Today Current Affairs: 19th March 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Electoral Bonds::

Chief Justice of India agreed to urgently hear a plea by NGO Association for Democratic Reforms to stay the sale of a new set of electoral bonds on April 1, before the Assembly elections in crucial states such as West Bengal and Tamil Nadu.
Arguments by petition:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Election Commission had both said that the sale of electoral bonds had become an avenue for shell corporations and entities to park illicit money and even proceeds of bribes with political parties.
- Data obtained through RTI has shown that illegal sale windows have been opened in the past to benefit certain political parties.
- There is a serious apprehension that any further sale of electoral bonds before the upcoming State elections in West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Assam would further increase illegal and illicit funding of political parties through shell companies.
- The scheme had “opened doors to unlimited political donations, even from foreign companies, thereby legitimizing electoral corruption at a huge scale, while at the same time ensuring complete non-transparency in political funding”.
- The government notified the scheme on January 2, 2018.
- It defended the scheme in court, saying it allowed anonymity to political donors to protect them from “political victimization”.
- The Ministry of Finance had dismissed the Election Commission’s version that the invisibility afforded to benefactors was a “retrograde step” and would wreck transparency in political funding.
- It said the earlier system of cash donations had raised a “concern among the donors that, with their identity revealed, there would be competitive pressure from different political parties receiving donation”.
Ration Cards Cancellation Case:

The Supreme Court has asked the Centre to respond to a plea related to the cancellation of over three-crore ration cards for not linking them to Aadhaar.
- Also, the SC has sought a report on the implementation of the grievances redressal mechanism. It is contained in Sections 14, 15, and 16 of the National Food Security Act, 2013.
- A petition has been filed in the Supreme Court which said that such cancellations had led to starvation deaths across the country.
- Right to food, which the ration card symbolized, cannot be curbed or canceled because of lack of Aadhaar, says the petitioner.
- The Court said the issue is concerning because the government has cancelled cards of even tribal people and the poor, solely because they could not be biometrically linked with Aadhaar.
- The Union of India casually gives an explanation that these cancelled cards were bogus.
- The real reason is that the technological system based on iris identification, thumbprints, non-possession of Aadhaar, non-functioning of the Internet in rural and remote areas, etc., led to largescale cancellation of ration cards, without notice to the family concerned.
Ration Cards:
- Ration card is an official document issued by state governments in India to households.
- The Household should be eligible to purchase subsidized food grain under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- They also serve as a common form of identification for many Indians.
- Under the NFSA, all state governments have to identify eligible households under the Public Distribution System and provide them with ration cards.
Insurance Amendment Bill, 2021 Passed by Rajya sabha:

The Rajya Sabha passed the Insurance Amendment Bill, 2021 which increases the maximum foreign investment allowed in an insurance company from 49% to 74%.
- The Bill amends the Insurance Act, 1938 to increase the maximum foreign investment allowed in an Indian insurance company.
- The Act provides the framework for the functioning of insurance businesses and regulates the relationship between an insurer, its policyholders, its shareholders, and the regulator (the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India).
- The Act allows foreign investors to hold up to 49% of the capital in an Indian insurance company, which must be owned and controlled by an Indian entity.
- The Bill increases the limit on foreign investment in an Indian insurance company from 49% to 74%, and removes restrictions on ownership and control.
- However, such foreign investment may be subject to additional conditions as prescribed by the central government.
- The Act requires insurers to hold a minimum investment in assets which would be sufficient to clear their insurance claim liabilities.
- If the insurer is incorporated or domiciled outside India, such assets must be held in India in a trust and vested with trustees who must be residents of India.
- The Act specifies in an explanation that this will also apply to an insurer incorporated in India, in which at least: (i) 33% capital is owned by investors domiciled outside India, or (ii) 33% of the members of the governing body are domiciled outside India.
Harayana Recovery Of Damages To Property During Disturbance To Public Order Bill, 2021:

The Government of Haryana has passed the Haraya Recovery of Damages to Property During Disturbance to Public Order Bill, 2021.
- It can be noted that earlier Uttar Pradesh Government too had passed a similar bill named “Uttar Pradesh Recovery of Damages to Public and Private Property Act, 2020.
About the Bill:
- Recovery of Damages: The Bill provides for recovery of damages to properties caused by persons during disturbances to public order by an assembly, lawful or unlawful, including riots and violent disorder.
- It also ensures compensation to the victims.
- The recovery will not only be made from those who indulge in violence but also from those who lead the protest, the organizers, those involved in its planning and provide encouragement, and the participants.
- Establishes a Claim Tribunal: The provision for the constitution of Claims Tribunal to determine the liability, to assess the damages caused, and to award compensation.
- The power to attach property or bank account of any person against whom an award has been passed by the Claims Tribunal to pay compensation.
- Any person aggrieved by the award passed by the Claims Tribunal may file an appeal before the High Court of Punjab and Haryana.
- No civil court shall have the jurisdiction to entertain any question relating to the claim for the compensation
Vehicle Scrapping Policy:

The Union Road and Transport Minister announced the Vehicle Scrapping Policy in the Lok Sabha.
- It was first announced in the Union Budget for 2021-22.
- The policy is estimated to cover 51 lakh Light Motor Vehicles (LMVs) that are above 20 years of age and another 34 lakh LMVs above 15 years of age.
- India will also implement a Global Positioning System (GPS)-based toll collection system and do away with all toll booths within a year.
- Aim: Reducing the population of old and defective vehicles, bringing down vehicular air pollutants, improving road and vehicular safety.
Provisions:
Fitness Test:
- Old vehicles will have to pass a fitness test before re-registration and as per the policy government commercial vehicles more than 15 years old and private vehicles which are over 20 years old will be scrapped.
- Old vehicles will be tested at the Automated Fitness Center and the fitness test of the vehicles will be conducted according to international standards.
- Emission test, braking system, safety components will be tested and the vehicles which fail in the fitness test will be scraped.
- The Ministry has also issued rules for the registration procedures for scrapping facilities, their powers, and scrapping procedures to be followed.
Road Tax Rebate:
- The state governments may be advised to offer a road-tax rebate of up to 25% for personal vehicles and up to 15% for commercial vehicles to provide an incentive to owners of old vehicles to scrap old and unfit vehicles
Vehicle Discount:
- Vehicle manufacturers will also give a discount of 5% to people who will produce the ‘Scrapping Certificate’ and registration fees will be waived off on the purchase of a new vehicle.
Disincentive:
- As a disincentive, increased re-registration fees would be applicable for vehicles 15 years or older from the initial date of registration.
Tomar king – Anangpal II:

A seminar highlighted the legacy of the long-forgotten Tomar king – Anangpal II.
About Anangpal II:
- Anangpal II, popularly known as Anangpal Tomar, belonged to the Tomar dynasty.
- He was the founder of Dhillika Puri, which eventually became Delhi.
- Evidence about the early history of Delhi is inscribed on the iron pillar of Masjid Quwaatul Islam, adjacent to Qutub Minar.
- Multiple inscriptions and coins suggest Anangpal Tomar was the ruler of present-day Delhi and Haryana in between the 8th-12th centuries.
- He had built the city from ruins and under his supervision, Anang Tal Baoli and Lal Kot were constructed.
Anangpal Tomar II was succeeded by his grandson Prithviraj Chauhan. - Delhi Sultanate was established in 1192 after Prithviraj Chauhan’s defeat in the Battle of Tarain (present-day Haryana) by the Ghurid forces.
About Tomar Dynasty:
- Tomara dynasty is one of the minor early medieval ruling houses of northern India.
- Puranic evidence (writings of the Puranas) gives its early location in the Himalayan region. According to bardic tradition, the dynasty was one of the 36 Rajput tribes.
- The history of the family spans the period between the reign of Anangpal, who founded the city of Delhi in the 11th century CE, and the incorporation of Delhi within the Chauhan (Chahamana) kingdom in 1164.
- Although Delhi subsequently became decisively a part of the Chauhan kingdom, numismatic and comparatively late literary evidence indicates that Tomara kings such as Anangapala and Madanapala continued to rule as feudatories, presumably until the final conquest of Delhi by the Muslims in 1192–93.
Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project:

Rajasthan Chief Minister Ashok Gehlot has been strongly demanding national project status for the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP).
Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP):
- The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project aims to harvest surplus water available during the rainy season in rivers in southern Rajasthan such as Chambal and its tributaries including Kunnu, Parvati, Kalisindh.
- Besides supplying drinking water in 13 districts, the mega project will also provide irrigation water to an additional 2 lakh hectares of land.
- It will also supply water to the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor and take care of the flood and drought situation in the area.
- According to the state Water Resources Department, Rajasthan, the largest state of India with a geographical area of 342.52 lakh hectares which amount to 10.4 per cent of the entire country, holds only 1.16 per cent of India’s surface water and 1.72 per cent of groundwater.
- Among the state’s water bodies, only the Chambal river basin has surplus water. But, this water cannot be tapped directly because the area around the Kota barrage is designated as a crocodile sanctuary.
- Therefore, the ERCP aims to create a network of water channels that will cover 23.67 percent area of Rajasthan along with a 41.13 percent population of the state.
National Technical Textiles Mission:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) had, in 2020, approved the setting up of a National Technical Textiles Mission at a total outlay of ₹1,480 Crore.
Aim:
- To position the country as a global leader in technical textiles and increase the use of technical textiles in the domestic market.
- The Mission will be implemented for four years from 2020-2021 and will have four components:
- The first component will focus on research and development and innovation and will have an outlay of ₹1,000 crores.
- The research will be at both, fiber level and application-based in geo, agro, medical, sports, and mobile textiles and the development of bio-degradable technical textiles.
- The second component will be for the promotion and development of the market for technical textiles.
- The Mission will aim at taking domestic market size to $40 billion to $50 billion by 2024.
- The third component will focus on export promotion so that technical textile exports from the country reach from the ₹14,000 crore now to ₹20,000 crore by 2021-2022 and ensure 10% average growth every year till the Mission ends.
- The last component will be on education, training, and skill development.
Technical textiles:
- Technical textiles are defined as textile materials and products manufactured primarily for their technical performance and functional properties rather than aesthetic and decorative characteristics.
- Depending upon their application areas, Technical Textiles products are divided into 12 broad categories: Agrotech, Buildtech, Clothtech, Geotech, Hometech, Indutech, Mobiltech, Meditech, Protech, Sportstech, Oekotech, Packtech.
Pritzker Architecture Prize:

Social housing architects Anne Lacaton and Jean-Philippe Vassal, founders of French studio Lacaton & Vassal, have been named the 2021 winners of the Pritzker Architecture Prize.
- French architects Lacaton and Vassal were named the winners of the award for their body of work that “reflects architecture’s democratic spirit” and their “commitment to a restorative architecture”.
- Their recognition marks the first time a French female architect has won the prize, with Lacaton becoming the sixth woman to receive the award since it was established in 1979.
Pritzker Architecture Prize:
- The Pritzker Architecture Prize is awarded annually to honor a living architect
- Founded in 1979 by Jay A. Pritzker and his wife Cindy, the award is funded by the Pritzker family and sponsored by the Hyatt Foundation.
- It is considered to be one of the world’s premier architecture prizes and is often referred to as the Nobel Prize of architecture.
Bihar Lokayukta (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

The Bihar Assembly passed the Bihar Lokayukta (Amendment) Bill, 2021 that proposes to punish people filing false cases before the anti-corruption ombudsman body to prevent any waste of time or misuse of the institution.
- Lokayukta carries out expeditious investigation and prosecution relating to allegations involving corruption against public servants of all grades.
- The proposed legislation has been brought keeping in view the misuse of the Lokayukta institution in false cases.
- It was proposed by the Lokayukta itself that there should be a provision for punishing people filing false cases before it. The Lokayukta acts of other States have the provision of punitive action against such erring persons.
- The Bill proposes that a case against a person filing a false case can be filed in the district court.
- If the person is found guilty of it or for giving false testimony or filed wrong affidavit, he/she will be sentenced to a jail term of upto three years besides a provision for fine.
High Electron Mobility Transistors (HEMTs):
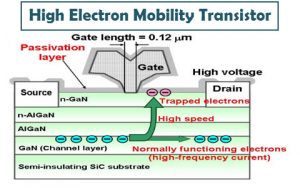
Indian scientists have developed a highly reliable HEMT from gallium nitride (GaN).
- This is the first-ever indigenous HEMT device and is useful in electric cars, locomotives, power transmission and other areas requiring high voltage and high-frequency switching.
- This would reduce the cost of importing such stable and efficient transistors required in power electronics.
- It will also make India self-reliant in power transistor technology.
High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) :
- It is a normally OFF device and can switch currents up to 4A and operates at 600 V.
- HEMTs are used in integrated circuits as digital on-off switches.
- HEMT transistors are able to operate at higher frequencies than ordinary transistors, up to millimeter-wave frequencies, and are used in high-frequency products such as cell phones, satellite television receivers, voltage converters, and radar equipment.
- They are widely used in satellite receivers, in low-power amplifiers, and in the defense industry.
Catch The Rain Campaign:

National Water Mission, Ministry of Jal Shakti had launched a campaign “Catch the Rain” with the tag line “Catch the rain, where it falls when it falls” in 2020.
- It aims to nudge the states and all stakeholders to create Rain Water Harvesting Structures (RWHS) suitable to the climatic conditions and sub-soil strata, with people’s active participation.
- Launched in collaboration with the “Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan” (NYKS) involving Youth Clubs in 623 districts across the country.
Champion state For the Van Dhan Yojana:

Manipur has emerged as the Champion state where the Van Dhan programme has emerged as a major source of employment for the local tribals.
- The Van Dhan Vikas Yojana is a programme for value addition, branding & marketing of Minor Forest Produces by establishing Van Dhan Kendras to facilitate the creation of sustainable livelihoods for the forest-based tribes.
- It is a major scheme that has contributed to increasing employment and income generation among the tribal population.
- The programme is implemented by TRIFED.
The ADR’s Analysis Of The Balance Sheets Of The National Parties:

According to a report released by the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR), BJP tops in declared assets.
- Over 54% of the assets declared by seven national parties for 2018-2019 belonged to the Bharatiya Janata Party, while the Congress accounted for 58% of all liabilities reported by the parties.
- The ADR’s analysis of the balance sheets of the national parties at that time — the BJP, the Congress, the Bahujan Samaj Party, the Communist Party of India, the Communist Party of India-Marxist and the All-India Trinamool Congress — showed assets of ₹5,349.25 crore.
- Forty-one regional parties declared assets of ₹2,023.71 crore that year. Of the national parties, the BJP declared assets of ₹2,904.18 crore or 54.29% of the total assets of the national parties.




