Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 30th November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Mission COVID Suraksha
- China’s New Dam on the Brahmaputra:
- Hidden Epidemic
- Guru Nanak Jayanti:
- Islamic Cooperation countries (OIC):
- Hayabusa2 project:
- One Health Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Other important current affairs
1.Mission COVID Suraksha:
The Government of India has announced the stimulus package of Rs. 900 crore for the Mission COVID Suraksha, the Indian Covid-19 Vaccine Development Mission, which will help the development process of the vaccine candidates.
- Mission COVID Suraksha is India’s targeted effort to enable the development of indigenous, affordable, and accessible vaccines for the country and will complement the ongoing mission of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The Centre had announced this package during the third economic stimulus.
- The Mission with its end-to-end focus from preclinical development through clinical development and manufacturing and regulatory facilitation for deployment would consolidate all available and funded resources towards accelerated product development.
- Phase-I of the Mission has been allotted Rs. 900 Crore for a period of 12 months.
- The grant will be provided to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) for Research and Development (R&D) of Indian Covid-19 vaccines.
- Stakeholders: It will be led by DBT and implemented by a dedicated Mission Implementation Unit at the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The existing activities under National Bio Pharma Mission (NBM) and Ind-CEPI Mission will provide complementary strengths to this Mission.
- The DBT is supporting the implementation of the Ind-CEPI Mission, “Epidemic preparedness through rapid vaccine development: Support of Indian vaccine development aligned with the global initiative of the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI)”.
- The Ind-CEPI Mission was approved in March 2019.
Vaccine Candidates:
- A total of 10 vaccine candidates have been supported by DBT so far in both academia and industry and as of the date and 5, vaccine candidates are in human trials.
- Covishield: The Serum Institute of India (SII) is conducting the phase-3 trial of the Oxford-Astrazeneca Covid-19 vaccine.
- Covaxin: The indigenously developed Bharat Biotech and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) vaccine has already started the phase III clinical trial.
- ZyCoV-D: Indigenously developed vaccine by Zydus Cadila has completed the phase-2 clinical trial in the country.
- Sputnik V: The combined phase 2 and 3 clinical trials of the Russian Covid-19 vaccine Sputnik V in India are about to get started.
- BNT162b2: India is focusing on training for conducting phase II and III human clinical trials of Pfizer’s Covid-19 vaccine candidate along lines of India’s regulatory mechanism.
2.China’s New Dam on the Brahmaputra:

Chinese authorities have given the go-ahead for a Chinese hydropower company to construct the first downstream hydropower project on the lower reaches of the river Brahmaputra (known as Yarlung Zangbo in Tibet).
About the Project:
- The state-owned hydropower company POWERCHINA signed a strategic cooperation agreement with the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) government to implement hydropower exploitation in downstream of the Yarlung Zangbo River as part of the new Five Year Plan (2021-2025).
- This will be the first time the downstream sections of the river will be tapped. However, the location of the planned project has not been mentioned anywhere.
- The Great Bend of the Brahmaputra and the Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon in Medog county, where the river turns sharply to flow across the border into f Arunachal Pradesh could be the potential spot for the project.
- This 50 km section alone offers the potential of developing 70 million kilowatt-hours (Kwh).
Brahmaputra:
- It originates under the name of Siang or Dihang, from the Chemayungdung glacier of the Kailash range near the Mansarovar lake. It enters India west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Dibang, Lohit, Siang, Burhi Dihing, Tista, and Dhansari.
- It is a perennial river and has several peculiar characteristics due to its geography and prevailing climatic conditions.
- It is flooded twice annually. One flood is caused by the melting of the Himalayan snow in summer and the other due to the monsoon flows.
- The frequency of these floods have increased and are devastating due to climate change and its impact on high and low flows.
- These pose a concern for the population and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- The river is in itself dynamic as frequent landslides and geological activity force it to change course very often.
3.Diabetes:
New research published recently in Diabetologia (journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) highlights the vulnerability of Indian youth towards diabetes.
- The research titled “Lifetime risk of diabetes in metropolitan cities in India,’’ was done by a team of authors in India, U.K. and U.S., led by Shammi Luhar, Department of Public Health and Primary Care, University of Cambridge, U.K.
Findings :
- More than half of men (55%) and two thirds (65%) of women aged 20 years in India are more likely to develop diabetes, with most of those cases (around 95%) likely to be type 2 diabetes (T2D) in their lifetime.
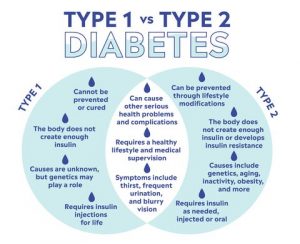
Type 2 diabetes:
- It affects the way the body uses insulin.
- While the body still makes insulin, unlike in type I, the cells in the body do not respond to it as effectively as they once did.
- The population with 45 and above age groups is the most affected with it.
- This is the most common type of diabetes and it has strong links with obesity.
- The lifetime risk of developing diabetes in 20-year-old men and women free of diabetes today is 56% and 65%, respectively.
- Obesity has a significant impact on vulnerability to diabetes.
- 86% higher among 20 year old women and 87% among men of metropolitan area.
- India currently has 77 million adults who have diabetes and this number is expected to almost double to 134 million by 2045.
- Women generally had a higher lifetime risk of developing diabetes across their lifespan.
- Remaining lifetime risk of developing diabetes declined with age. As per researchers, those currently aged 60 years and free of diabetes, are less likely to develop diabetes in their remaining life.
Sources of data for the study:
- Sex and BMI-specific incidence rates of diabetes in urban India taken from the Centre for Cardiometabolic Risk Reduction in South Asia (2010–2018);
- age, sex and urban-specific rates of mortality from period lifetables reported by the Government of India (2014);
- Prevalence of diabetes from the Indian Council for Medical Research India Diabetes study (2008–2015).
4.Guru Nanak Jayanti:

The President of India has greeted the citizens on the occasion of Guru Nanak Jayanti.
- It is a sacred festival of the Sikh community and is celebrated to commemorate the birth anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev, who is believed to be born on Poornima (full moon) of the Kartika (8th month of Hindu calendar), which falls on the 30th of November in 2020.
Guru Nanak Dev:
- Birth: In 1459 at Talwandi Rai Bhoe village near Lahore, which was later renamed as Nankana Sahib.
- He was the first of the 10 gurus of Sikhism.
- Contributions: Initiated inter-faith dialogue way back in the 16th century and had conversations with most of the religious denominations of his times.
- Wrote compositions which were included in the Adi Granth, compiled by Guru Arjan (1563-1606), the fifth Sikh guru.
- This came to be known as Guru Granth Sahib after the additions made by the 10th sikh guru Gobind Singh (1666-1708).
- Advocated the ‘Nirguna’ (devotion to and worship of formless divine) form of bhakti.
- Rejected sacrifices, ritual baths, image worship, austerities.
- Set up rules for congregational worship (Sangat) involving collective recitation.
- Gave the basic mantra of ‘Ek Onkar’ to his followers and insisted on treating all human beings equally, without discriminating on the basis of caste, creed and gender.
- Death: In 1539 at Kartarpur, Punjab.
- Building an Egalitarian Society: His idea of equality can be deduced by the following innovative social institutions, as given by him:
- Langar: Collective cooking and sharing of food.
- Pangat: Partaking food without distinctions of high and low caste.
- Sangat: Collective decision making.
- According to him, the whole world is God’s creation and all are born equal. There is only one universal creator i.e. “Ek Onkar Satnam”.
- Apart from it, forgiveness, patience, forbearance, and kindness are the core of his teachings.
- He placed the motto of “kirat karo, naam japo and vand chhako” (work, worship and share) before his disciples.
- He stood for karma as the basis of dharma, and he transformed the idea of spiritualism into the ideology of social responsibility and social change.
- He advocated the concept of “dasvandh” or donating one-tenth of one’s earning among needy persons.
- According to him, “Women as well as men share the grace of God and are equally responsible for their actions to him.”
- Respect for women and gender equality is perhaps the most important lesson to be learnt from his life.
Bringing Peace: - According to Indian philosophy, a Guru is the one who provides illumination, dispels doubt and shows the right path. In this context, the ideas of Guru Nanak Dev can help promote peace, equality and prosperity across the globe.
- In 2019, the 550th birth anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev was celebrated and the Kartarpur corridor was inaugurated, which is an important step towards easing the tensions between India and Pakistan.
5.Islamic Cooperation countries (OIC):

India has lashed out at Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) (formerly Organization of the Islamic Conference) and rejected unwarranted references about Jammu & Kashmir made in resolutions adopted at the 47th Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM) session.
- India has said that OIC has “no locus standi in matters strictly internal to India, including that of Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir”.
About OIC:
- It is an international organization founded in 1969, consisting of 57 member states.
- It is the second largest inter-governmental organization after the United Nations.
- The organisation states that it is “the collective voice of the Muslim world” and works to “safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony “.
- The OIC has permanent delegations to the United Nations and the European Union.
Permanent Secretariat is in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. - OIC’s growing economic and energy interdependence with India has become important in recent times.
6.Hayabusa2 project:

Japan’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft carrying asteroid soil samples nears Earth:
- Japan’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft left the asteroid Ryugu a year ago and is expected to reach Earth and drop a capsule containing the precious samples in southern Australia on December 6.
- The soil samples and data from the asteroid could provide clues to the origins of the solar system.
Hayabusa2 project:
- It is an asteroid sample-return mission operated by the Japanese space agency, JAXA.
- It was launched on 3 December 2014 and rendezvoused with Ryugu on 27 June 2018.
- It carried multiple science payloads for remote sensing, sampling, and four small rovers that will investigate the asteroid surface to inform the environmental and geological context of the samples collected.
- The scientific objectives of Hayabusa2 mission are twofold:
- To characterize the asteroid from remote sensing observations (with multispectral cameras, near-infrared spectrometer, thermal infrared imager, laser altimeter) on a macroscopic scale
- To analyse the samples returned from the asteroid on a microscopic scale.
- Ryugu is a C-type asteroid – a relic from the early days of the Solar System. Scientists think that C-type asteroids contain both organic matter, and trapped water, and might have been responsible for bringing both to Earth, thereby providing the planet with the materials necessary for life to originate.
7.One Health Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance:

Launched recently by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- This 20-member group comprises heads of states, current and former ministers of different countries, leaders from the private sector and civil society.
- It is co-chaired by the prime ministers of Barbados and Bangladesh, Mia Mottley and Sheikh Hasina Wazed, respectively.
- The heads of FAO, OIE and WHO are ex-officio members of the group.
- It seeks to catalyze global attention and action to preserve antimicrobial medicines and avert the disastrous consequences of antimicrobial resistance.
- The group has to:
- Monitor the global response to antimicrobial resistance.
- Maintain public momentum.
- Provide regular reports on the science and evidence related to AMR to the UN member states.
Other important current affairs:
1.Bibi Jagir Kaur, the first woman to be elected SGPC president more than 20 years ago, has made a comeback and has been elected as the new SGPC president.
- The Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee (or SGPC) is an organization in India responsible for the management of gurdwaras, Sikh places of worship in three states of Punjab, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh and the union territory of Chandigarh.
- SGPC also administers Darbar Sahib in Amritsar.
- The SGPC is governed by the chief minister of Punjab.
- The SGPC manages the security, financial, facility maintenance and religious aspects of Gurdwaras as well as keeping archaeologically rare and sacred artifacts, including weapons, clothes, books and writings of the Sikh Gurus.
- It was formed in 1920.
- The first and the only woman and also incumbent President of SGPC is Jagir Kaur .
2.Following years of public outcry and campaigning by American pop star Cher, the “world’s loneliest elephant” embarked on a mammoth move from Pakistan to retirement in a Cambodian sanctuary.
- Kaavan is dubbed the “world’s loneliest elephant” after languishing alone for years in a Pakistani zoo.
- The plight of the male Asian elephant, who’s been alone since the death of his partner Saheli in 2012, has captured worldwide attention.
- The loss of his mate Saheli in 2012 took a toll on Kaavan’s mental health. Elephants are social animals that thrive on the company of other elephants.
3.India’s power and renewable energy minister R K Singh said the government is aiming at meeting the complete power demand of Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands through renewable energy sources.
- The government is aiming for 100 per cent renewable energy in Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep and India is ready to share expertise among other small island nations.
- India has installed about 1,36,000 megawatts (MW) of Renewable Energy capacity with capacity addition of another 57,000 MW under implementation. The target is now to achieve 450 gigawatts of Renewable Energy capacity by 2030.
- He was addressing delegates from multiple countries including Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago and South Africa here under the Know India Programme.
- The programme is managed by the ministry of external affairs for engagement with Indian origin youth to enhance their awareness about India’s art and culture.
4.An asteroid named (153201) 2000 WO107, which is more than 800 metres high and over 500 metre wide – bigger than skyscraper Burj Khalifa – flew past earth on November 29.
- Burj Khalifa is the world’s tallest building with a height of 829.8 metre and asteroid 2000 WO107, which was discovered in 2000, has a diameter is 820 metre.
- The massive asteroid has been classified as a Near-Earth Asteroid (NEA). NEA is a group of comets and asteroids pulled into the orbit due to the gravitational forces of nearby planets, which allows them to enter the Earth’s neighbourhood.
- Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory has classified it as a ‘Potentially Hazardous Asteroid’ due to its predicted close pass with Earth.
5. The Minister of Railways has inaugurated the newly electrified Dhigawara-Bandikui section of North Western Railway and flagged off the first train on this electrified route from Dhigawara station in Alwar District, Rajasthan.Current Electrification:
- Indian Railways has set a target to complete the Electrification of its Broad gauge network by December 2023.
More than 66% of the Broad gauge route has already been electrified. - With 18065 km of electrification, Railways recorded a 371% increase in electrification during the 2014-20 period as compared to 2009-2014.
6.To ramp up COVID-19 testing, ICMR approves dry swab-direct RT-PCR method.
- It has been Developed by CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB).
- In the conventional testing method, nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swab samples collected are generally placed in a liquid called Viral Transport Medium (VTM).
- To avoid leakage, they are packed heavily that adds on to sample processing times at both the sample collection and testing centres.
- Dry Swab-Direct RT-PCR method is a simple variation of the existing gold standard RT-PCR method.
- This method involves collecting and transporting the nasal swab in dry state which makes the transportation and handling of the samples easy and less prone to spillage and spread of infection.
- In this method, the step of RNA isolation from the sample has been omitted, and it involves only simple processing of the sample followed by direct RT-PCR using the kit recommended by the ICMR.




