatly.
- Among the most affected European Union is to take a hit of 15.6 billion USD, followed by the US with 5.8 billion USD. Japan at 5.2 billion USD and South Korea and Vietnam at 3.8 billion USD and 2.3 billion USD respectively.
- Though India will receive the 10th largest economic blow in the world due to the virus, its economic slow-down will be low as compared to the other economies.
- In India, the chemical sector is to receive heavy blow followed by textiles, automotive sector, electrical machinery, leather products, and metal products.
6. A study by researchers from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai (TIFR) has revealed that glucose in the body controls the function of SIRT1 directly.
- SIRT1 is an enzyme that deacetylates (removal of acetyl) proteins that contribute to cellular regulation (reaction to stressors, longevity).
- A shortage or absence of the control by glucose may lead to a diabetic-like state, while excess feeding and sustained low levels of SIRT1 can lead to obesity and enhanced aging.
- This study paves the way that might be beneficial in tackling lifestyle disorders and aging-related diseases.
- In normal healthy individuals, SIRT1 protein levels are known to increase during fasting and decrease during the feed, which is essential to maintain a balance between glucose and fat metabolism.
- The glucose controls the functions of a protein SIRT1 which in turn maintains everyday feed-fast cycles and is also associated with longevity.
7. At a political delegation, Home Minister Amit Shah announced that statehood of Jammu and Kashmir is to be restored.
- While resuming statehood of the state, the GoI is to release people from detention, relax curfew and restore the internet.
- Also, industrial policy is to be created soon for the rapid industrial development of the territory.
- This is the first political delegation that is being held after the Abrogation of Article 370.
8. With more than 80 confirmed COVID-19 cases, India has declared “notified Disaster”.
- With this, the SDRF funds are to be temporarily used for the supply of food, medical care and water for patients in quarantine camps.
- Under Disaster Management Act, 2005, the SDRF funds shall be used only for cyclone, earthquake, drought, landslide, hailstorm, cloudburst, avalanche, frost, pest attack, and cold waves.
- Critical Medical conditions or pandemic situations were not under the notified disaster lists.
- Therefore, the Central Government has included the COVID-19 outbreak under notified Disaster.
- This will now enable the state government to utilize the funds for treating Corona Virus.
9. The water level in the Krishna Raja Sagar (KRS) Dam in Mandya district (Karnataka) is coming down rapidly owing to the increase in the evaporation rate and the decrease in the inflows as a result of summer.
- The Krishna Raja Sagar Dam was built across river Kaveri for the Mysore and Mandya districts in Karnataka in 1932.
- The dam is named for the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV.
- The Dam is the creation of one of the greatest engineers that India had produced, Sir M. Vishweshwaraiah.
- His birthday, 15th September is celebrated as Engineers Day.
10. In South Korea, which has recorded the third-highest number of coronavirus cases outside China, a so-called mysterious Christian cult has been linked to the spread of the disease.
- Shincheonji Church of Jesus or simply Shincheonji is a Christian new religious movement established in 1984 in South Korea by Lee Man-hee.
- The sect is known for its secretive nature; adherents believe that the group’s founder Lee is the returned Jesus Christ and that the Holy Bible is written in secret metaphors which only Lee can correctly interpret.
- The sect became the center of controversy during the 2020 coronavirus outbreak in South Korea.
- The disease spread among Shincheonji’s members; the refusal of the group’s founder and senior leaders to get tested, citing their religious beliefs to privacy, resulted in a national outcry against the group.
11. Ignaz Semmelweis is regarded as the first doctor to recommend ‘wash your hands’ by scrubbing hands with soap and water as one of the most effective methods to stop the spread of several illnesses including COVID-19.
- Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis (1818 – 1865) was a Hungarian physician and scientist, now known as an early pioneer of antiseptic procedures.
- Described as the “savior of mothers”, Semmelweis discovered that the incidence of puerperal fever (also known as “childbed fever”) could be drastically cut by the use of hand disinfection in obstetrical clinics.
- Semmelweis proposed the practice of washing hands with chlorinated lime solutions in 1847.
- He published a book of his findings in Etiology, Concept, and Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever.
- Semmelweis’s practice earned widespread acceptance only years after his death when Louis Pasteur confirmed the germ theory.
12. The government of India ordered to suspend 18 of the 37 international borders from March 15, 2020.
- It includes borders across Nepal, Myanmar, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- As the Corona Virus outbreak has reached 93 in numbers, the Government of India has ordered to close international borders in the country.
13. The Kerala Government ordered poultry culling. Parappanagadi has been identified as the Epicenter of bird flu. The Government of Kerala is to cull poultry within a one-kilometer radius.
- Poultry Culling is the process by which unwanted chicks or male embryos are disposed of.
- This is done in industrial egg production. Culling does not involve anesthetics.
- Culling is done using carbon dioxide, cervical dislocation, and maceration.
14. The President of the United States of America Donald Trump has declared a national emergency over the spread of coronavirus. Also, the government has allocated 50 billion USD to fight against the disease.
- This kind of emergency in the country is rare. Earlier, the same kind of emergency was declared by President Bill Clinton over widespread West Nile Virus.
15. The Indian Council of Medical Research developed the COVID-19 testing strategy for people infected with the virus. The Council has given a detailed explanation of the methodology to test the people.
- The three main testing centres of Corona Virus are AIIMS, National Institute of Virology and National Centre for Disease control. Apart from these major centres, GoI has also built 50 new exclusive centers that are to test for the virus.
- The World Health Organization recently shifted the epicenter of Corona Virus from China to Europe.
- This is mainly because while the rate of infections is being controlled in China, it is increasing exponentially in European Nations.
- Also, the number of deaths due to the virus in Europe is more than any other part of the world.
16. Erstwhile royals of the state of Rampur in Uttar Pradesh are fighting over the assets and legacy of Nawab Raza Ali Khan.
- The Supreme Court ended India’s longest-running civil dispute last year, and the process of evaluating the inheritance is currently ongoing.
- The state of Rampur was founded by Nawab Ali Muhammad Khan, the adopted son of Sardar Daud Khan, the chief of the Rohillas in Northern India.
- The Rohillas were Afghans who entered India in the 18th century as the Mughal Empire was in decline, and took control of Rohilkhand, at the time known as Katehr.
- Rampur, under Nawab Raza Ali, was the first kingdom to accede to India in 1949, becoming the only Muslim-majority district in Uttar Pradesh. Soon after accession, the Nawab handed over the official royal residence, the Rampur Qila or Fort, built-in 1775, to the Indian government.
- Rampur District is the only Muslim majority district in the state of Uttar Pradesh, according to the 2011 Census of India.
17. The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Labour in its report has flagged the under-utilization of funds by the Union Labour and Employment Ministry, which was yet to spend almost 20% of its 2019-2020 Budget (revised estimate) as on February 10.
- The report noted that the utilization of funds for the National Career Services (NCS) scheme of the Ministry, which facilitates job-seekers, was the worst compared to other schemes.
- (NATIONAL CAREER SERVICE): It is one of the mission mode projects under the umbrella of the E-Governance Plan.
- It works towards bridging the gap between job-seekers and employers, candidates seeking training and career guidance and agencies providing training and career counseling by transforming the National Employment Service.
- NCS provides a host of career-related services such as dynamic job matching, career counseling, job notifications, vocational guidance, information on skill development courses, internships and alike.
18. Launch of ExoMars rover delayed to 2022.
- The European-built Rosalind Franklin rover, named for the famed British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work contributed to DNA research, recently passed final pre-launch thermal and vacuum tests at an Airbus facility in Toulouse, France.
- Rosalind Franklin is the first European Mars rover.
- About ExoMars: It is a joint endeavor between ESA and the Russian space agency, Roscosmos.
- The primary goal of the ExoMars program is to address the question of whether life has ever existed on Mars.
19. Guidelines by the World Health Organization, to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, specify that one of the ways to reduce the risk of infection is by regularly and thoroughly cleaning one’s hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or washing them with soap and water.
- Using soap is more effective in removing microbes on our hands.
- Viruses such as coronavirus, influenza-causing viruses, Ebola, Zika have their genetic material encased in a layer of fat called the lipid envelop.
- Soap molecules are pin-shaped with a head that is water-loving (hydrophilic) and a tail that is oil-loving (oleophilic). Being oleophilic, the tail portion of the molecule tends to have an affinity for and ‘competes’ with the lipids in the virus envelope.
- Since the chemical bonds holding the virus together are not very strong, the long oleophilic tail gets inserted into the envelope and tends to have a ‘crowbar’ effect that breaks the lipid envelope of the virus.
- The tail also competes with the bond that binds the RNA and the lipid envelop thus dissolving the virus into its components which are then removed by water.
20. The UK’s Chief Scientific Adviser has said a degree of herd immunity will help the UK population as Covid-19 spreads.
- Herd immunity is when a large number of people are vaccinated against a disease, lowering the chances of others being infected by it.
- When a sufficient percentage of a population is vaccinated, it slows the spread of disease.
- It is also referred to as community immunity or herd protection.




