Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 28th September 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Nagorno-Karabakh region
- Swiss people have rejected a bid to reduce immigration from the European Union (EU):
- Sandalwood Spike Disease:
- Bhagat Singh.:
- Report of a survey titled ‘Health in India’
- Other important current affairs:
1.Nagorno-Karabakh region:
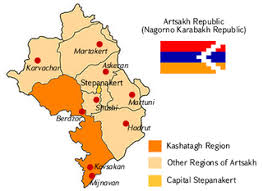
Clashes erupted between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the volatile Nagorno-Karabakh region, reigniting concern about instability in the South Caucasus, a corridor for pipelines transporting oil and gas to world markets.
- Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh, a breakaway region that is inside Azerbaijan but is run by ethnic Armenians, declared martial law and mobilized their male populations.
- Armenia said Azerbaijan had carried out an air and artillery attack on Nagorno-Karabakh.
- This is a decades-old conflict between majority Christian Armenia and mainly Muslim Azerbaijan.
- Nagorno-Karabakh broke away from Azerbaijan in a conflict that broke out as the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991.
- Though a ceasefire was agreed in 1994, after thousands of people were killed and many more displaced, Azerbaijan and Armenia frequently accuse each other of attacks around Nagorno-Karabakh and along the separate Azeri-Armenian frontier.
Effect on India
- India- Armenia: In recent years, Indian-Armenian bilateral cooperation has seen rapid growth.
- The then Vice-President of India visited Yerevan (Armenia) in 2017.
- Armenia bought the India SWATHI military radar system in March 2020.
- Many Indian students study in Armenian medical Universities and in recent years Armenia has witnessed an increasing flow of Indian labour migrants.
- For Armenia, close relations with India are vitally important as India provides a counterbalance to the rival strategic axis between Azerbaijan, Pakistan, and Turkey.
- India-Azerbaijan: India is part of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), a multimodal network of ship, rail, and road route for moving freight between India, Iran, Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe.
- Azerbaijan is a dialogue partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), which India is a member of.
- In 2018, the then Indian External affairs minister had visited Baku (Azerbaijan), the first-ever bilateral visit of an Indian External Affairs Minister to Azerbaijan.
- India’s ONGC-Videsh is an investor in Azeri-Chirag-Gunashli (ACG) oil fields and the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline.
2.Swiss people have rejected a bid to reduce immigration from the European Union (EU):

In a recent referendum, the Swiss people have rejected a bid to reduce immigration from the European Union (EU). Over five million Swiss voters cast ballots to decide whether to abandon an agreement with the EU which allows for the free movement of people across the country.
Agreement:
- Switzerland is not a member of the EU but has a series of interdependent treaties with Brussels (EU Headquarter) which allow it access to Europe’s free trade area.
- 1992-2002: Switzerland negotiated and signed first bilateral agreements with the EU, making them interdependent and included the free movement of people which was again backed by a vote in 2000.
- It is a member of the EU’s Single Market, which allows people to move and work freely in all 27 EU countries as well as in Switzerland.
- Around 1.4 million out of the 8.2 million people residing in Switzerland are EU citizens and an average of 5,00,000 Swiss citizens are believed to be living in other EU countries at the moment.
- If people choose to end the agreement, the Swiss government will have to unilaterally void its free movement agreement with the EU by invoking a so-called guillotine clause.
- This clause would have impacted other bilateral deals on transport, research and trade with the EU, disrupting economic activity.
Current Referendum:
- The right-wing Swiss People’s Party (SVP) initiated it, believing that the agreement has resulted in a significant strain on the welfare system and has led to overpopulation in the country.
- The vote was initially slated to take place in May but was postponed due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- A similar referendum took place in 2014, where a majority voted in favour of limiting access of EU citizens to live and work in Switzerland but lawmakers refused to enforce the referendum.
- The move, sometimes called Swexit, has not been very popular among Swiss voters.
- A recent survey showed that more than 60% of respondents were against it, while a mere 35% backed it and the remaining were undecided.
3.Sandalwood Spike Disease:

India’s sandalwood trees are facing a serious threat due to Sandalwood Spike Disease (SSD).
- The natural population of sandalwood in Marymoor Sandal Forest of Kerala and various reserve forests in Karnataka, including MM Hills (Malai Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary), are heavily infected with SSD.
Sandalwood Spike Disease:
- It is an infectious disease which is caused by phytoplasma.
- Phytoplasmas are bacterial parasites of plant tissues which are transmitted by insect vectors and involved in plant-to-plant transmission.
- There is no cure as of now for the infection.
- Presently, there is no option but to cut down and remove the infected tree to prevent the spread of the disease.
- The disease was first reported in Kodagu, Karnataka in 1899.
- More than a million sandalwood trees were removed in the Kodagu and Mysore region between 1903 and 1916.
- About 1% to 5% of sandalwood trees lost every year due to the disease, scientists warn that it could wipe out the entire natural population if measures are not taken to prevent its spread.
- Any delay in arresting the trend may result in the disease spreading to cultivated sandalwood trees.
- The present rapid spread of the infection is largely due to restrictions on green felling in forests, which has allowed vectors to spread the disease to healthy trees.
- Green felling (silviculture felling) is the felling of green trees of one or more types.
- Silviculture is the art and science of controlling the establishment, growth, composition, health, and quality of forests and woodlands to meet the diverse needs and values of landowners and society such as wildlife habitat, timber, water resources, restoration, and recreation on a sustainable basis.
In an effort to combat the killer disease, the Institute of Wood Science and Technology (IWST), Bangalore will join hands with the Pune-based National Centre for Cell Sciences for a three-year study, initiated by the Union Ministry of AYUSH with a financial allocation of Rs. 50 lakh.
- IWST is a Centre of Excellence for Sandalwood Research and Wood Science.
4. Bhagat Singh.:

28th September is the birth anniversary of revolutionary freedom fighter Bhagat Singh.
- Born in 1907 in Lyallpur district (now in Pakistan), Bhagat Singh grew up in a Sikh family deeply involved in political activities.
- He belonged to a generation that was to intervene between two decisive phases of the Indian national movement – the phase of the ‘Extremism’ of Lal-Bal-Pal and the Gandhian phase of nonviolent mass action.
- In 1923, Bhagat Singh joined the National College, Lahore which was founded and managed by Lala Lajpat Rai and Bhai Parmanand.
- The College was set up as an alternative to the institutions run by the Government, bringing to the field of education the idea of Swadeshi.
- In 1924 in Kanpur, he became a member of the Hindustan Republican Association (HRA), started by Sachindranath Sanyal a year earlier.
- The main organiser of the Association was Chandra Shekhar Azad and Bhagat Singh became very close to him.
- It was as a member of the HRA that Bhagat Singh began to take seriously the philosophy of the Bomb.
- The armed revolution was understood to be the only weapon with which to fight British imperialism.
- In 1928, HRA was renamed from Hindustan Republican Association to Hindustan Socialist Republic Association (HSRA).
- In 1925, Bhagat Singh returned to Lahore and within the next year, he and his colleagues started a militant youth organisation called the Naujawan Bharat Sabha.
- In April 1926, Bhagat Singh established contact with Sohan Singh Josh and through him the ‘Kirti Kisan Party’ which brought out the monthly magazine Kirti in Punjabi.
- For the next year Bhagat Singh worked with Josh and joined the editorial board of Kirti.
- In 1927, he was first arrested on charges of association with the Kakori Case accused for an article written under the pseudonym Vidrohi (Rebel).
- To take revenge for the death of Lala Lajpat Rai, Bhagat Singh and his associates plotted the assassination of James A. Scott, the Superintendent of Police. However, the revolutionaries mistakenly killed J.P. Saunders. The incident is famously known as Lahore Conspiracy case (1929).
- In 1928, Lala Lajpat Rai had led a procession to protest against the arrival of the Simon Commission. The police resorted to a brutal lathi-charge, in which Lala Lajpat Rai was severely injured and later succumbed to his injuries.
- Bhagat Singh and B.K. Dutt threw a bomb on 8 April 1929 in the Central Legislative Assembly, in response to the formulation of Defence of India Act.
- The aim, as their leaflet explained, was not to kill but to make the deaf hear, and to remind the foreign government of its callous exploitation.
- Both Bhagat Singh and B.K. Dutt surrendered thereafter and faced trial so they could further promote their cause. They were awarded life imprisonment for this incident.
- However, Bhagat Singh was re-arrested for the murder of J.P. Saunders and bomb manufacturing in the Lahore Conspiracy case. He was found guilty in this case and was hanged on 23rd March 1931 in Lahore along with Sukhdev and Rajguru.
- Every year, March 23 is observed as Martyrs’ Day as a tribute to freedom fighters Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev, and Rajguru.
5. Report of a survey titled ‘Health in India’, :
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has released the report of a survey titled ‘Health in India’, whose main objective was to gather basic quantitative information on India’s health sector.
Findings of the report:
- Around 7.5 % of Indians reported that they were suffering from ailments.
- While in rural India only 6.8 % said that they were suffering from an ailment, this number in urban India was 9.1 %.
Religion-based classification:
- The Zoroastrian community remains the most susceptible to ailments.
- Results from the National Sample Survey (NSS)’s 75th Round released in July show that 31.1 % of Zoroastrians reported that they were suffering from an ailment at the time the survey was conducted.
- This number for other communities is: Jains, 11.2 %; Sikhs 11 %; Christians 10.5 %; Muslims 8.1 %; Buddhists 8 %; and Hindus 7.2 %.
Sex-based classification:
- The survey shows that women remain more susceptible to suffering from ailments than men.
- In rural India, 6.1 % of males said that they were suffering from ailments, while 7.6 % of rural women said the same.
- While 8.2 % of urban males said that they were sick, 10 % of urban females said the same.
Other important current affairs:
1.27th September has been celebrated as World Tourism Day since 1980. It was on this day in 1970 when the Statutes of the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) were adopted which are considered a milestone in global tourism.
- The UNWTO is the United Nations specialised agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism.
- World Tourism Day highlights the unique role of the tourism sector in preserving cultural and natural heritage all around the world. It acts as an auxiliary in safeguarding habitat and endangered species.
- It addresses the importance of the tourism sector in providing jobs and opportunities, mostly for women and youth, in rural as well as big cities.
- The theme for 2020: ‘Tourism and Rural Development’.
- Joint Hosts: In the history of 40 years, the official celebration of World Tourism Day will not be hosted by a single member state of the UNWTO.
- Nations from the MERCOSUR bloc (Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay, with Chile joining as member associate status) will also be the joint hosts.
2.Scientists note that human-induced climate change promotes the conditions on which wildfires depend.
- Wildfire: Also called a forest, bush or vegetation fire, can be described as any uncontrolled and non-prescribed combustion or burning of plants in a natural setting such as a forest, grassland, brushland or tundra, which consumes the natural fuels and spreads based on environmental conditions (e.g., wind, topography).
- Wildfires can be incited by human actions, such as land clearing, extreme drought or in rare cases by lightning.
- There are three conditions that need to be present in order for a wildfire to burn: fuel, oxygen, and a heat source.
- Human-induced Climate Change: Increases in greenhouse gases resulting from human activities have led to a net effect of warming of the climate system leading to direct impacts including increased air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of snow and ice, and rising global average sea level. The increases in greenhouse gases can be attributed to fossil fuel use, land-use change, etc.
3.Union Health Minister Harsh Vardhan said that the government is committed to increasing the public healthcare spending from the existing 1.15 % of the GDP to 2.5 % by 2025.
- He added that the 15th Finance Commission’s high-level group on health has concurred that healthcare spending must be raised substantially in the next five years in view of the present pandemic.
- Harsh Vardhan was answering questions posed by his social media interactors on the third episode of Sunday Samvaad.
- Besides the present COVID crisis, these questions covered a multitude of queries concerning the medical infrastructure, the future of Public Health in India, India’s contribution to Climate Change Research and advancements in Meteorology.
4.NCDC has sanctioned as the first instalment, funds amounting to Rs 19444 crores to the states of Chhattisgarh, Haryana and Telangana for Kharif paddy procurement under Minimum Support Price (MSP) operations.
- NCDC: It is a statutory corporation set up under the National Cooperative Development Corporation Act, 1962.
- The objectives of NCDC are planning and promoting programmes for production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, foodstuffs, industrial goods, livestock and certain other notified commodities and services on cooperative principles.
- NCDC is a major financial institution for cooperatives and has started Mission Sahakar 22, which aims to double farmers’ income by 2022.
5.To ensure availability of medical oxygen in the country at a reasonable price amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, the national drug pricing regulator National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) has capped the price of medical oxygen cylinders and liquid medical oxygen for six months.
- Related provisions:
- The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare delegated powers under Section 10(2) (l) of Disaster Management Act, 2005 to NPPA to take all necessary steps to immediately regulate the availability and pricing of liquid medical oxygen (LMO) and medical oxygen cylinders.
- Oxygen Inhalation (Medicinal Gas) is a scheduled formulation, covered under the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM).
- National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM:
- Under the provisions of Drug Prices Control Order, 2013, only the prices of drugs that figure in the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) are monitored and controlled by the regulator, the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority.
6.Union Home Minister inaugurated the “Destination North East -2020”. The Union Home Minister is also the Chairman of the North-East Council.
- Destination North East is a calendar event of the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region. It has been conceptualized with the objective of taking the North East Region to other parts of the country.
- “The ‘Destination North East-2020′, which runs till 30 September, aims to introduce various cultures of the country to each other along with the tourist destinations of the North East.
- For Destination North East 2020, the theme is “The Emerging Delightful Destinations” which speaks of the tourism destinations emerging stronger and more attractive when the Sector picks up momentum.




