Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 16th September 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- The National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Bill, 2020:
- The Abraham Accord
- Salary, Allowances, and Pension of Members of Parliament (Amendment) Bill, 2020 passed in Lok Sabah:
- Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020.:
- Adjournment motion:
- INDIAN TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC COOPERATION (ITEC) program:
- Haryana Orbital Rail Corridor Project
- Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2020.:
- Other important current affairs:
1.The National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Bill, 2020::
The bill is proposed to be introduced in this Parliament session.
- It seeks to amend the Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991 pertaining to the powers and function of the Delhi government and the Lieutenant Governor.
Highlights:
- It proposes to clearly spell out the functions of the Council of Ministers and the Lieutenant-Governor (L-G) by giving more discretionary powers to the L-G.
- As per a provision, the L-G could act in his discretion in any matter that is beyond the purview of the powers of the Legislative Assembly of Delhi in matters related to the All India (Civil) Services and the Anti Corruption Branch.
- It will also give more teeth to the L-G, and the validity of any decision taken as per such discretion shall not be questioned.
The Union Territory of Delhi with a Legislative Assembly came into being in 1991 under Article 239AA of the Constitution inserted by ‘the Constitution (Sixty-ninth Amendment) Act, 1991’.
- It said that the UT of Delhi shall be called the National Capital Territory of Delhi, and the administrator thereof appointed under Article 239 shall be designated as the Lieutenant-Governor.
- According to the existing Act, the Legislative Assembly of Delhi has the power to make laws in all matters except public order, police, and land.
- Due to the co-existence of Article 239 and 239AA, there is a jurisdictional conflict between the government of NCT and the Union Government and its representative, the Lieutenant Governor.
- According to the Union government, New Delhi being a Union Territory Article 239 empowers the Lieutenant Governor to act independently of his Council of Ministers.
- However, the state government of Delhi held that the Article 239AA of the Constitution bestows special status to Delhi of having its own legislatively elected government.
- This creates a tussle around the administrative powers of the LG and state government of NCT of Delhi.
2.The Abraham Accord :

The Abraham Accord between Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain is mediated by the USA. It is the first Arab-Israeli peace deal in 26 years.
- Previous Agreements: There were the only two peace deals between Israel and the Arab States in more than a quarter of a century.
- Egypt was the first Arab state to sign a peace deal with Israel in 1979.
- Jordan signed a peace pact in 1994.
The Agreement:
- As per the agreements, the UAE and Bahrain will establish:
- Embassies and exchange ambassadors.
- Working together with Israel across a range of sectors, including tourism, trade, healthcare and security.
- The Abraham Accords also open the door for Muslims around the world to visit the historic sites in Israel and to peacefully pray at Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem, the third holiest site in Islam.
- In the Islamic tradition, the Kaaba in Mecca is considered the holiest site, followed by the Prophet’s Mosque in Medina, and the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem.
- Bringing Israel, the UAE and Bahrain together reflect their shared concern about Iran’s rising influence in the region and development of ballistic missiles. Iran has been critical of both deals.
- The agreement shows how the Arab countries are gradually decoupling themselves from the Palestine question.
- Palestine was among former Ottoman territories placed under UK administration by the League of Nations in 1922. All of these territories eventually became fully independent States, except Palestine.
- Full diplomatic ties will be established between Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain which will have a positive impact on the entire region.
- The deal buys UAE a lot of goodwill in the US, where its image has been tarnished by its involvement in the Yemen war.
- In South Asia, it will put Pakistan in a bind, whether to follow UAE’s steps (will be seen as giving up the Islamic cause of Palestine) or not to follow the UAE (since it is already in a feud with the Saudis over not taking up the Kashmir case, Pakistan cannot afford another hostile Islamic Country).
- In the upcoming presidential election in the USA, the accord could help shore up support among pro-Israel Christian evangelical voters, an important part of the current President’s political base.
3.Salary, Allowances, and Pension of Members of Parliament (Amendment) Bill, 2020 passed in Lok Sabah::
The bill seeks to amend:
- The Salary, Allowances, and Pension of Members of Parliament Act, 1954 to reduce the salaries of MPs by 30%.
- The Salaries and Allowances of Ministers Act, 1952, to reduce the sumptuary allowance of Ministers by 30%.
Rules notified under the 1954 Act to reduce certain allowances of MPs for one year. These include constituency allowance and office expenses allowance. - These changes have been made for a period of one year effective from April 1, 2020.
Background:
- These reductions are being made to supplement the financial resources of the center to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Article 106 of the Constitution empowers MPs to determine their salaries by enacting laws.
- In 1985, Parliament enacted a law that delegated the power to set and revise certain allowances of MPs such as constituency allowance, office allowance, and housing allowance to the central government.
- Till 2018, MPs periodically passed laws to revise their salaries.
- The Finance Act, 2018 provided that the salary, daily allowance, and pension of MPs will be increased every five years, on the basis of the cost inflation index provided under the Income-tax Act, 1961.
4.Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020.:
Lok Sabha passed the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020. The Bill will replace the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Ordinance which was promulgated in June this year.
- The Bill seeks to amend the Essential Commodities Act, 1955 and empowers the central government in terms of production, supply, distribution, trade, and commerce of certain commodities.
- The bill empowers the central government to designate certain commodities including food items, fertilizers, and petroleum products as essential commodities.
- Supply of certain food items including cereals, pulses, potato, onions, edible oilseeds, and oils, can be regulated by the government under extraordinary circumstances as per the provisions of this bill.
- The extraordinary circumstances include war, famine, extraordinary price rise, and natural calamity of grave nature.
- The Bill empowers the central government to regulate the stock of an essential commodity that a person can hold.
- The provisions of the bill regarding the regulation of food items and the imposition of stock limits will however not apply to any government order relating to the Public Distribution System or the Targeted Public Distribution System.
5.Adjournment motion:
An adjournment motion notice was moved in the Lok Sabha over the surveillance of key Indian personalities by a firm linked to the Chinese government.
- Adjournment motion is introduced only in the Lok Sabha to draw the attention of the House to a definite matter of urgent public importance.
- It involves an element of censure against the government, therefore Rajya Sabha is not permitted to make use of this device
- It is regarded as an extraordinary device as it interrupts the normal business of the House. It needs the support of 50 members to be admitted.
- The discussion on this motion should last for not less than two hours and thirty minutes.
- However, the right to move a motion for an adjournment of the business of the House is subject to the following restrictions. i.e. It should:
- Raise a matter which is definite, factual, urgent, and of public importance.
- Not cover more than one matter.
- Be restricted to a specific matter of recent occurrence.
- Not raise a question of privilege.
- Not revive discussion on a matter that has been discussed in the same session.
- Not deal with any matter that is under adjudication of court.
- Not raise any question that can be raised in a distinct motion.
6.INDIAN TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC COOPERATION (ITEC) program:

The 56th ITEC day was observed online by the High Commission of India in Dhaka on September 15, 2020.
About:
- The Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Programme was instituted by a decision of the Indian Cabinet in 1964 as a flagship program of the Government of India to provide development assistance to developing countries across the globe.
- ITEC is administered by the Ministry of External Affairs, India, and is fully funded by the Government of India.
- More than 10,000 training slots are offered every year to more than 160 partner countries for training courses in various areas like Accounts, Audit, Management, SME, Rural Development, Parliamentary Affairs, etc.
- Under ITEC and its sister program SCAAP (Special Commonwealth African Assistance Programme), 161 countries in Asia, Africa, East Europe, Latin America, the Caribbean as well as Pacific and Small Island countries are invited to share in the Indian developmental experience
- The ITEC/SCAAP Programme has the following components:
- Training (civilian and defense) in India of nominees from ITEC partner countries;
- Projects and project-related activities such as feasibility studies and consultancy services;
- Deputation of Indian experts abroad;
- Study Tours;
- Gifts/Donations of equipment at the request of ITEC partner countries; and
- Aid for Disaster Relief.
7.Haryana Orbital Rail Corridor Project
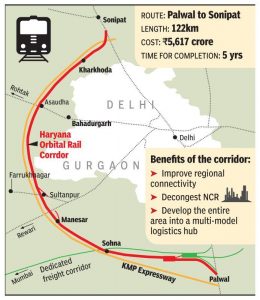
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has given its approval to the Haryana Orbital Rail Corridor Project from Palwal to Sonipat via Sohna-Manesar-Kharkhauda.
- This Rail Line will start from Palwal and end at the existing Harsana Kalan station (On Delhi-Ambala section). This will also give connectivity en route to existing Patli Station (On Delhi-Rewari line), Sultanpur station (On Garhi Harsaru-Farukhnagar Line), and Asaudha Station (On Delhi Rohtak Line).
- The project will be implemented by Haryana Rail Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (HRIDC), a Joint Venture company set up by the Ministry of Railways with the Government of Haryana.
- The project will have the joint participation of the Ministry of Railways, the Government of Haryana, and private stakeholders.
- The project is likely to be completed for 5 years.
- The districts of Palwal, Nuh, Gurugram, Jhajjar and Sonipat districts of Haryana will be benefitted through this rail line.
- This will facilitate diversion of traffic not meant for Delhi and will help in developing multimodal logistics hubs in the Haryana State sub-region of NCR.
8.Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2020.:

RBI has released the draft version of Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2020.
- They are aimed at encouraging higher non-resident participation, enhance the role of domestic market makers in the offshore market, improve transparency, and achieve better regulatory oversight.
- It seeks to allow foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) to undertake exchange-traded rupee interest rate derivatives transactions subject to an overall ceiling of Rs 5,000 crore.
- The net short position of an FPI on exchange-traded IRDs should not exceed its long position in government securities and other rupee debt securities.
- The purpose of offering Rupee IRD contracts to a user, the market-maker (entities which provide bid and offer prices to users in order to provide liquidity to the market) should classify the user either as a retail user or as a non-retail user.
- Non-retail users, as per the draft, are entities regulated by RBI, SEBI, IRDAI or PFRDA; resident companies with a minimum net worth of Rs 500 crore; and non-residents, other than individuals.
Interest Rate Derivatives (IRD) are contracts whose value is derived from one or more interest rates, prices of interest-rate instruments, or interest rate indices. These may include interest rate futures, options, swaps, swaptions, and FRA’s.
Other important current affairs:
1.Scientists from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) have discovered a way to measure the quantity of chlorophyll-a that indicates an abundance of phytoplankton in the Bay of Bengal in real-time.
- Phytoplanktons: They are tiny microscopic floating plants found in water bodies.
- The study of phytoplankton biomass is done by analyzing chlorophyll-a, a dominant pigment found in phytoplankton cells.
- Significance of Phytoplanktons:
- They contribute more than half of the oxygen in the environment.
- They reduce global warming by absorbing human-induced carbon dioxide.
- They also serve as the base of the ocean food chain.
- They are important bioindicators regulating life in oceans. Their abundance determines the overall health of the ocean ecosystem.
2.Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance tabled a report related to startups in Parliament. The Government of India has initiated a Startup India Scheme in 2016.
- Indian start-ups need to reduce their dependence on China and the USA so that India becomes self-reliant by having several large domestic growth funds powered by domestic capital.
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) Fund-of-Funds vehicle should be expanded and fully operationalized to play an investment role.
- A fund-of-funds also is known as a multi-manager investment—is a pooled investment fund that invests in other types of funds.
- Foreign development finance institutions may also be encouraged to participate with local asset management companies to set up fund-of-funds structures.
- The companies and Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) should be allowed to invest in start-ups without being classified as Non-banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to expand capital sources for start-ups.
- Abolition of Long Term Capital Gains (LTCG) tax on Collective Investment Vehicles (CIVs) for at least the next two years to encourage investment in start-ups and to drive a sharp post-pandemic revival.
- At present, LTCG earned by foreign investors in private companies attracts taxation at a rate of 10%, in comparison to the domestic venture capital investments which are taxed at 20% (for LTCG) with an enhanced surcharge of 37%.
- After a two-year period, the Securities Transaction Tax (STT) may be applied to CIVs so that revenue neutrality is maintained.
- A CIV is any entity that allows investors to pool their money and invest the pooled funds, rather than buying securities directly as individuals. It is usually managed by a fund management company that is paid a fee for doing so.
3.China and Nepal are soon expected to announce Mount Everest’s latest official height.
- In 2019, both countries agreed to re-measure the elevation of the world’s highest mountain and announce the findings together.
- Mount Everest (also called Sagarmatha in Nepal) is Earth’s highest mountain above sea level, located in the Himalayas between China and Nepal with their borders running across its summit point.
- Its current official elevation is 8,848m which places it more than 200m above the world’s second-highest mountain, K2, which is 8,611m tall and located in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- Mount Everest gets its English name from Sir George Everest, a colonial-era geographer who served as the Surveyor General of India in the mid-19th century.
- It was first scaled in 1953 by the Indian-Nepalese Tenzing Norgay and New Zealander Edmund Hillary.
- First Survey of Everest: The first effort was carried out in 1847 by a team led by Andrew Waugh, Surveyor General of India.
- The survey was based on trigonometric calculations and is known as the Great Trigonometric Survey of India.
- The team discovered that ‘Peak 15’ (as Mount Everest was referred to then) was the highest mountain, contrary to the then-prevailing belief that Mount Kanchenjunga (8,582m and the 3rd highest peak in the world now) was the highest peak in the world.
5.A Customized My Stamp on India’s First Anti Satellite Missile (A-SAT) launch was released by the Department of Posts on the occasion of Engineers Day.My Stamp: It is the brand name for personalized sheets of Postage Stamps of India Post.
- ‘My Stamp’ was first introduced in India during the World Philatelic Exhibition, ‘INDIPEX-2011’.
- Customized My Stamp is a personalized sheet of Postage Stamps wherein the corporate, organizations, and institutions can get their customized sheets printed from India Post.
- A-SAT Missile: It is an interceptor missile that destroys or jams satellites in space.
- Two types of A-SATs: Kinetic and Non-Kinetic A-SATs.
- Kinetic A-SATs, like ballistic missiles, physically strike an object in order to destroy it.
- Non-Kinetic A-SATs: A variety of nonphysical means can be used to disable or destroy a space object.
- These include frequency jamming, blinding lasers, or cyberattacks.
6.The Karnataka government is likely to pressurize the Centre for approval of the construction of the Mekedatu Project on the Cauvery river.
- Mekedatu, meaning goat’s leap, is a deep gorge situated at the confluence of the rivers Cauvery and its tributary Arkavathi.
- Ontigondlu is the proposed reservoir site, situated at Ramanagara district in Karnataka about 100 km away from Bengaluru.
- It is the midst of the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The Rs. 9,000 crore project aims to store and supply water for drinking purposes for the Bengaluru city. Around 400 megawatts (MW) of power is also proposed to be generated through the project.
7.Cabinet approves the establishment of the new All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) at Darbhanga, Bihar under the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY).
- PMSSY was announced in 2003 with the objectives of correcting regional imbalances in the availability of affordable/ reliable tertiary healthcare services and also to augment facilities for quality medical education in the country.
- The PMSSY is implemented by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It has two components:
- Setting up new AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences)
- Upgradation of government medical colleges in various states.
- The project cost for up-gradation of each medical college institution is shared by the Centre and the state.
8.Aircraft (Amendment) Bill, 2020 passed in Parliament:
- The Act regulates the manufacture, possession, use, operation, sale, import and export of civil aircrafts and licensing of aerodromes.
- Key Features of the Bill:
- Provides statutory status to regulatory institutions like the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) and the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB).
- DGCA powers: It will carry out oversight and regulatory functions with respect to matters under the Bill.
- Powers of BCAS: It carries out regulatory oversight functions related to civil aviation security.
- AAIB carries out investigations related to aircraft accidents and incidents.
- Penalty: The Bill proposes to increase the fine amount for violations of rules from ₹10 lakh to ₹1 crore for aviation industry players.
- Powers of central government: It may cancel the licences, certificates or approvals granted to a person under the Act if the person contravenes any provision of the Act.
- Exemptions: The Act exempted aircrafts belonging to the naval, military, or air forces of the Union.
- The Bill expands this exemption to include aircraft belonging to any other armed forces other than these three.
9.Engineer’s Day:
- India celebrates Engineer’s Day every year on September 15 as a tribute to the greatest Indian Engineer Bharat Ratna Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya on his birthday.
- He was the chief engineer responsible for the construction of the Krishna Raja Sagara Dam in Mysore.
- He was knighted as a Knight Commander of the British Indian Empire by King George V for his contributions to the public good in 1915.




