Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:17th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- The Health Ministry about coronavirus.:
- ICMR to test for Community Transmission of COVID-19
- Modified New Pricing Scheme-III
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for females
- Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
- Floor test from Madhya Pradesh State Government:
- Defense sector
- Privatization of companies
- Sheikh Mujibur Rehman
- Jasmonic Acid
- Mission Solar Charkha
- Starred questions
- Parliament Passes Central Sanskrit Universities Bill 2020
- Bharat Stage Emission Standards (BSES):
- Other important current affairs
1. The Health Ministry has issued a toll-free number 1075 for the public for inquiry about coronavirus.:

Travel of passengers from member countries of the European Union, the European Free Trade Association, Turkey and the United Kingdom to India is prohibited with effect from Wednesday.
- Other important measures include encouraging private sector organizations or employers to allow employees to work from home wherever feasible. Meetings, as far as feasible, shall be done through video conferences.
- Restaurants must ensure handwashing protocol and proper cleanliness of frequently touched surfaces.
- They must ensure physical distancing a minimum of 1 meter between tables and encourage open-air seating with adequate distancing.
2.ICMR to test for Community Transmission of COVID-19:

The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has announced that it would start testing influenza patients without any travel history or contact with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) for signs of community transmission.
Four Stages of Transmission of COVID-19
- Stage 1-Imported Transmission
- It is reported among the travelers entering the country via the borders and airports.
- These can be controlled through thermal screening and quarantine.
- To prevent imported transmissions, India has suspended visas to foreign nationals and the facility of visa-free travel to Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) card-holders.
- Stage 2-Local Transmission
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines it as the transmission through direct contact with an infected person within the country.
- Stage 3-Community Transmission
- It signifies that a virus is circulating in the community and can affect people with no history of travel to affected areas or of contact with an infected person.
- India’s current emphasis on social distancing and discouragement of public gatherings is aimed at checking community transmission.
- Once community transmission begins, it is more difficult to trace contacts.
- As one unknown source of infection can infect many people unknowingly.
- Among the countries where community transmission seems to have begun are China, Italy, and South Korea.
- Stage 4- Epidemic
- An epidemic is a large outbreak, one that spreads among a population or region.
- It is less severe than pandemic due to a limited area of spread.
So far, most of the cases in India have had a history of travel abroad or have contracted the disease from somebody around them.
- Currently, India is at Stage 2 of Local Transmission and precautions are being taken to prevent it from entering Stage 3 of Community Transmission.
3.Modified New Pricing Scheme-III:
The Union Cabinet chaired by PM Modi recently gave its nod to remove ambiguities in Modified New Pricing Scheme-III. This was done to determine the costs of urea units.
- The Modified NPS scheme-III was launched in 2014.
- So far, there have been four NPS schemes.
- The latest NPS-3 scheme was modified in April 2014 and has been extended for a year.
- The scheme was modified to give a boost to PM’s Make in India Campaign
- The Modified scheme provided incentives to the domestic urea manufacturers, encouraged investment in the urea production sector, reduced urea imports. It mainly aimed to achieve self-sufficiency in urea production.
- However, the scheme could not be implemented due to its ambiguous language. The new notification is to facilitate the smooth implementation of the scheme with an additional grant of Rs 350 per metric tonne.
- The GoI has restricted the import of Urea greatly
4. Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for females.:
Union Minister for Human Resource Development informed Lok Sabha about Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for females.
- As per All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) 2018-19, there are 39931 colleges in India, out of which 60.53% are located in rural areas.
- Further, the majority of the colleges provide higher education to both males and females and 11.04% of colleges are exclusively for females.
- Additionally, as per AISHE 2018-19, females constitute 48.6% of the total enrolment in higher education and the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for females in higher education at 26.4% is higher than the national GER of boys at 26.3%.
- Also, the Gender Parity Index (GPI) has increased during the last 5 years, from 0.92 in 2014-15 to 1 in 2018-19.
5.Unnat Bharat Abhiyan:

Recently, information related to the Unnat Bharat Abhiyan (UBA) was given by the Ministry for Human Resource Development (MHRD).
- Unnat Bharat Abhiyan is a flagship program of the Ministry for Human Resource Development (MHRD).
- It aims to link the Higher Education Institutions with a set of at least (5) villages, so that these institutions can contribute to the economic and social betterment of these village communities using their knowledge base.
- Main Objectives:
- To engage the faculty and students of Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) in identifying development issues in rural areas and finding sustainable solutions for the same.
- Identify & select existing innovative technologies, enable customization of technologies, or devise implementation methods for innovative solutions, as required by the people.
- To allow HEIs to contribute to devising systems for smooth implementation of various Government programs.
- Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 2.0
- It is the upgraded version of Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 1.0.
- It was launched in 2018.
- The scheme is extended to all educational institutes; however, under Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 2.0 participating institutes are selected based on the fulfillment of certain criteria.
- Currently, under the scheme, 13072 villages have been adopted by 2474 Institutes.
- The technological interventions under the UBA cover different subjects broadly categorized as in the area of sustainable agriculture; water resource management; artisans, industries and livelihood; basic amenities (infrastructure & services) and rural energy system.
- This has transformed the living conditions in villages and has been beneficial for rural India
6. Floor test from Madhya Pradesh State Government:

The Supreme Court of India issued notice to the Madhya Pradesh State Government to conduct a floor test. A bench headed by Justice Chandrachud issued the notice.
- Jyotiraditya Scindia, who lost the 2019 election in Madya Pradesh ended his 18 years association with Congress party and joined BJP. Following this, 16 Members of the Legislative Assembly who won elections with congress ticket submitted their resignation letter to the speaker of the assembly.
- The assembly commenced for the budget session recently.
- The speaker accepted their resignation.
- Now, there is a question of majority in the house for which when appealed by the MLAs to the SC, the apex court has ordered for a floor test.
- The Floor test is conducted in order to prove the majority of a government. The Chief Minister or Prime Minister moves a vote of confidence. If he gains majority support, he continues to remain in power else he has to resign.
7.Defense sector:

Raksha Mantri informed Rajya Sabha about the efforts made by the Government to boost country’s defense sector during the last two years.
- Industrial licensing: Defence Products list requiring Industrial Licences has been rationalized and the manufacture of most of the parts and components does not require Industrial Licence.
- FDI: Foreign Investment is allowed under automatic route up to 49% and above 49% through the government route.
- Defense Procurement Procedure (DPP): A new category of procurement ‘Buy {Indian-IDDM (Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured)}’ has been introduced in DPP-2016 to promote indigenous design and development of defense equipment.
- “Make” Procedure: In February 2018 a separate procedure for the ‘Make-II’ sub-category has been notified wherein a number of industry-friendly provisions have been introduced.
- The government has notified the ‘Strategic Partnership (SP)’ Model which envisages the establishment of long-term strategic partnerships with Indian entities, wherein they would tie-up with global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to seek technology transfers to set up domestic manufacturing infrastructure and supply chains.
- iDEX: Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) framework, was launched with the aim to achieve self-reliance and to foster innovation in Defence Sector by engaging Industries including MSMEs, startups, individual innovators, R&D institutes and academia.
- Defense Corridors: The government has decided to establish two defense industrial corridors in Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh to serve as engines of economic development and growth of defense industrial base in the country.
- The Ministry has instituted a new framework titled ‘Mission Raksha Gyan Shakti’ which aims to provide boost to the IPR culture in the indigenous defense industry.
- Defense Investor Cell has been created in the Ministry to provide all necessary information including addressing queries related to investment opportunities, procedures and regulatory requirements for investment in the sector.
8. Privatization of companies.:

Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs informed Lok Sabha about the privatization of companies.
- The Government has given ‘in-principle’ approval for Privatisation of 24 CPSEs including Subsidiaries, Units and Joint Ventures with the sale of majority stake and transfer of management control.
- The Government follows a policy of strategic disinvestment of CPSEs, which are not in ‘priority sectors’.
- For this purpose, NITI Aayog has been mandated to identify such CPSEs based on the criteria of
- (i) National Security;
- (ii) Sovereign function at arm’s length, and
- (iii) Market Imperfections and Public Purpose.
9.Sheikh Mujibur Rehman:

The 100th Birth Anniversary celebrations of ‘Jatir Pita’ Bangabandhu, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, is being celebrated on 17th March 2020 in Bangladesh.
- Mujibur Rahman was born on 17th March 1920 in Tungipara, India (now in Bangladesh) and passed away on 15th August 1975 in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- He was a Bengali leader who became the first prime minister of Bangladesh (1972–75) and later became the president of the same in 1975.
- He began his formal political career in 1949 as a co-founder of the Awami League.
- He played a crucial role in advocating political autonomy for East Pakistan, the detached eastern part of Pakistan (now Bangladesh).
- Sheikh Hasina Wazed, the current prime minister of Bangladesh, is the daughter of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman.
10.Jasmonic Acid:
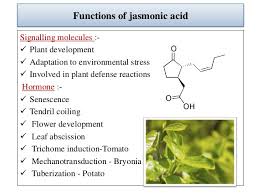
Researchers in the United States have discovered a communication network in plants that helps them respond to a hormone involved in pest resistance.
- The study observed that the hormone called Jasmonic Acid is particularly important for a plant’s defense response against fungi and insects.
- They identified genes important for the plant’s response to jasmonic acid, and for the cellular cross-communication with other plant hormone pathways.
- The genes MYC2 and MYC3 rose to the top in their degree of importance across the system. The two genes are involved in producing proteins that regulate the activity of thousands of other genes.
- By assessing these gene networks and subnetworks, researchers could understand the architecture of the whole plant hormone system. It also helped them to understand which genes are turned on and off during a plant’s defense response.
- Ultimately, the process helps in identifying breeding crops that are able to better withstand attacks from pests.
11.Mission Solar Charkha:

Union Minister for MSME informed Rajya Sabha about Mission Solar Charkha.
- The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) has launched the Mission Solar Charkha in 2018-19 for implementation of 50 Solar Charkha Clusters across the country.
- The aim is to ensure inclusive growth by a generation of employment, especially for women and youth and sustainable development through the solar charkha cluster in rural areas.
- To boost the rural economy and help in arresting migration from rural to urban areas.
- To leverage low-cost, innovative technologies and processes for substance.
- To date, 10 projects have been approved under Mission Solar Charkha. One Solar Charkha cluster has been identified in Andhra Pradesh.
- The scheme envisages generating direct employment to nearly one lakh persons.
12.Starred questions:

Congress leader Rahul Gandhi recently said his right as an MP to ask a supplementary question in Lok Sabha was taken away as Speaker Om Birla did not allow him to ask one.
- Rahul Gandhi was asking the government to name wilful bank loan defaulters but was not allowed another supplementary question amid uproar in the lower house.
- Members of Parliament have a right to ask questions which is one of the devices available to them to seek information on matters of public importance.
- The Question Hour is one such mechanism in which the members ask questions on varied aspects of administration and governmental activity.
- The first hour of every parliamentary sitting is termed as Question hour.
- It is mentioned in the Rules of Procedure of the House.
- During this time, the members ask questions and the ministers usually give answers.
- The number of starred questions was fixed at 20 per Question Hour from the fourth session of the fifth Lok Sabha in 1972.
Type of Questions:
Members have a right to ask questions to elicit information on matters of public importance within the special cognizance of the Ministers concerned. The questions are of three types:
- Starred Questions: A Starred Question is one to which a member desires an oral answer from the Minister in the House and is required to be distinguished by him/her with an asterisk. Answer to such a question may be followed by supplementary questions by members.
- Unstarred Questions: An Unstarred Question is one to which written answer is desired by the member and is deemed to be laid on the Table of the House by Minister. Thus it is not called for oral answer in the House and no supplementary question can be asked thereon.
- Short Notice Questions: A member may give notice of question on a matter of public importance and of urgent character for an oral answer at a notice less than 10 days prescribed as the minimum period of notice for asking a question in the ordinary course. Such a question is known as ‘Short Notice Question’.
13.Parliament Passes Central Sanskrit Universities Bill 2020:

Recently, a Bill to grant the status of Central universities to three deemed Sanskrit universities was passed by the Rajya Sabha.
- The Central Sanskrit Universities Bill, 2019 gives Central status to the Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan and Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Delhi and the Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Tirupati.
- The government has been accused of neglecting other classical languages in India.
- Currently, there are six languages that enjoy the ‘Classical’ status in India:
- Tamil (declared in 2004),
- Sanskrit (2005),
- Kannada (2008),
- Telugu (2008),
- Malayalam (2013), and
- Odia (2014).
- All the Classical Languages are listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
- The Ministry of Culture provides the guidelines regarding Classical languages.
Guidelines for declaring a language as ‘Classical’ are:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500-2000 years;
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generations of speakers;
- The literary tradition be original and not borrowed from another speech community;
- The classical language and literature being distinct from modern, there may also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or its offshoots.
- Once a language is notified as a Classical language, the Human Resource and Development Ministry provides certain benefits to promote it:
- Two major annual international awards for scholars of eminence in classical Indian languages
- A Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages is set up
- The University Grants Commission is requested to create, to start with at least in the Central Universities, a certain number of Professional Chairs for the Classical Languages so declared.
14. Bharat Stage Emission Standards (BSES):

The Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers has said it has approached the Supreme Court seeking directions to ensure that sale and registration of BS-IV complaint is allowed till March 31, 2020.
- The move follows circulars from some State governments setting a cut-off date ranging between February 29 and March 25, 2020, for accepting registration applications for BS-IV-compliant vehicles.
Bharat Stage Emission Standards (BSES):
- Introduced in the year 2000.
- They are set by the Central Pollution Control Board under the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change.
- Objective: To keep air pollutants emitted by the internal combustion engine of vehicles under control.
- They are based on European (EURO) emission standards.
- Bharat Stage (BS) emission norms were first brought into effect in 2000 under the head “India 2000”. This was followed by BS2 in 2001 and BS3 in 2005.
- However, the emission norms were made more stringent only with the enforcement of Bharat Stage IV (BS4).
- Thereafter, the Government of India skipped the implementation of BS5 in 2016 and decided to introduce Bharat Stage VI (BS6) in 2020 instead.
Other important current affairs:
1. Recently, Maharashtra surpassed Tamil Nadu and Telangana and became the top performer in the field of organ donation.
- Sensitization drives and the meticulous efforts of Regional Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation – State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (ROTTO-SOTTO) along with four Zonal Transplant Coordination Centres (ZTCCs) are important contributing factors behind this achievement.
- ROTTO-SOTTO: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has established National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) at National level, State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (SOTTO) in States and Regional Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (ROTTO) at the regional level.
- National Network division of NOTTO functions as an apex center for coordinating all activities and networking for procurement and distribution of organs and tissues and maintaining the registry of organs and tissue donation and transplantation in the country.
2. A team from the Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad, and Ohio State University has created a superhydrophobic coating to save steel from rusting.
- The coating was made from polyurethane and silicon dioxide nanoparticles.
- The superhydrophobic coating is a nanoscopic surface layer that repels water.
- Adding a superhydrophobic coating makes a surface liquid and water repellent, easy to clean, and boosts its anti-icing performance (ability to delay the formation of ice for a certain period of time)
- Super-hydrophobic coatings are also found in nature; they appear on plant leaves, such as the Lotus leaf, and some insect wings.
- Apart from steel, the coating can be done on other metallic surfaces, such as aluminum, copper, brass.
- The coatings have also been developed for glass, cloth, paper, and wood.
3. Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas informed Lok Sabha today about the Demand and Import of Oil.
- The percentage of Import Dependency on Oil based on the consumption of petroleum products during 2018-19 was about 83.8%.
- Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserve Limited (ISPRL), a Government of India Special Purpose Vehicle, has established Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) facilities with total capacity of 5.33 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) at 3 locations, namely (i) Vishakhapatnam, (ii) Mangaluru and (iii) Padur.
- As per the consumption pattern of 2017-18, the total capacity is estimated to provide for about 9.5 days of crude oil requirement. Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) currently have stock for 64.5 days.
- Hence, the total capacity storage of petroleum products is 74 days.
4. Recently, the Minister of State for Shipping has informed in the Rajya Sabha that significant savings in the cost of transportation are expected by using the Inland Water Transport (IWT) mode.
- IWT mode is widely recognized as an environment-friendly and cost-effective mode of transport.
- It aims to create for the shippers and logistic players, an alternative to the two dominant modes of transport viz. road and rail.
- As per RITES Report of 2014 on Integrated National Waterways Transportation Grid, the cost comparison on the modes of surface transport is given below: India has about 14,500 km of navigable waterways which comprise of rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks, etc.
- About 55 million tonnes of cargo is being moved annually by IWT, a fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode.
- As per the National Waterways Act 2016, 111 waterways have been declared as National Waterways (NWs).
- National Waterway-1 (Prayagraj-Haldia) with length 1620 km is the longest National waterway in India.
- The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is implementing the Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) at an estimated cost of ₹5369.18 crores for capacity augmentation of navigation on the Haldia-Varanasi stretch of Ganga (part of NW-1) with the technical and financial assistance of the World Bank.
5. The veteran journalist and Rajya Sabha member Patil Puttappa passed away at the Karnataka Institute of Medical Sciences (KIMS). He died due to age-related ailments.
- Puttappa represented the state of Karnataka for two terms. He was a hardcore Kannada activist, popular writer, and a journalist.
- He was the founder and editor of the weekly magazine “Prapancha”.
- He actively participated in the freedom struggle. He was also the president of the Kannada Watchdog Committee. He was also the founder president of the Border Advisory Committee.
- He was fondly called “Papu”.
- Puttappa has authored several Kannada language books such as Kavi Lekhakaru, Neevu Nagabeku,, Karnataka Sangeetha Kalaratnaru, etc.
6. Heavy Industries Minister informed Rajya Sabha that the Government has set an ambitious target to achieve sales of around 70 lakh hybrid and electric vehicles by the end of this year.
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles in India, the FAME scheme was initiated in 2015.
- The scheme was formulated to promote the manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicle technology under the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020.
- In the 2nd phase of the scheme, it is aimed to support through demand incentives about seven thousand E-buses, 5 lakh E-3 wheelers, 55 thousand E-4 wheelers passenger cars and 10 lakh E-2 wheelers.
7.The company Verily has gone live with its Project Baseline website for COVID-19 testing.
- The website helps in determining whether a coronavirus screening test is required for a person living in the United States.
- Verily is the life sciences and healthcare subsidiary owned by Google’s parent company Alphabet.
8. India signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Nepal for the construction of new schools in the country. Under the MoU, India is to provide 107.01 million Nepali rupees.
- India as an initial step of the agreement handed over a cheque of 8 lakh rupees (INR).
- The India-Nepal Development Partnership Programme is to construct the schools.
- The Kapilavastu District Coordination Committee will also help in the construction.
9. The United States of America began the first human trial evaluating the COVID-19 vaccine.
- The US National Institute of Health will enroll 45 healthy adult volunteers between ages 18 and 55 for a period of 6 weeks in order to test the vaccine.
- A healthy volunteer from Seattle, Kaiser Permante of Washington was injected with the vaccine.
- The vaccine was developed by a private firm called Moderna.
- Under the vaccination of COVID-19, three different doses are to be tested. During the trial phase, it is to be studied if the vaccines are safe and whether they stimulate the immune system of humans to create antibodies to stop COVID-19.
- The vaccine has been synthesized from a stretch of RNA embedded in a lipid nanoparticle.
- The Food and Drug Administration recently permitted the trial tests of the vaccine.
10. The President of India Ramnath Kovind nominated the former Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi to Rajya Sabha. The former chief justice retired in November 2019.
- Article 80-Clause (3):
- Under Clause (3) of Article 80, the President has powers to nominate persons with special knowledge to the council of states. Such person shall have special knowledge in science, art, literature and social service.
11. The Andhra Pradesh government has filed petitions in the Supreme Court and the High Court over the issue of the State Election Commission (SEC) postponing the local body elections citing the COVID-19 threat.
- The government, in its petition before the apex court, accused the SEC of not taking it into confidence while taking the major decision of deferring the polls and called the move anti-constitutional.
- The government also found fault with the SEC for not consulting the High Court on whose instructions the elections were scheduled.
12. The Lok Sabha has passed the Appropriation Bill 2020-21 that empowers the government to draw over ₹110 lakh crore from the Consolidated Fund of India for its working, as well as for the implementation of its programs and schemes.
- Now, only the Finance Bill that pertains to the government’s taxation proposal awaiting passage.
- The Appropriation Bill was passed by a voice vote.
- Following this, Speaker Om Birla applied “guillotine” — the Parliamentary tool to club all other pending subjects for discussion.
- Appropriation Bill is a money bill that allows the government to withdraw funds from the Consolidated Fund of India to meet its expenses during the course of a financial year.
- As per article 114 of the Constitution, the government can withdraw money from the Consolidated Fund only after receiving approval from Parliament.
- To put it simply, the Finance Bill contains provisions on financing the expenditure of the government, and the Appropriation Bill specifies the quantum and purpose for withdrawing money.
13. A report on Uranium Contamination in groundwater in Parliament.
- The Indian Standard IS 10500: 2012 for Drinking Water specification has specified the maximum acceptable limits for radioactive residues as alpha and beta emitters, values in excess of which render the water not suitable.
- These requirements take into account all radioactive elements including uranium. No individual radioactive elements have been specifically identified.
- As per the Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS), the maximum permissible limit of Uranium is 0.03 mg/l (as per WHO provisional guidelines) in all drinking water standards after following due process.
14. The Arunachal Pradesh government has decided to “keep in abeyance” the survey work for a road through the Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR).
- A 40-km stretch of the East-West Industrial Corridor road proposed to connect Seijosa in Pakke Kessang district and Bhalukpong in West Kameng district of the State passes through PTR, a biodiversity hotspot of the eastern Himalayas.
- Pakke Tiger Reserve is also known as Pakhui Tiger Reserve.
- This Tiger Reserve has won India Biodiversity Award 2016 in the category of ‘Conservation of threatened species’ for its Hornbill Nest Adoption Programme.




