Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 29th June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Floating Rate Savings Bonds 2020 (Taxable):
- lightning strikes
- Zealandia’:
- Statistics Day
- Anthropause:
- P.V. Narasimha Rao
- Other important current affairs:
1. Floating Rate Savings Bonds 2020 (Taxable):

The Union Finance Ministry has decided to launch Floating Rate Savings Bonds 2020 (Taxable) from July 1, giving an opportunity to invest in secured government instruments.
- The new scheme has been brought in place of 7.75 percent Savings (Taxable) Bonds, 2018, which was withdrawn from the close of banking business on May 28, 2020,
- The interest on the seven-year bond will be paid semi-annually on January 1 and July 1 every year.
- The interest on January 1, 2021, will be paid at 7.15 percent.
- The rate for the next half-year will be reset every six months, the first reset being on January 1, 2021.
- The bonds will be repaid on the expiry of seven years from the date of issue.
- However, premature redemption will be allowed for specified categories of senior citizens.
- The interest on the Bonds will be taxable under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will be issuing the bonds on behalf of the government.
- The Bonds could be held by a person resident in India and a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
2.lightning strikes:

- Brazil recorded a lightning strike that traveled a distance of 709 kilometers in 2018.
- The previous record for the longest detected distance for a single lightning flash was 321 km on June 20, 2007, across the US state of Oklahoma.
- Brazil has the highest incidence of lightning in the world — an average of 77.8 million strikes per year.
Argentina recorded a strike that lasted for 16.73 seconds in 2019. - The previous record was a single lightning flash that lasted continuously for 7.74 seconds on August 30, 2012 over Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, France.
- The lightning flashes that have now entered the record books are known as ‘Megaflashes’ in scientific parlance.
Lightning strikes in India:
- Bihar is second after Uttar Pradesh with the maximum number of deaths due to lightning.
- At least 170 people died in Bihar due to lightning in 2019 between April 1 and July 31.
- The number of lightning days across India has been increasing significantly every month.
- Lightning strikes kill more people in India than any other extreme weather event.
lightning:
- It is a very rapid and massive discharge of electricity in the atmosphere, some of which is directed towards the Earth’s surface.
- These discharges are generated in giant moisture-bearing clouds that are 10-12 km tall.
- The base of these clouds typically lies within 1-2 km of the Earth’s surface, while their top is 12-13 km away. Temperatures towards the top of these clouds are in the range of minus 35 to minus 45 degrees Celsius.
- As water vapor moves upward in the cloud, the falling temperature causes it to condense.
- Heat is generated in the process, which pushes the molecules of water further up.
- As they move to temperatures below zero degrees celsius, the water droplets change into small ice crystals. They continue to move up, gathering mass — until they are so heavy that they start to fall to Earth.
- This leads to a system in which, simultaneously, smaller ice crystals are moving up and bigger crystals are coming down.
- Collisions follow, and trigger the release of electrons a process that is very similar to the generation of sparks of electricity. As the moving free electrons cause more collisions and more electrons, a chain reaction ensues.
- This process results in a situation in which the top layer of the cloud gets positively charged, while the middle layer is negatively charged. The electrical potential difference between the two layers is huge — of the order of a billion to 10 billion volts. In very little time, a massive current, of the order of 100,000 to a million amperes, starts to flow between the layers.
- An enormous amount of heat is produced, and this leads to the heating of the air column between the two layers of the cloud. This heat gives the air column a reddish appearance during lightning. As the heated air column expands, it produces shock waves that result in thunder.
- While the Earth is a good conductor of electricity,it is electrically neutral.
3.Zealandia’:
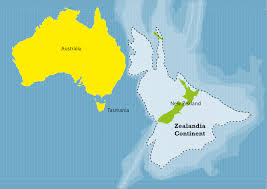
GNS Science, a New Zealand research institute, has published two new maps covering Zealandia’s tectonic profile and shape.
- Zealandia is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust located in the southern Pacific Ocean that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.
- It has variously been described as a continental fragment, a microcontinent, a submerged continent, and a continent.
- The landmass may have been completely submerged by about 23 million years ago, and most of it (93%) remains submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean.
- Political Divisions Under Zealandia Are New Zealand, New Caledonia, Norfolk island, Lord howe island group, and Elizabeth and Middleton Reefs.
- Names: It is also known as Tasmantis due to its proximity to the Tasman sea. Te Riu-a-Māui is another name for Zealandia.
- The name and concept for Zealandia were proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995.
- Originally the term “continent” was applied to any area of land, of any size, not separated by water, including islands.
- However, today, continents are understood to be large, continuous, distinct masses of land, ideally (but not necessarily) separated by expanses of water.
- No required minimum size to qualify as “large” (or “very large”) has been defined, nor the requisite degree of physical separation. Continents are therefore defined by convention rather than some strict criteria.
- The criteria used can be of geographical, historical, cultural, anthropological, political, or even of philosophical nature.
- The number of continents varies from 4 to 7 depending on the criteria.
4.Statistics Day:

Statistics Day of India is being celebrated on June 29, 2020, on the birth anniversary of Prof. P C Mahalanobis. This year’s Theme is “SDG- 3 (Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages) & SDG- 5 (Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls)”.
- PC Mahalanobis (1893 –1972) was an Indian scientist and applied statistician.
- He is referred to as the chief architect of the Indian statistical system as well as the father of statistical science in India.
- He established the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in 1931 in Kolkata. The institute founded the journal Sankhya, along the lines of Karl Pearson’s Biometrika. In 1959 it was made an autonomous body of Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
- Post-independence, he helped in the establishment of Central Statistical Organisation (CSO), the National Sample Survey (NSS), and the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI).
- His most important contributions are related to Large-Scale Sample Surveys. He introduced three key concepts to the theory and practice of sample surveys which are: Pilot surveys, Optimum survey design and Inter Penetrating Network of sub-samples technique (IPNS)
- He also advocated the usefulness of sampling methods. He was elected Chairman of the United Nations Sub-Commission on Statistical Sampling in 1947 and held this post until 1951.
- In 1936 he introduced a statistical measure named the Mahalanobis distance. It is widely used in cluster analysis and classification techniques.
- In 1926, he analysed 60 years’ data related to floods in Orissa, which led to the construction, after three decades, of the Hirakud dam on the Mahanadi.
- He was one of the members of the first Planning commission of free India. The Mahalanobis model was employed in the Second Five Year Plan, which worked towards the rapid industrialization of India.
- In 2019, the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI) instituted a new award, namely, Prof. P.C. Mahalanobis National Award in Official statistics for recognizing outstanding achievement of official statisticians in Central Government, State Governments, and Institutions.
- The award will be given on Statistics Day.
5.Anthropause:

- Also called the “Great Pause”, it is a term coined by the researchers in the UK.
- It refers to the coronavirus-induced lockdown period and its impact on other species.
- There were pumas sighted in Chile’s Santiago, jackals in the parks of Tel Aviv in Israel, dolphins in the waters of Italy, and even a monkey fight on the streets of Thailand.
- As a result of the lockdown, nature appears to have changed, especially in urban environments, since not only are there now more animals, but also some “unexpected visitors.”
- On the other hand, there are some animals for whom the lockdown may have made things more challenging.
- For instance, for various urban-dwelling animals, such as rats, gulls, and monkeys who depend on food provided or discarded by humans, the lockdown would have made life more difficult.
- The researchers believe studying this period will provide valuable insights into the relationship between human-wildlife interactions in the 21st century.
- It might also be useful in preserving global biodiversity, maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and predicting global zoonoses and environmental changes
6. Vice President Venkaiah Naidu paid tributes to former Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao on his birth anniversary (June 28, 2020).

Pamulaparthi Venkata Narasimha Rao (1921 –2004) was a politician who served as the 9th Prime Minister of India from 1991 to 1996. He also became the Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1971.
- Father of Economic reforms: He sought to dismantle the License Raj system, reduce red tape and make Indian industries more competitive. He laid the foundation for trade liberalization and re-integration of the Indian economy with the global economy, especially East Asian economies.
- Among his bold moves in foreign policy were establishing diplomatic relations with Israel and reversing decades of frosty relations between India and the United States by bringing them together. He also launched the Look East policy.
- He energized the national nuclear security and ballistic missiles program, which ultimately resulted in the 1998 Pokhran nuclear tests by the Vajpayee-led NDA government (the tests were planned in 1996 but they were not carried out as government at the centre got changed due to 1996 general election).
- He was also fairly successful in controlling the separatist movements in Punjab and Kashmir.
- The path-breaking 73rd and 74th Constitutional amendments empowering local bodies during Narasimha Rao’s tenure as the Prime Minister are worthy of mentioning.
- Rao’s term also saw the destruction of the Babri Mosque in Ayodhya in Uttar Pradesh when BJP’s Kalyan Singh was Chief Minister, which triggered one of the worst Hindu-Muslim riots in the country since its independence.
- He was also referred to as Chanakya for his ability to steer economic and political legislation through the parliament at a time when he headed a minority government.
Other important current affairs:
1. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has extended the relaxation relating to the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) scheme till 30th September 2020.
- It has also extended the relaxation relating to maintenance of the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) up to 25th September 2020.
- This was done in view of the hardships being faced by banks in terms of social distancing at work and consequent strain on reporting requirements.
- Marginal Standing Facility: The RBI, as a temporary measure, had increased the borrowing limit of scheduled banks under the MSF scheme from 2% to 3% of their deposits with effect from 27th March 2020.
- Earlier, the above relaxation was granted till 30th June 2020.
- MSF is a window for scheduled banks to borrow overnight from the RBI in an emergency situation when interbank liquidity dries up completely.
- Under interbank lending, banks lend funds to one another for a specified term.
- Banks borrow from the RBI by pledging government securities at a rate higher than the repo rate under the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF).
2. The Supreme Court has refused to review its 2018 judgment which decriminalized adultery.
- The original judgment was by a Constitution Bench led by then chief justice Dipak Misra who found that Section 497 (adultery) of the Indian Penal Code cannot “command” married couples to remain loyal to each other for the fear of penal punishment.
- Two individuals may part if one cheats, but to attach criminality to infidelity is going too far.
- The court had reasoned that there was no data whatsoever to support claims that the abolition of adultery as a crime would result in “chaos in sexual morality” or an increase of divorce.
- Section 497 perpetuates the subordinate status of women, denies dignity, sexual autonomy, and is based on gender stereotypes. Section 497 based on women as chattel, seeks to control the sexuality of women, hits the autonomy and dignity of women.
- It also violates rights guaranteed under Articles 14 and 21.
3. The Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Ministry has issued consolidated notification for classification and registration of MSMEs to be effected from July 1.
- This notification would supersede all earlier notifications with regard to classification or registration of MSMEs.
- As per the latest notification:
- An MSME would hereafter be referred to as Udyam and the registration process as Udyam Registration.
- The Registration can be filed online based on self-declaration. Uploading of documents, papers or certificates as proof would not be necessary henceforth.
- The basic criteria for MSME classification would be on investment in plant, machinery and equipment and turnover.
- Export of goods or services or both would be excluded while calculating the turnover of any enterprise and investment calculation linked to the IT return of the previous year.
- Champions Control Room across the country have been made legally responsible for facilitating entrepreneurs in registration and thereafter.
4. Ministry of Culture is celebrating ‘Sankalp Parva’ to plant trees from 28th June to 12th July 2020.
- The initiative has been taken on the call of the Prime Minister to plant at least five trees either in-office campus or wherever it is possible, to ensure a clean and healthy environment of the country.
- The Ministry of Culture has recommended planting five trees that represent the herbal heritage of the country.
These trees are: Bargad, Awla, Pepal, Ashok and Bel. These are also medicinal plants.




