Today Current Affairs: 1st October 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Elderly Line:

On the occassion of International Day of Older Persons (1st October), Vice President of India will dedicate the Elderly Line 14567 to the Nation.
- Government of Telangana and Tata Trusts piloted the helpline in Telangana between March 2019 and September 2020.
- Based on this experience, MOSJE decided to establish state helplines at each state level and have a single call management platform and unique number (14567) that will enable services for the senior citizens through a National level structure. Thus Elder Line was conceptualised.
- Elder Line will operate on all seven days of the week from 8 AM to 8 PM since it is categorised under non-emergency service and extension of working hours will be backed by findings and requirement.
- Elder Line is a National Helpline for Senior Citizens (NHSC) set up by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in collaboration with National Institute of Social Defence (NISD) and State Governments.
- National Implementing Agency (an empowered Committee) set up by MOSJE along with NISD (National Institute for Social Defence) is currently hosting the Elder Line along with the States.
- Operationally, the state agencies will be working closely with all state departments and district functionaries to deliver services.
- Elder Line 14567 is a toll-free number open 12 Hours a day (8:00 AM to 8:00 PM), that provides free information, guidance, emotional support, field intervention in cases of abuse & rescues in order to improve the quality of life of senior citizens.
- In case of emergencies like pandemic, this helpline can support senior citizens with the right and on-time information for medical needs, emotional support and other associated needs in collaboration with all the state departments.
IndiaXports 2021 Portal:

Union Minister for MSMEs virtually inaugurated the India Export Initiative and IndiaXports 2021 Portal of India SME Forum in New Delhi.
- IndiaXports aims to orient MSMEs free of cost, with the objective of focussing on the untapped export potential in existing tariff lines and supporting MSMEs in order to grow the number of exporting MSMEs and increase MSME exports by 50% in 2022 and contributing to the PM’s dream of the US $5 Trillion Economy.
- This initiative features an Info Portal which serves as a knowledge base for exports by Indian MSMEs with the required information related to export potential for all the 456 tariff lines along with the potential markets as well as trends in exports, export procedures and lots more.
- Apart from an export help desk, Instructor led orientation will also be provided to MSMEs through a series of sessions for specific sectors highlighting the opportunities in specific products in international markets.
- The initiative targets 1 lakh+ MSMEs desirous of knowing more about exports and hand holding 30,000+ MSMEs to start exporting, doubling the base of active exporters.
Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) Mechanism:
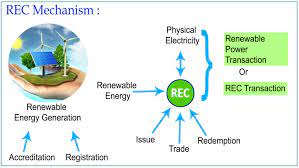
Union Minister of Power and New & Renewable Energy has given his assent to amendments in the existing Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) mechanism. The intent behind this decision is to align the ‘mechanism’ with the emerging changes in the power scenario and also to promote new renewable technologies.
The Salient features of changes proposed in revamped REC mechanism are:
- Validity of REC would be perpetual i.e., till it is sold.
- Floor and forbearance prices are not required to be specified.
- CERC to have monitoring and the surveillance mechanism to ensure that there is no hoarding of RECs.
- The RE generator who are eligible for REC, will be eligible for issuance of RECs for the period of PPA as per the prevailing guidelines. The existing RE projects that are eligible for REC would continue to get RECs for 25 years.
- A technology multiplier can be introduced for promotion of new and high priced RE technologies, which can be allocated in various baskets specific to technologies depending on maturity.
- RECs can be issued to obligated entities (including DISCOMs and open access consumers) which purchase RE Power beyond their RPO compliance notified by the Central Government.
- No REC to be issued to the beneficiary of subsidies/concessions or waiver of any other charges. The FOR to define concessional charges uniformly for denying the RECs.
- Allowing traders and bilateral transactions in REC mechanism.
- The changes proposed in revamped REC mechanism will be implemented by CERC through regulatory process.
- To address mismatch between availability of RE sources and the requirement of the obligated entities to meet their renewable purchase obligation (RPO), Pan-India market-based Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) Mechanism was introduced in the year 2010.
- The proposed changes will provide some flexibility to the players, additional avenues, rationalization and also addressing the RECs validity period uncertainty issues.
Defence Acquisition Council (DAC):

The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) in its meeting of 29 September 2021 held under the Chairmanship of Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh accorded Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for Capital Acquisitions proposals for modernization and operational needs of the Indian Armed Forces amounting to approx. Rs.13,165 cr.
- Of the total amount approved, procurement worth Rs. 11,486cr. (87%) is from the domestic sources.
- Key approvals include helicopters, guided munition and rocket ammunition.
- Looking into the need of the Indian Army for an Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH) Squadron, to improve its integral lift capability ensuring its operational preparedness, the DAC accorded approval of procurement of 25 ALH Mark III helicopters from M/s HAL under Buy Indian-IDDM at an approx. cost of Rs.3,850 crore.
- Giving boost to Indigenous Design and Development of ammunitions, DAC accorded approval for procurement of Terminally Guided Munition (TGM) and HEPF/RHE Rocket Ammunition under Buy(Indian-IDDM) category at an approx cost ofRs.4,962 cr.from domestic sources.
- In addition, the DAC also approved a few amendments to the DAP 2020 as a part of Business Process Re-engineering to ensure further ease of doing business for the industry as well as measures to enhance procurement efficiency and reducing timelines.
Mekedatu Issue:

Facing strong objection from Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Puducherry, the Cauvery Water Management Authority’s (CWMA) had urged Karnataka to promptly deliver the balance quantum of water owed to Tamil Nadu, whilst dropping debate on the Mekedatu project.
- The release should be as per the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal’s decision of 2007, which was modified by the Supreme Court in 2018.
- Tamil Nadu noted that Karnataka had only provided 85.8 TMC water instead of 119.5 TMC water until September 26. Tamil Nadu contended that Karnataka should indeed be ordered to deliver the surplus as well as the quota for the month of October promptly so that paddy planting in the Delta region may be protected.
About CWMA:
- It has been created as per the Cauvery Management Scheme earlier framed by Centre and approved by Supreme Court.
Composition and Powers of CMA:
- The authority will comprise a chairman, a secretary and eight members.
- Out of the eight members, two will be full time, while two will be part time members from centre’s side.
- Rest four will be part time members from states.
Functions:
- The main mandate of the CMA will be to secure implementation and compliance of the Supreme Court’s order in relation to “storage, apportionment, regulation and control of Cauvery waters”.
- CMA will also advise the states to take suitable measures to improve water use efficiency.
- It will do so by promoting use of micro-irrigation, change in cropping patterns, improved farm practices and development of command areas.
- The CMA will also prepare an annual report covering its activities during the preceding year.
About Mekedatu Project:
- Mekedatu is a multipurpose (drinking and power) project.
- It involves building a balancing reservoir, near Kanakapura in Ramanagara district in Karnataka.
- The project once completed is aimed at ensuring drinking water to Bengaluru and neighboring areas (4.75 TMC) and also can generate 400 MW power.
- The estimated cost of the project is Rs 9,000 crore.
Section 66A Of The Information Technology Act:

The Delhi High Court has asked the Centre to consider as representation a petition seeking to remove provisions from the statute such as Section 66A of the Information and Technology Act, which have already been declared unconstitutional.
- There are several criminal law sections that were struck down by the Supreme Court but continue to be used by police officers. In some cases, trial courts went ahead with framing charges under the defunct IT Act provision, even after taking cognisance of the Supreme Court’s 2015 judgment.
- Section 66A defines the punishment for sending “offensive” messages through a computer or any other communication device like a mobile phone or a tablet.
- A conviction can fetch a maximum of three years in jail and a fine.
- It empowered police to make arrests over what policemen, in terms of their subjective discretion, could construe as “offensive” or “menacing” or for the purposes of causing annoyance, inconvenience, etc.
- The SC had noted that Section 66A arbitrarily, excessively and disproportionately invades the right of free speech, under article 19(1) (a) of the Constitution, and upsets the balance between such right and the reasonable restrictions that may be imposed on such right and the definition of offences under the provision was open-ended and undefined.
- On July 5, the Supreme Court had expressed shock and dismay over police continuing to register cases under section 66A despite it being quashed six years ago.
- As of March 2021, a total of 745 cases are still pending and active before the district courts in 11 states, wherein the accused persons are being prosecuted for offences under Section 66A of the IT Act.
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:

The Government has launched the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for the textiles sector worth Rs 10,683 crore.
- This is part of a larger PLI scheme for 13 sectors, with a total budgetary outlay of 1.97 lakh crore.
- The PLI scheme for textiles aims to promote the production of high value Man-Made Fibre (MMF) fabrics, garments and technical textiles.
- Eligibility:
- Any person or company willing to invest a minimum of Rs 300 crore in plant, machinery, equipment and civil works (excluding land and administrative building cost) to produce products of MMF fabrics, garments and products of technical textiles will be eligible to participate in the first part of the scheme.
- Investors willing to spend a minimum of Rs 100 crore under the same conditions shall be eligible to apply in the second part of the scheme.
- Under PLI, the Centre will subsidise eligible manufacturers by paying incentives on incremental production.
- Companies investing over Rs 300 crore in plant, machinery, equipment and civil works to produce the identified products will get an incentive of 15 percent of their turnover, which needs to be Rs 600 crore in the third year.
- The companies investing between Rs 100 crore and Rs 300 crore will also be eligible to receive duty refunds and incentives (lower than 15 percent of their turnover).
- The government expects to achieve “fresh investment of over Rs 19,000 crore and a cumulative turnover of more than Rs 3 lakh crore”.
- The PLI scheme will provide an immense boost to domestic manufacturing, and prepare the industry for making a big impact in global markets in sync with the spirit of Atmanirbhar Bharat. It will also help attract more investment into this sector.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor:
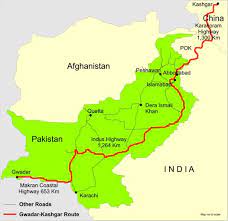
Pakistan has discussed Taliban-led Afghanistan joining the multibillion-dollar China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) infrastructure project.
- China has proposed construction of the Peshawar-Kabul motorway as an extension of CPEC in Afghanistan.
- Taliban takeover of Afghanistan and China emerging as a major challenge in the form of the extension of its ambitious CPEC, has raised India’s concerns on economic, political and security fronts.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor:
- The CPEC is a bilateral project between Pakistan and China.
- It is intended to promote connectivity across Pakistan with a network of highways, railways, and pipelines accompanied by energy, industrial, and other infrastructure development projects.
- It aims to link the Western part of China (Xinjiang province) to the Gwadar Port in Balochistan, Pakistan via Khunjerab Pass in the Northern Parts of Pakistan.
- It will pave the way for China to access the Middle East and Africa from Gwadar Port, enabling China to access the Indian Ocean.
- CPEC is a part of the Belt and Road Initiative. The BRI, launched in 2013, aims to link Southeast Asia, Central Asia, the Gulf region, Africa and Europe with a network of land and sea routes.
- India has been severely critical of the CPEC, as it passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which is a disputed territory between India and Pakistan.
Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC):

The Union Cabinet has approved capital infusion in the Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) and its listing through an initial public offering.
- The government will inject Rs 4,400 crore in the ECGC over a period of five years beginning 2021-22.
- The Cabinet also approved continuation of the National Export Insurance Account (NEIA) scheme and infusion of Rs 1,650 crore Grant-in-Aid over five years.
About the ECGC:
- Establishment: The ECGC Ltd is wholly owned by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The Government of India had initially set up the Export Risks Insurance Corporation in 1957.
- After the introduction of insurance covers to banks during the period 1962-64, the name was changed to Export Credit & Guarantee Corporation Ltd in 1964.
- It was changed to ECGC Ltd in August 2014.
- Objectives: ECGC was established to promote exports by providing credit insurance services to exporters against non-payment risks by the overseas buyers due to commercial and political reasons.
- Significance of Capital infusion: It will enable it to expand its coverage to export-oriented industries, particularly labour-intensive sectors.
- ECGC is a market leader with around 85% market share in the export credit insurance market in India and provided support to exports worth Rs 6.02 lakh, or 28% of merchandise exports, in FY21.
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) form 97% of the client base of ECGC.
- The process of listing ECGC on the stock market is also being initiated so that it can raise more funds.
National Export Insurance Account (NEIA) Scheme:
- NEIA Trust was established in 2006 to promote project exports from India that are of strategic and national importance.
- It promotes Medium and Long Term (MLT)/project exports by extending (partial/full) support to covers issued by ECGC to MLT/project export.
- Exim Bank, in April 2011, in conjunction with ECGC Ltd., introduced a new initiative, viz. Buyer’s Credit under the NEIA scheme, under which the Bank finances and facilitates project exports from India.
Special Category Status:
The Bihar Government has asserted that it has not dropped the demand of special category status to Bihar.
About Special Category Status (SCS):
- Special category status is a classification given by the Centre to assist development of states that face geographical and socio-economic disadvantages.
- This classification was done on the recommendations of the Fifth Finance Commission in 1969.
- It was based on the Gadgil formula.
The parameters for SCS were:
- Hilly Terrain;
- Low Population Density And/Or Sizeable Share of Tribal Population;
- Strategic Location along Borders With Neighbouring Countries;
- Economic and Infrastructure Backwardness; and
- Nonviable Nature of State finances.
SCS was first accorded in 1969 to Jammu and Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland. Since then eight more states have been included (Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tripura and Uttarakhand).
- There is no provision of SCS in the Constitution.
- Special Category Status for plan assistance was granted in the past by the National Development Council to the States that are characterized by a number of features necessitating special consideration.
- Now, it is done by the central government.
- The 14th Finance Commission has done away with the ‘special category status’ for states, except for the Northeastern and three hill states.
- Instead, it suggested that the resource gap of each state be filled through ‘tax devolution’, urging the Centre to increase the states’ share of tax revenues from 32% to 42%, which has been implemented since 2015.
PM Poshan Scheme:

The Union Cabinet has approved the Prime Minister POSHAN scheme or PM-POSHAN for providing one hot cooked meal in Government and Government-aided schools.
- The scheme will replace the existing national programme for mid-day meal in schools or Mid-day Meal Scheme.
- It has been launched for an initial period of five years (2021-22 to 2025-26).
PM POSHAN:
- The scheme will cover 11.8 crore students enrolled in classes 1 to 8 in over 11.2 lakh schools across the country.
- Primary (1-5) and upper primary (6-8) schoolchildren are currently entitled to 100 grams and 150 grams of food grains per working day each, to ensure a minimum of 700 calories.
- The scheme will be extended to students studying in pre-primary or Balvatikas running in government and government aided primary schools.
- Balvatika is the pre-school that was started in government schools last year to include children aged younger than six years in the formal education system.
Nutritional Gardens:
- The government will promote nutritional gardens in schools. The gardens are being provided to offer additional micro-nutrients to students.
Supplementary Nutrition: - The new scheme has a provision for supplementary nutrition for children in aspirational districts and those with high prevalence of anaemia.
- It does away with the restriction on the part of the Centre to provide funds only for wheat, rice, pulses and vegetables.
- Currently, if a state decides to add any component like milk or eggs to the menu, the Centre does not bear the additional cost. Now that restriction has been lifted.




