Today’s Current Affairs: 19th March 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Foot-And-Mouth Disease : Study
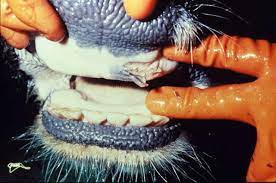
The Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) has affected around 60% of milch cattle in Pilibhit district, Uttar Pradesh.
- Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease of livestock that has a significant economic impact.
- The disease affects cattle, swine, sheep, goats and other cloven-hoofed ruminants.
- Intensively reared animals are more susceptible to the disease than traditional breeds.
- It does not affect horses, dogs, or cats.
- It is a Transboundary Animal Disease (TAD) that deeply affects the production of livestock and disrupts regional and international trade in animals and animal products.
- It is also not related to hand, foot and mouth disease, which is a common childhood illness caused by a different virus.
- The organism which causes FMD is an aphthovirus of the family Picornaviridae.
- There are seven strains (A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, and Asia1) which are endemic in different countries worldwide.
- Immunity to one type does not protect an animal against other types or subtypes.
- FMD is characterised by fever and blister-like sores on the tongue and lips, in the mouth, on the teats and between the hooves.
- The disease is rarely fatal in adult animals, but there is often high mortality in young animals.
- The disease causes severe production losses, and while the majority of affected animals recover, the disease often leaves them weakened and debilitated.
- It was the first disease for which the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE) established official status recognition.
Ballistic Missiles:

North Korea recently fired short-range ballistic missiles towards its eastern waters as the United States Secretary of State prepared to open a democracy summit in neighbouring South Korea.
- A ballistic missile is a rocket-propelled, self-guided strategic-weapons system that follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver a payload from its launch site to a predetermined target.
- They are powered initially by a rocket or series of rockets in stages, but then follow an unpowered trajectory that arches upwards before descending to reach its intended target.
- They can carry conventional high explosives as well as chemical, biological, or nuclear munitions.
- They can be launched from aircraft, ships and submarines, in addition to land-based silos and mobile platforms.
- There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles:
- Short-range: less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles), also known as “tactical” ballistic missiles.
- Medium-range: between 1,000 and 3,000 kilometers also known as “theater” ballistic missiles.
- Intermediate-range: between 3,000 and 5,500 kilometers
- Long-range: more than 5,500 kilometers, also known as intercontinental or strategic ballistic missiles.
Exercise LAMITIYE:

Indian Army contingent departed for Seychelles to participate in the Tenth edition of Joint Military Exercise “LAMITIYE-2024”.
- Exercise LAMITIYE is a joint military exercise between the Indian Army and Seychelles Defence Forces (SDF). ‘LAMITIYE’ meaning ‘Friendship’ in the Creole language is a biennial training event and has been conducted in Seychelles since 2001.
- 45 personnel each from the GORKHA RIFLES of the Indian Army and Seychelles Defence Forces (SDF) will participate in the 2024 exercise.
- The Exercise will enhance cooperation and interoperability between both the sides during Peace Keeping Operations.
- The exercise will also build and promote bilateral military relations in addition to exchanging skills, experiences and good practices between both armies
- Both sides will jointly train, plan and execute a series of well-developed tactical drills for neutralization of likely threats that may be encountered in Semi-Urban environment, while exploiting and showcasing new-generation equipment and technology.
Integrated Assessment Models:

The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) uses ‘modelled pathways’ drawn using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) to estimate what it will take to limit the warming of the earth’s surface.
- Integrated Assessment Models are complex models that examine possible futures of the energy and climate system and economies. They are “integrated” because they combine different strands of knowledge to model human society alongside parts of the Earth system.
- Its macroeconomic models can point to future growth levels in terms of GDP; its energy models can project future consumption; vegetation models can examine land-use changes; and earth-system models use the laws of physics to understand how climate evolves.
- With such integration across disciplines, IAMs are meant to provide policy-relevant guidelines on climate action.
- They also prioritise least-cost assessments — for example, the absolute cost of setting up a solar plant or undertaking afforestation in India is lower than in the U.S.
- However, experts have said they could exercise the option of enabling countries to equitably share the burden of action, where the richest undertake more drastic mitigation action more immediately.
- They capture human-society interactions by describing them as coupled systems on the relevant geographical and intertemporal scales for policy-making.
- They typically include a description of human activity (e.g. energy and land use), direct drivers of environmental change (e.g. emissions, land use and resource use), resulting impacts (e.g. climate change and consequences for crop yields) and response options.
Renaming Mumbai Central Station:

The Maharashtra cabinet has decided to propose renaming Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth, a renowned social reformer and philanthropist who played a crucial role in shaping Mumbai.
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth is often hailed as the architect of Mumbai (formerly Bombay).
- His notable contributions include being the first Indian nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay and founding the Bombay Association in 1852.
- He championed education for girls and women and established the Native School of Bombay (1849), which later became the esteemed Elphinstone College. Shankarseth was instrumental in the committee that propelled India’s first train project, connecting Boribunder and Thane in 1853.
- Shankarsheth was instrumental in founding the Great Indian Peninsula Railway, alongside notable figures like Sir Jamsetjee Jejeebhoy and David Sassoon.
- Shankarsheth’s legacy lives on through the institutions he established and the development projects he spearheaded, leaving an indelible mark on Mumbai’s history.
Fluoride Contamination : Survey

Fluoride contamination was detected in three districts of Kerala.
- According to the State Environment department, the source of contamination is likely geogenic, meaning these constituents are naturally present in the rock or soil matrix and enter groundwater through various chemical processes.
- Fluoride contamination in water is a critical issue worldwide.
- While fluoride is essential for dental health at low concentrations, excessive exposure can lead to health problems.
- Fluoride is naturally present in water and certain foods. It plays a crucial role in preventing tooth decay.
- However, when fluoride levels exceed 1.5 mg/L, it becomes toxic to humans.
- According to the Bureau of Indian Standards, the maximum permissible limit of arsenic in groundwater meant for drinking is 0.01 mg/l, while the corresponding limit of fluoride is 1.0 mg/l, which can be extended to 1.5 mg/l in case no alternative source of water is available.
- Excessive fluoride causes dental fluorosis, characterized by staining, pitting, and weakening of tooth enamel.
- Chronic exposure leads to skeletal fluorosis, affecting bones and joints.
- High fluoride levels may impact the nervous system.
Electoral Bonds Data : EC

The Election Commission of India (ECI) has released detailed data on electoral bonds, following a directive from the Supreme Court.
- Among the major corporate donors revealed in the data, two companies stand out for their substantial contributions through electoral bonds.
- Future Gaming and Hotel Services Private Limited, a little-known entity that is currently under the scanner of the Enforcement Directorate (ED), emerged as the top purchaser of electoral bonds, with total purchases of Rs. 1,368 crore.
- The second-largest donor was Megha Engineering and Infrastructure Limited, a Hyderabad-based company that has bagged several major government contracts in recent years.
- Megha Engineering bought electoral bonds worth Rs. 966 crore during the period covered by the data.
- Other prominent corporate contributors include Vedanta Limited (Rs. 400 crore), the Bharti Group (Rs. 247 crore), Essel Mining and Industries Limited (Rs. 224 crore), and DLF Group (Rs. 170 crore).
- The data also shows significant purchases by Haldia Energy (Rs. 377 crore), Qwik Supply Chain Private Limited (Rs. 410 crore), and Keventer Foodpark Infra Limited (Rs. 194 crore).




