Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:14th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Delhi Assembly passes resolution against NPR, NRC
- “Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)”
- Generation of Red Blood Cells(RBCs) outside the body (in vitro)
- Modified New Pricing Scheme -III (NPS-III)
- Masks and Hand Sanitizers Under EC Act, 1955.
- National Creche Scheme:
- Reconstruction scheme for Yes Bank
- Bhoomi Rashi Portal
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Rules, 2020(POSCO RULE):
- National Biopharma Mission (NBM):
- Public Financial Management System (PFMS),:
- Floor test
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- Other important current affairs:
1. Delhi Assembly passes resolution against NPR, NRC:

Delhi Assembly passes resolution against NPR, NRC.
- As many as 11 Indian States have passed a resolution against the NRC and the NPR.
- Under Seventh Schedule of the Constitution, the subject of citizenship, naturalization, and aliens (foreigners) finds mention exclusively in the Union List which contains a total of 97 subjects.
- So, citizenship and the laws related to it are exclusively in the domain of the central government and the refusal by states to implement NRC or NPR has no legal ground.
- The state governments can move the courts to challenge the central government but a refusal to implement is not within their powers.
- Article 365 of the Constitution makes it mandatory for the state governments to follow and implement the directions of the Central government, failing which the President can hold that the state government cannot carry on.
2. “Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)” :

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a scheme for “Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)” to boost exports to International Markets.
- Under this scheme, a mechanism would be created for reimbursement of taxes/ duties/ levies, at the central, state and local levels, which are currently not being refunded under any other mechanism, but which are incurred in the process of manufacture and distribution of exported products.
- This scheme is going to give a boost to Indian exports providing a level playing field for Indian producers in the International market so that domestic taxes/duties are not exported.
- An inter-ministerial committee will determine the rates and items for which the reimbursement of taxes and duties would be provided.
- Refund under the Scheme, in the form of transferable duty credit/electronic scrip will be issued to the exporters, which will be maintained in an electronic ledger. The Scheme will be implemented with end to end digitization.
- The refunds under the RoDTEP scheme would be a step towards “zero-rating” of exports, along with refunds such as Drawback and IGST.
3.Generation of Red Blood Cells(RBCs) outside the body (in vitro) :
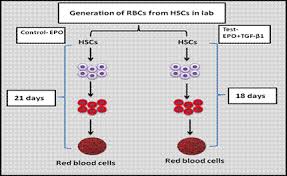
A team of Indian researchers has invented a process through which generation of Red Blood Cells(RBCs) outside the body (in vitro) from Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) can be speeded up.
- The invented process would help to fasten the process of transfusion of RBCs in life-saving treatments for numerous conditions such as severe anemia, transplant surgery, pregnancy-related complications, and blood-related cancers.
- The blood banks, particularly in developing countries, often face a severe shortage of whole blood as well as components of blood like red blood cells.
- Various groups have been able to produce RBCs in the laboratory from HSCs. However, the process takes a long time – around 21 days.
- The umbilical cord blood contains special cells called hematopoietic stem cells that can be used to treat some types of diseases.
- Hematopoietic stem cells can mature into different types of blood cells in the body.
- The resources required to grow cells in the laboratory over such a long duration can be very expensive for the generation of RBCs on a large scale for clinical purposes.
- The process of generation of RBCs in the laboratory from HSCs can be speeded up by adding a very low concentration of a small protein molecule called `Transforming Growth Factor β1’ (TGF-β1), along with a hormone called `Erythropoietin’ (EPO). The whole process takes 18 days.
- Usually, the addition of only Erythropoietin (EPO) to HSCs generate RBCs in 21 days.
- Indian researchers have found that the addition of TGF-β1 with EPO has cut down the processing time by three days.
- The physical appearance and the quality of the cells formed has revealed that the RBCs formed using this procedure are normal.
4. Modified New Pricing Scheme -III (NPS-III):
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved the proposal of the Department of Fertilizers to remove ambiguities in the Modified New Pricing Scheme -III (NPS-III) for determination of fixed costs for the urea units.
- Modified NPS-III was notified on 2nd April 2014.
- However, due to the ambiguous language of the notification, it could not be implemented.
- The above decision will facilitate its smooth implementation which will result in the grant of Additional Fixed Cost of Rs.350/MT to 30 urea manufacturing units.
- The approval will also grant the special compensation of Rs. 150/MT to urea units which are more than 30 years old and converted to gas which will incentivize these units to remain viable for sustained production.
- The measures will ensure maximum domestic production of urea and reduce will reduce import dependency.
5.Masks and Hand Sanitizers Under EC Act, 1955:

Recently, the central government has notified that masks (2 plies and 3 ply surgical masks, N95 masks) and hand sanitizers as essential commodities up to June 30, 2020, under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955 (EC Act).
- The invocation of the EC Act aims to ensure that these products, key for preventing the spread of Covid-19 infection, are available to people at the right price and of the right quality.
- The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution has also issued an advisory under the Legal Metrology Act, 2009 to ensure these items are not sold for more than the Maximum Retail Price (MRP).
- Under the EC Act, the States and Union Territories can ensure that manufacturers enhance their production capacity so that masks and hand sanitizers are widely available to consumers.
- The invocation of EC Act has empowered the Centre as well as states to regulate the production, quality, distributions of masks and hand sanitizers.
- It will also help to smoothen the sale and availability of the above items and carry out operations against speculators.
- The Consumer Affairs Ministry has also invoked the Prevention of Black Marketing and Maintenance of Supplies of Essential Commodities Act, 1980 which would carry out action against those involved in overpricing and black marketing of the products.
6.National Creche Scheme:

The National Crèche Scheme is a centrally sponsored scheme being implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- The scheme was earlier named as Rajiv Gandhi National Creche Scheme.
- It aims to provide daycare facilities to children (age group of 6 months to 6 years) of working mothers.
- The salient features of the National Creche Scheme are as follows:
- Daycare Facilities including Sleeping Facilities.
- Early Stimulation for children below 3 years and pre-school education for 3 to 6 years old children.
- Supplementary Nutrition ( to be locally sourced)
- Growth Monitoring
- Health Check-up and Immunization
- Crèches shall be open for 26 days in a month and for seven and a half (7-1/2) hours per day.
- The number of children in the crèche should not be more than 25 per crèche.
- User charges will be levied to bring in an element of community ownership.
- The fund sharing pattern under National Creche Scheme amongst Centre, States/UTs & Non-Governmental Organisations/Voluntary Organisations is in the ratio of 60:30:10 for States, 80:10:10 for the North Eastern States and the Himalayan States and 90:0:10 for UTs.
7.Reconstruction scheme for Yes Bank :

The Union Cabinet has approved a reconstruction scheme for Yes Bank as proposed by the Reserve Bank of India.
- State Bank of India will invest 49 percent equity in Yes Bank with other investors also being invited.
- The scheme has been approved with the objective of protecting the interest of depositors and providing stability to Yes Bank as well as to the entire financial system.
- The moratorium on withdrawals from Yes bank will be lifted within 3 days of notification of the reconstruction scheme, while its board will be in place in seven days. On the 5th of this month, the RBI imposed the moratorium, restricting withdrawals to 50 thousand rupees per depositor till the 3rd of April.
- There will be a three year lock-in period for all the investors but in the case of SBI, the lock-in period would be only for 26 percent of the shareholding.
- The authorized capital of the lender has been raised from 1100 crore rupees to 6200 crore rupees to accommodate immediate and subsequent raising of capital requirements.
8.Bhoomi Rashi Portal:

The Bhoomi Rashi Portal is an e-Governance initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
- The portal intends to expedite the process of land acquisition for National Highways.
- It has fully digitized and automated the entire process of land acquisition.
- It has helped to make land acquisition error-free & more transparent with notifications at every stage being processed on a real-time basis.
- Earlier, the acquisition of land for the purpose of National Highway projects, payment of compensation to the landowners, etc. was done manually by the physical movement of documents.
- It had some constraints viz. delay in issuing land acquisition notification, errors in the land/ area details, etc.
- The portal is integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) for depositing the compensation in the account of affected/ interested persons on a real-time basis.
9.Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Rules, 2020(POSCO RULE):

The Centre has notified the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Rules, 2020 which enables the implementation of recent amendments to the Act under which provisions of punishment for child abuse have been made more stringent.
- Some of the significant additions in the new rules include the provision of mandatory police verification of staff in schools and care homes, procedures to report sexual abuse material (pornography), imparting age-appropriate child rights education among others.
- For crackdown on child pornography, any person who has received any pornographic material involving a child or any information regarding such pornographic material shall report the contents to the Special Juvenile Police Unit (SJPU) or police, or the cybercrime portal.
- Under the rules, the State Governments have been asked to formulate a child protection policy.
- The Central Government and every State Government shall provide periodic training including orientation programs, sensitization workshops and refresher courses to all persons coming in contact with the children, to sensitize them about child safety and protection.
- Any institution housing children or coming in regular contact with children, including schools, creches, sports academies or any other facility for children must ensure a police verification and background check on a periodic basis of every staff.
- The new POCSO rules became effective from the 9th of March.
11.National Biopharma Mission (NBM):

The National Biopharma Mission (NBM) is an industry-academia collaborative mission for accelerating biopharmaceutical development in the country.
- It was launched in 2017 at a total cost of Rs 1500 crore and is 50% co-funded by the World Bank loan.
- It is being implemented by the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- BIRAC is a Public Sector Enterprise, set up by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- The oversight of the mission activities is provided by the inter-ministerial Steering Committee chaired by the Secretary-DBT (Ministry of Science & Technology).
- The Technical Advisory Group (TAG) chaired by an eminent scientist provides scientific leadership to the mission drawing upon global expertise.
- Under this Mission, the Government has launched Innovate in India (i3) program to create an enabling ecosystem to promote entrepreneurship and indigenous manufacturing in the biopharma sector.
- It has a focus on the following four:
- Development of product leads for Vaccines, Biosimilars and Medical Devices that are relevant to the public health need by focussing on managed partnerships.
- Upgradation of shared infrastructure facilities and establishing them as centers of product discovery/discovery validations and manufacturing.
- Developing human capital by providing specific training.
- Developing technology transfer offices to help enhance industry-academia inter-linkages.
12. Public Financial Management System (PFMS),:

The Public Financial Management System (PFMS), earlier known as Central Plan Schemes Monitoring System (CPSMS), is a web-based online software application developed and implemented by the Office of Controller General of Accounts (CGA), Ministry of Finance.
- PFMS was initially started during 2009 as a Central Sector Scheme of Planning Commission with the objective of tracking funds released under all Plan schemes of the Government of India, and real-time reporting of expenditure at all levels of Programme implementation.
- Subsequently in the year 2013, the scope was enlarged to cover direct payment to beneficiaries under both Plan and non-Plan Schemes.
- In 2017, the Government scrapped the distinction between plan and non-plan expenditure.
- The primary objective of PFMS is to facilitate a sound Public Financial Management System for the Government of India (GoI) by establishing an efficient fund flow system as well as a payment cum accounting network.
- At present, the ambit of PFMS coverage includes Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes as well as other expenditures including the Finance Commission Grants.
- PFMS provides various stakeholders with a real-time, reliable and meaningful management information system and an effective decision support system, as part of the Digital India initiative of GoI.
- PFMS is integrated with the core banking system in the country.
13.Floor test:
Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister Kamal Nath has requested Governor Lalji Tandon to hold a floor test in the Assembly session starting from March 16, on a date fixed by the Speaker.
- A floor test is a constitutional mechanism. It is used to determine if the incumbent government enjoys the support of the legislature.
- This voting process happens in the state’s Legislative Assembly or the Lok Sabha at the central level.
- Technically, the chief minister of a state is appointed by the Governor.
- The appointed chief minister usually belongs to the single largest party or the coalition which has the ‘magic number’.
- The magic number is the total number of seats required to form a government or stay in power.
- It is the half-way mark, plus one. In case of a tie, the Speaker casts the deciding vote.
- However, at times, a government’s majority can be questioned.
- The leader of the party claiming the majority has to move a vote of confidence.
- If some MLAs remain absent or abstain from voting, the majority is counted on the basis of those present and voting. This effectively reduces the strength of the House and in turn, brings down the majority-mark.
- The voting process can happen orally, with electronic gadgets or a ballot process.
- The Governor can also ask the Chief Minister to prove his or her majority in the House if the stability of the government comes into question.
14.National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):

- Union Environment Ministry has asked for city-level plans for the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) as these problems need to be dealt with at the local level.
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): Launched in January 2019, it is the first-ever effort in the country to frame a national framework for air quality management with a time-bound reduction target.
- The program will not be notified under the Environment Protection Act or any other Act to create a firm mandate with a strong legal back up for cities and regions to implement NCAP in a time-bound manner for effective reduction.
- The plan includes 102 non-attainment cities, across 23 states and Union territories, which were identified by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) on the basis of their ambient air quality data between 2011 and 2015.
Other important current affairs:
1. The Reserve Bank of India revised exposure limits of Urban Cooperative Banks.
- Earlier the RBI permitted 15% of its capital funds to single borrowers and 40% of its funds to a group of borrowers. It has now revised the group of borrower fund limit to 25% of its funds.
- Apart from the Exposure limit, the central bank also increased the Priority Sector lending to 75%.
- These changes were introduced by the Reserve Bank of India through a notification.
- The Exposure Limit is the maximum credit a bank avails to its borrower. In simple terms, the higher the exposure limit, the higher are the loans available to its customers.
2. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved Rehabilitation and Upgradation of stretches of various National Highways covering a total length of over 780 km in the States of Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh.
- The project involves an investment of Rs 7662.47 crore which includes a loan component of Rs. 3500 crore (USD 500 Million).
- The loan assistance of the World Bank will be under Green National Highways Corridor Project (GNHCP).
- The project also includes the maintenance of these National Highways stretches for 5 years (in the case of flexible pavement)/10 years (in the case of rigid pavement) after completion of construction.
3.Namaste: With the declaration of coronavirus pandemic, Namaste, an Indian way of greeting, instead of the normal handshake, has emerged as the most preferred form of pleasantries to reduce physical contact with others.
- Namaste, sometimes spoken as Namaskar and Namaskaram, is a customary Hindu greeting.
- It is used both for greeting and leave-taking.
- Namaste is usually spoken with a slight bow and hands pressed together, palms touching and fingers pointing upwards, thumbs close to the chest. This gesture is called Añjali Mudrā; the standing posture incorporating it is
- In Hinduism, it means “I bow to the divine in you”. Namaste may also be spoken without the gesture, or the gesture may be performed wordlessly.
4. Pi Day is celebrated on March 14 dedicated to Pi (Greek letter π). The idea originated in the United States, where the convention is to write dates in a format that expresses March 14 as 3/14.
- These three digits match the value of pi up to two decimal places, at 3.14.
- By definition, pi is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
- Pi is also the area of a circle divided by the square of its radius. The ratio is always constant.
- A pi is an irrational number, it is denoted by a symbol ‘π’.
- Pi has its use in geometry, trigonometry, physics, astronomy, and other sciences.
- It appears in various formulae. Few important formulae are:
- The area of a circle is πr2.
- The volume of a cylinder is πr2h.
5. The Karnataka government has insisted that private companies provide 80% reservation in jobs for locals (Kannada-speaking people) in all categories.
- The government has already amended the Karnataka Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Rules, 1961, to reserve 100% for group ‘C’ and group ‘D’ jobs for locals in the private sector.
- The government last year amended the rules to allow this.
- Competition from outsiders: In the last few years, Bangalore has witnessed a huge population influx from all corners of India naturally upsetting the local and migrant balance and causing social friction primarily owing to economic reasons.
- With not enough jobs being created and the poor spread of those that are getting created, the pressure on, and in, relatively better-performing states is growing.
6.blue chip stocks
- Blue-chip stocks are shares of very large and well-recognized companies with a long history of sound financial performance.
- These stocks are known to have capabilities to endure tough market conditions and give high returns in good market conditions.
- Blue-chip stocks generally cost high, as they have a good reputation and are often market leaders in their respective industries
7.Coronavirus strain isolated in India:
- India is only the fifth country in the world besides Japan, Thailand, the U.S., and China to have successfully isolated the COVID-19 virus strain, helping it take the first step towards expediting the development of drugs, vaccines and rapid diagnostic kits in the country.
8.sepsis, a common cause of death from coronavirus
- Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by the body’s immune system overreacting in response to an infection.
- This overactive, toxic response can lead to tissue damage, multiple organ failure, and death.
- Viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites — sepsis can be triggered by a variety of pathogens.
- The causes of sepsis are usually pneumonia, wound infections, urinary tract infections or infections in the abdominal cavity.
- Ebola and yellow fever viruses, dengue, swine flu or bird flu viruses can also cause sepsis.




