Today Current Affairs: 4th May 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Sixth Edition Of The India-Germany Inter-Governmental Consultations:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi and German Chancellor Olaf Scholz today co-chaired the sixth edition of the India-Germany Inter-Governmental Consultations-IGC in Berlin
- The biennial IGC is a unique dialogue format that also sees participation of several Ministers from both sides.
- This was the Prime Minister’s first IGC with Chancellor Scholz and also the first such Government-to-Government consultations of the new German Government, which assumed office in December last year.
- PM Modi expressed happiness that his first foregn visit this year was to Germany.
- He informed that Germany has committed to support Green Goal Plans of India. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz invited Prime Minister Modi for G-7 summit to be held in Germany.
- Prime Minister Modi and Chancellor Scholz signed the Joint Declaration of Intent establishing the Green and Sustainable Development Partnership.
- This Partnership envisages a whole-of-government approach to India-Germany cooperation on SDGs and climate action, under which Germany has agreed to make an advance commitment of 10 billion Euros of new and additional development assistance until 2030.
- This JDI will also create a Ministerial mechanism within the framework of the IGC to provide high-level coordination and political direction to the Partnership.
- A number of agreements were concluded during the Ministerial bilateral meetings.
National Open Access Registry (NOAR):

National Open Access Registry (NOAR) has successfully gone live from 1st May 2022.
- NOAR is an integrated single window electronic platform accessible to all stakeholders including open access participants, traders, power exchanges, national/regional/state load despatch centres for electronic processing of short-term open access application thereby automating the administration of the short-term open access in inter-state transmission system.
- The NOAR platform shall act as a repository of information related to short term open access in inter-state transmission including standing clearance issued by RLDCs or SLDCs and short-term open access granted to the open access customers etc. and make such information available to the stakeholders online.
- National Load Despatch Centre (NLDC) operated by Power System Operation Corporation Limited (POSOCO) has been designated as the nodal agency for implementation and operation of NOAR.
- NOAR would be the key to facilitate faster electricity markets and enable integration of Renewable Energy (RE) resources into the grid.
- NOAR is part of the Ministry of Power, Government of India’s initiative and the required regulatory framework has been notified by the CERC through operationalization of the 5th Amendment Regulation of Open Access in inter- State Transmission.
Basava Jayanti:

Basava Jayanti marks the birth anniversary of Lord Basavanna, the 12th-century poet-philosopher, and the founding saint of the Lingayat faith.
- This year it falls on 3rd May 2022
- Basavanna was a philosopher, statesman, Kannada poet and a social reformer during the reign of the Kalachuri-dynasty king Bijjala I in Karnataka.
- Basavanna spread social awareness through his poetry, popularly known as
- Basavanna rejected gender or social discrimination, superstitions and rituals.
- He introduced new public institutions such as the Anubhava Mantapa (or, the “hall of spiritual experience”), which welcomed men and women from all socio-economic backgrounds to discuss spiritual and mundane questions of life, in open.
- As a leader, he developed and inspired a new devotional movement named Virashaivas, or “ardent, heroic worshippers of Shiva”.
- This movement shared its roots in the ongoing Tamil Bhakti movement, particularly the Shaiva Nayanars traditions, over the 7th- to 11th-century.
- Basava championed devotional worship that rejected temple worship and rituals led by Brahmins, and replaced it with personalized direct worship of Shiva through practices such as individually worn icons and symbols like a small linga.
- The Sharana movement he presided over attracted people from all castes, and like most strands of the Bhakti movement, produced a corpus of literature, the vachanas, that unveiled the spiritual universe of the Veerashaiva saints.
- The egalitarianism of Basavanna’s Sharana movement was too radical for its times.
What Is Stubble Burning?

With wheat yield down this year, the rate of tudi is very high and farmers can earn huge profits by selling it. But despite that, 3,895 field fires have been reported from April 1 to April 29 in Punjab.
- Farmers opt for stubble burning because they do not have alternatives for utilising them effectively.
- The farmers are ill-equipped to deal with waste because they cannot afford the new technology that is available to handle the waste material.
- With less income due to crop damage, farmers are likely to be inclined to light up their fields to cut costs and not spend on scientific ways of stubble management.
- Stubble burning is a common practice followed by farmers to prepare fields for sowing of wheat in November as there is little time left between the harvesting of paddy and sowing of wheat.
- Stubble burning results in emission of harmful gases such carbon diaoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide along with particulate matter.
Advantages of stubble burning:
- It quickly clears the field and is the cheapest alternative.
- Kills weeds, including those resistant to herbicide.
- Kills slugs and other pests.
- Can reduce nitrogen tie-up.
Effects of Stubble Burning:
- Pollution: Open stubble burning emits large amounts of toxic pollutants in the atmosphere which contain harmful gases like methane (CH4), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Volatile organic compound (VOC) and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. They may eventually cause smog.
- Soil Fertility: Burning husk on ground destroys the nutrients in the soil, making it less fertile.
- Heat Penetration: Heat generated by stubble burning penetrates into the soil, leading to the loss of moisture and useful microbes.
Chhattisgarh Model:
- An innovative experiment has been undertaken by the Chhattisgarh government by setting up gauthans.
- A gauthan is a dedicated five-acre plot, held in common by each village, where all the unused stubble is collected through parali daan (people’s donations) and is converted into organic fertiliser by mixing with cow dung and few natural enzymes.
- The scheme also generates employment among rural youth.
- The government supports the transportation of parali from the farm to the nearest gauthan.
- The state has successfully developed 2,000 gauthans.
Transnistria:
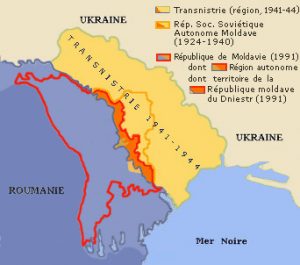
Transnistria, the tiny breakaway region of Moldova, risks being dragged into the Russia-Ukraine war because of reports of a series of explosions in its territory.
- The de facto state lies between Moldova to its west and Ukraine towards its east.
- Often described as a “remnant of the Soviet Union”, Transnistria declared independence like Moldova did soon after the break-up of the Soviet Union.
- When Moldovan troops attempted to take over the territory in 1990-1992, Transnistria was able to resist them because of Russian soldiers based in Transnistria.
- Since then, it has remained free of Moldovan control. However, most countries continue to see Transnistria as part of Moldova.
- Transnistria is not recognised as independent even by Russia and its economy is dependent on Russia for subsidies and free gas.
- Most Transnistrians have dual citizenship of Russia and Transnistria or triple citizenship of Moldova, Transnistria, and Russia.
- Unlike the rest of Moldova, which speaks Romanian, the majority of people in Transnistria speak Russian and use the cyrillic script like Russians.
India Semiconductor Mission:

Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology has inaugurated the first ever Semicon India 2022 Conference under India Semiconductor Mission in Bengaluru.
- Semicon India – 2022 has been organized to take forward the vision of the Prime Minister to make India a leader in the electronics manufacturing, semiconductor design, manufacturing & innovation.
- Theme of the Conference: Catalyzing India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem.
- Semiconductors are Any of a class of crystalline solids intermediate in electrical conductivity between a conductor and an insulator.
- Semiconductors are employed in the manufacture of various kinds of electronic devices, including diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Such devices have found wide application because of their compactness, reliability, power efficiency, and low cost.
- As discrete components, they have found use in power devices, optical sensors, and light emitters, including solid-state lasers.
India Semiconductor Mission:
- The ISM was launched in 2021 with a total financial outlay of Rs76,000 crore under the aegis of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY).
- It is part of the comprehensive program for the development of sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
- The programme aims to provide financial support to companies investing in semiconductors, display manufacturing and design ecosystem.
- Envisioned to be led by global experts in the Semiconductor and Display industry, ISM will serve as the nodal agency for efficient, coherent and smooth implementation of the schemes.
- Components:
- Scheme for setting up of Semiconductor Fabs in India:
- It provides fiscal support to eligible applicants for setting up of Semiconductor Fabs which is aimed at attracting large investments for setting up semiconductor wafer fabrication facilities in the country.
- Scheme for setting up of Display Fabs in India:
- It provides fiscal support to eligible applicants for setting up of Display Fabs which is aimed at attracting large investments for setting up TFT LCD / AMOLED based display fabrication facilities in the country.
- Scheme for setting up of Compound Semiconductors / Silicon Photonics / Sensors Fab and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT facilities in India:
- The Scheme provides a fiscal support of 30% of the Capital Expenditure to the eligible applicants for setting up of Compound Semiconductors / Silicon Photonics (SiPh) / Sensors (including MEMS) Fab and Semiconductor ATMP / OSAT(Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme:
- It offers financial incentives, design infrastructure support across various stages of development and deployment of semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design.
- Scheme for setting up of Semiconductor Fabs in India:
- Vision: To build a vibrant semiconductor and display design and innovation ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
16th Steering Committee Meeting Of Project Elephant:

At the 16th Steering Committee meeting of Project Elephant, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched a field manual named-Field Manual for Managing Human-Elephant Conflicts (HEC) in India-to guide forest staffers dealing with HEC in major elephant range states.
- The manual has been prepared by the ministry, along with the Wildlife Institute of India (WWI) and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF India).
- It contains the detailed best practices of minimizing human-elephant conflict.
- It is drafted with the aim of providing forest officials/ departments and other stakeholders with guidance towards interventions to help mitigate Human Elephant Conflict, both in emergencies and when conflict poses a recurring challenge.
Current Data on Elephants in India:
- India is home to approximately around 27,000 Asian Elephants, which is the world’s largest population of the species.
- As per Elephant Census (2017), Karnataka has the highest number of elephants (6,049), followed by Assam (5,719) and Kerala (3,054).
Sloth bear

Two sloth bears were rescued by forest officials from a village in Jharkhand by the People for Animals group.
- The People for Animals (PFA) is an animal welfare organization founded by Maneka Gandhi.
- The PFA was informed by Madaris. Madaris is a nomadic community that earns a living by performing street acts with animals.
- Sloth bears are found in Sri Lanka, India, Bhutan and Nepal, predominantly in lowland areas.
- Sloth bears primarily eat termites and ants, and unlike other bear species, they routinely carry their cubs on their backs.
- They are also very fond of honey, hence their alternative name of “honey bear”.
- Sloth bears do not hibernate.
- Scientific Name: Melursus ursinus
- Habitat: It is a forest-dwelling member of the family Ursidae (comprises 8 species of bears) that inhabits tropical or subtropical regions of India and Sri Lanka.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable’
- CITES listing: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching for body parts and are sometimes captured for use in performances or hunted because of their aggressive behavior and destruction of crops.
What Are Anabolic Steroids?
Two of India’s track-and-field Tokyo Olympians failed dope tests for using banned anabolic steroids.
- Anabolic steroids are usually used by bodybuilders.
- They are essentially lab-made versions of the male hormone testosterone and have a similar effect of increasing muscle mass as the natural hormone does.
- It also increases male characteristics in a person, such as facial hair and a deeper voice.
- Anabolic steroids, however, very different from the steroids that are prescribed by doctors for inflammations, several autoimmune diseases, or to suppress the body’s immune system during a Covid-19 infection.
- These medicines/steroids are called corticosteroids and are lab-made molecules that mimic the action of the hormone called cortisol that controls the body’s stress response, metabolism, and inflammation.
- Unlike corticosteroids, anabolic steroids have limited medical use.
- The anabolic steroids have a very limited medical role and are mainly used by doctors to help patients gain weight after a severe illness or injury.
- It could also be prescribed in small doses to the elderly to build muscle mass and in some cases also helps to treat anemia.
- Doctors may also prescribe the medicine to men who have low levels of natural testosterone.
- Some doctors use it for the treatment of osteoarthritis (a condition where bones wear down over time).
Ion Concentration Polarisation:
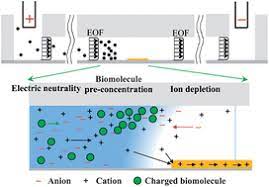
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers have developed a portable desalination unit, weighing less than 10 kg, that can remove particles and salts to generate drinking water.
- This device utilises electrical power to remove particles from drinking water.
- The unit relies on a technique called ion concentration polarisation.
- Rather than filtering water, the process applies an electrical field that causes positively or negatively charged particles — including salt molecules, bacteria, viruses — to be repelled as they flow past.
- The charged particles are funnelled into a second stream of water that is eventually discharged.
- The process removes solids, allowing clean water to pass through the channel.
100 Years Of Delhi University:

On May 1, 2022 Delhi University marked the beginning of its centennial celebrations.
- The idea for the university began taking shape in 1911 when it was decided to shift the capital of India to Delhi from Calcutta.
- The onset of World War I, differences over the nature of the would-be university, and lack of funds kept the idea from coming to fruition for another 11 years.
- On January 16, 1922, the Delhi University Bill was introduced in the Imperial Legislative Assembly with the objective of establishing a unitary teaching and residential university in the capital of British India.
- At that time, Delhi had three arts colleges — St Stephen’s College, which was founded in 1882 by the Cambridge Mission; Hindu College, which was founded in 1899; and Ramjas College which was founded in 1917 — and Lady Hardinge Medical College.
- These three colleges were to become the first constituent colleges of the university.
- The Bill was passed by the Assembly on February 22, and by the Council of States on February 28. The Viceroy gave his assent on April 6, and the DU Act came into force on May 1, 1922, with Viceroy Lord Reading as the first Chancellor and Hari Singh Gour as the first Vice-Chancellor.
- DU began with just two faculties — arts and science — and eight departments — English, history, economics, Sanskrit, Arabic, Persian, physics, and chemistry.
Koilastila Gas Field : Bangladesh

Bangladesh has discovered a new gas field with the capacity to produce 20 million cubic feet of gas per day (MMCFD) at the Koilastila Gas field.
- Koilastila Gas Field is one of the five gas fields purchased from the Shell Oil company by Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman in 1975
- So far 7 wells have been drilled in the Koilastila gas field of Sylhet Gas Fields Limited (SGFL).
- The first gas field in Bangladesh was made in Sylhet in 1955.
- Bangladesh currently produces 2370 MMCFD from its 26 commercial gas fields out of which 85 percent comes from the top 4 gas fields. Bibiyana Gas Field and Titas Gas field are its major locations for production of gas.
- It is estimated that Bangladesh has a remaining gas reserve of 11 trillion cubic feet.




