Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 2nd November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Annual MBBS Admissions Regulations (2020)
- Gilgit-Baltistan :
- Code on Social Security, 2020:
- Bulk Drug parks:
- Asteroid 16 Psyche:
- Other important current affairs
1.Annual MBBS Admissions Regulations (2020):

Notified recently by the National Medical Commission (NMC).
- It replaces the “Minimum Standard Requirements for Medical Colleges, 1999 of the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI).
Highlights of the new Regulation :
- Applicable to all new medical colleges proposing to be established, and to the established medical colleges proposing to increase their annual MBBS intake from the academic year 2021-22.
- The new Regulation has deleted the quantum of land required for setting up a medical college and its affiliated teaching hospitals.
- Under the new Regulation, a well-equipped “Skills Laboratory” for training students is essential now.
- It also defines a Medical Education Unit for training medical teachers in educational pedagogy.
- Student counseling services have been mandated recognizing the increasing stress observed amongst medical students and residents in recent times.
- The regulation now mandates the availability of a fully functional 300 bed multi-specialty hospital for at least 2 years at the time of application for establishing a new medical college (the earlier regulations did not specify the period of functionality).
- Two new teaching departments have now become mandatory in all medical college hospitals for the training of undergraduate medical students. These include the Department of Emergency Medicine and the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
About the National Medical Commission:
- The Centre has recently notified the 33-member NMC, which will be chaired for three years by Suresh Chandra Sharma.
- Apart from the Chairman, the NMC will consist of 10 ex-officio members and 22 part-time members appointed by the Central government.
- Functions of NMC:
- laying down policies for regulating medical institutions and medical professionals.
- assessing the requirements of human resources and infrastructure in healthcare.
- ensuring compliance by the State Medical Councils with the regulations made under the Bill.
- framing guidelines for the determination of fee for up to 50% of the seats in the private medical institutions.
2.Gilgit-Baltistan :
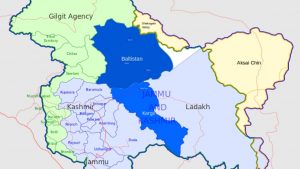
India has strongly rejected Pakistan’s move to grant provisional provincial status to Gilgit – Baltistan.
- Gilgit-Baltistan is one of the disputed territories of India.
Background:
- Recently, Saudi Arabia, a key ally of Pakistan, had removed Pakistan-occupied-Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan from the Pakistan map on its new banknote after India asked it to take “urgent corrective steps” about the “gross misrepresentation”.
- On the first anniversary of the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir’s special status, the Pakistan government had released a new “political map” which included Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, and parts of western Gujarat as part of its territory.
- Describing it as “political absurdity” and a “ridiculous assertion”, India said it “confirms the reality of Pakistan’s obsession with territorial aggrandizement supported by cross-border terrorism”.
- The Gilgit-Baltistan region is at the center of the USD 65 billion China Pakistan Economic Corridor Infrastructure development plan.
Gilgit-Baltistan:
- It is a chunk of high-altitude territory located on the northwestern corner of the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- It is located strategically as it borders Pakistan, Afghanistan, and China.
- The region was a part of the erstwhile princely state of Jammu and Kashmir but has been under Pakistan’s control since 4th November 1947, following the invasion of Kashmir by tribal militias and the Pakistan army.
Maharaja Hari Singh, the last Dogra ruler of J&K, had signed the Instrument of Accession with India on 26th October 1947. - India moved to the United Nations Security Council to raise the issue of Pakistan’s invasion on 1st January 1948.
- The UN Security Council passed a resolution calling for Pakistan to withdraw from all of Jammu and Kashmir and then India had to reduce its forces to the minimum level following which a plebiscite would be held to ascertain people’s wishes.
- However, no withdrawal was ever carried out and it remains a point of contention between two countries.
India’s Stand:
- India claims that the entire Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh including Gilgit-Baltistan are an integral part of
- India by the virtue of legal, complete, and irrevocable accession of Jammu and Kashmir to the union of India in 1947.
- Pakistan’s move to name Gilgit-Baltistan as its fifth province is meant to “camouflage its illegal occupation” of the area but it cannot “hide the grave human rights violations, exploitation, and denial of freedom” to the people for over seven decades.
3. Code on Social Security, 2020:

The Code on Social Security, 2020, for the first time in Indian law, attempted to define ‘platform work’ outside of the traditional employment category.
Background
- Labour falls under the Concurrent List of the Constitution. Recently, the Parliament passed three labor codes — on industrial relations; occupational safety, health and working conditions; and social security proposing to simplify the country’s archaic labor laws and give impetus to economic activity without compromising with the workers’ benefits.
- These labor codes can have a transformative impact on labor relations in India. Along with the ‘Code on Wages Act- 2019’, these can significantly ease the conduct of business by amalgamating a plethora of Central and State laws on labor.
Code on Social Security, 2020 has the following provisions:
- This will replace nine social security laws, including the Maternity Benefit Act, Employees’ Provident Fund Act, Employees’ Pension Scheme, Employees’ Compensation Act, among others.
- The code universalizes social security coverage to those working in the unorganized sector, such as migrant workers, gig workers, and platform workers.
- Aggregators, meaning “digital intermediaries or a market place for a buyer or users of a service to connect with the seller or the service provider”, are specifically required to contribute to the social security fund.
- For the first time, provisions of social security will also be extended to agricultural workers also.
- The code also reduces the time limit for receiving gratuity payment from the continuous service of five years to one year for all kinds of employees, including fixed-term employees, contract labor, daily, and monthly wage workers.
Platform Work:
- Platform work means a work arrangement outside of a traditional employer-employee relationship in which organizations or individuals use an online platform to access other organizations or individuals to solve specific problems or to provide specific services or any such other activities which may be notified by the Central Government, in exchange for payment.
- Platform work promises workers flexibility and ownership over the delivery of work.
Important for delivery of essential services as seen during the pandemic. - Employment Intensive Sector.
- Potential Sector for growth due to fast pace of Urbanisation.
- Development of rural areas due to remittances sent by platform workers.
4.Bulk Drug parks::

Himachal Pradesh is vying for the allotment of a bulk drug park under a central government scheme.
- The Central Government is planning to set up three such parks across the country.
Bulk drugs:
- A bulk drug is also called an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
- It is the key ingredient of a drug or medicine, which lends it the desired therapeutic effect or produces the intended pharmacological activity.
- They are prepared from multiple reactions involving chemicals and solvents.
- The primary chemical or the basic raw material which undergoes reactions to form an API is called the key starting material, or KSM.
- Chemical compounds formed during the intermediate stages during these reactions are called drug intermediates or DIs.
- India has one of the largest pharmaceutical industries in the world (third largest by volume).
- But this industry largely depends on other countries, particularly China, for importing APIs, DIs and KSMs.
- So, any disruptions in those countries would definitely affect the pharmaceutical industries here in India.
- For instance, this year, drug manufacturers in India suffered repeated setbacks due to disruption in imports due to Covid 19.
- The border conflict between India and China exacerbated the situation.
A bulk drug park will have a designated contiguous area of land with common infrastructure facilities for the exclusive manufacture of APIs, DIs or KSMs, and also a common waste management system.
- These parks are expected to bring down manufacturing costs of bulk drugs in the country and increase competitiveness in the domestic bulk drug industry.
- The scheme will support three selected parks in the country by providing a one-time grant-in-aid for the creation of common infrastructure facilities.
- The grant-in-aid will be 70 percent of the cost of the common facilities but in the case of Himachal Pradesh and other hill states, it will be 90 percent.
- The Centre will provide a maximum of Rs 1,000 crore per park.
- A state can only propose one site, which is not less than a thousand acres in area, or not less than 700 acres in the case of hill states.
5.Asteroid 16 Psyche:

A recent study at National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has found out that asteroid 16 Psyche, which orbits between Mars and Jupiter, could be made entirely of metal and is worth an estimated 10,000 quadrillion US dollars.
About Asteroid 16 Psyche:
- Asteroid 16 Psyche is located 370 million kilometers away from earth between Mars and Jupiter and has a diameter of 140 miles.
- It was discovered in the year 1853 by the Italian astronomer Annibale de Gaspard and was named after the ancient Greek goddess of the soul, Psyche.
- Unlike most asteroids that are made up of rocks or ice, scientists believe that Psyche is a dense and largely metallic object thought to be the core of an earlier planet that failed formation.
- Psyche’s shape is like a potato that takes about five earth years to complete one orbit of the sun but only a bit over 4 hours to rotate once on its axis.
Latest Findings:
- The latest study through the Hubble Space Telescope and ultraviolet observation gives a clearer picture of Psyche’s composition.
- The Hubble Space Telescope was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation.
- It was found that Psyche could be a unique asteroid composed of iron and nickel almost completely which is similar to earth’s core.
- The iron alone would be worth more than 10,000 quadrillion US dollars.
- Scientists noted that the manner in which Psyche reflected ultraviolet light was very similar to the way iron reflects sunlight.
NASA’s Psyche mission:
- The primary target of the Psyche mission to be launched in 2022 by NASA is to study this asteroid completely and confirm the assumptions being made by the scientists.
- Psyche’s mission will be the first mission to investigate this metallic asteroid. Psyche spacecraft will land on the asteroid in early 2026.
- As the composition of Psyche is very similar to earth’s own core, its study will also give an insight to earth’s violent history of collisions and accretion that created it.
Other important current affairs:
1.Ministry of AYUSH and M/s Invest India will form a collaboration to set up a strategic policy unit called “Strategic Policy & Facilitation Bureau (SPFB)” to facilitate planned and systematic growth of the Ayush Sector.
- This Bureau will support the Ministry in strategic and policy-making initiatives that shall help pave the way to reach the full potential of the Sector and stimulate growth and investment.
- As a partner in the project, M/S Invest India would collaborate extensively with the Ministry to frame the work plan of the Bureau and define its short-and long-term targets.
- The activities to be undertaken by the SPFB would include :
- Knowledge Creation and Management,
- Strategic & Policy-Making Support,
- State Policy Benchmarking: Undertaking State Policy benchmarking to formulate uniform guidelines/regulations regarding the AYUSH sector in India,
- Investment Facilitation: Follow up and facilitation of investment cases and MoUs, and coordination among different departments, organisations and States.
- Issue Resolution: Invest India would work with companies and other institutions on issue resolution across States and among various sub-sectors.
2.Typhoon Rolly or Goni has hit the Philippines.
- Hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones: They are all the same thing: tropical storms.
- But they are known by different names in different locations.
- In the North Atlantic Ocean and Northeast Pacific, they are called hurricanes.
- But if the same type of disturbance takes place in the Northwest Pacific Ocean, it is known as a typhoon.
- And in the South Pacific and the Indian Ocean, a cyclone is the correct term.
3.According to the recent data released by the Finance Ministry, the gross Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenue collected in October 2020 was Rs. 1.05 lakh crore.
- It is 10.25% higher than in 2019 and 10.1% more than the revenue garnered in September 2020.
- The total revenue earned in October by the Central and State governments stood at Rs. 44,285 crore and Rs. 44,839 crore, respectively.
- GST cess collections, used to compensate the States for switching to the GST regime, rose to Rs. 8,011 crore, which is over 5% more than in 2019 and 12.5% higher than September 2020.
- October’s revenues from import of goods were 9% higher, while domestic transactions (including import of services) yielded 11% higher revenues, on a year-on-year basis.
- Status of the States:
- Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh recorded the highest 26% growth in GST collections in October year-on-year, followed by Jharkhand (23%) and Rajasthan (22%).
- The trend in the more industrially developed States was mixed, with 15% growth in Gujarat, 13% in Tamil Nadu, and just 5% in Maharashtra.
4.The Union Home Ministry has written to all States to examine and register FIRs based on the complaints received on the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal, www.cybercrime.gov.in.
- Only 2.5% of the total complaints registered on the portal are converted into First Information Reports (FIRs).
- According to data compiled by NCRB, the number of registered cybercrimes increased by 63.5% in the year 2019 compared with the previous year’s.
- Through the above-mentioned portal, the Ministry aims to raise a group of “cybercrime volunteers” to flag “unlawful content” on the Internet.
- It has invited Good Samaritans to register as Cybercrime Volunteers in the role of Unlawful Content Flaggers for facilitating law enforcement agencies in identifying, reporting, and removal of illegal/unlawful online content.
5.Army Aviation Corps (AAC) celebrated its 35th Corps Day on November 1.
- It is the youngest Corps of the Indian Army.
- The Corps was raised as a separate formation on November 1 in 1986.
- Composition: The AAC now draws its officers and men from all arms of the Army, including a significant number from the artillery.
- Roles and functions:
- The main roles played by the AAC choppers are that of reconnaissance, observation, casualty evacuation, essential load drops, combat search, and rescue.
- The AAC helicopters also participate in Humanitarian Aid and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations in peace times.




