Today’s Current Affairs: 6th Feb 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
GRAPES-3 Experiment:

The GRAPES-3 experiment discovered a new feature in the cosmic-ray proton spectrum at about 166 tera-electron-volt (TeV) energy while measuring the spectrum spanning from 50 TeV to a little over 1 peta-electron-volt (PeV).
- Gamma Ray Astronomy PeV EnergieS phase-3 (GRAPES-3) is designed to study cosmic rays with an array of air shower detectors and a large area muon detector.
- It is located in Ooty, India.
- It is operated by the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research.
- It aims to probe the acceleration of cosmic rays in different astrophysical settings.
- Its objectives are to study:
- The origin, acceleration and propagation of >1014 eV cosmic rays in the galaxy and beyond.
- Existence of “Knee” in the energy spectrum of cosmic rays.
- Production and/or acceleration of the highest energy (~1020 eV) cosmic rays in the universe.
- Astronomy of multi-TeV γ-rays from neutron stars and other compact objects.
- Cosmic rays were discovered more than a century ago.
- They are considered to be the most energetic particles in the universe.
Dusted Apollo : High-Altitude Butterfly

Dusted Apollo (Parnassius stenosemus), a rare high-altitude butterfly, has been sighted and photographed for the first time in Himachal Pradesh.
- Dusted Apollo is an extremely rare butterfly and has never been photographed before in Himachal Pradesh.
- It is found from Ladakh to West Nepal and it flies between 3,500 to 4,800 metres in the inner Himalayas.
- It closely resembles Ladakh Banded Apollo (Parnnasius stoliczkanus) but the discal band on the upper fore wing in dusted Apollo is complete and extends from costa to vein one while this discal band is incomplete and extends only up to vein four in Ladakh Banded Apollo.
- There are 11 Apollo species recorded from Himachal Pradesh and five of them are declared as Scheduled species.
- It is an encouraging indication of the flourishing diversity of Apollo butterflies in the region.
- Apollos are considered commercially important butterflies and they fetch high prices in the poaching industry.
- Most of the Apollo butterflies are now endangered and need immediate attention for their conservation and protection.
InTranSE Program:

During the launch event of “Digital India FutureLABS Summit 2024” held at IIIT- Delhi, three Indigenous Technologies – Thermal camera, CMOS camera and Fleet Management System designed and developed by CDAC Thiruvananthapuram under InTranSE Program of MeitY were transferred to 12 Industries.
- The Intelligent Transportation System Endeavor (InTranSE) is a revolutionary collaborative research and development programme.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- Purpose is to synergize the transformation in Intelligent Transportation Systems the Ministry of Electronics & IT took early steps by bringing together premier academic institutes like the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Indian Institute of Management (IIM) etc. and Premier R&D Centre like C-DAC under one umbrella.
- This initiative formulated the Collaborative Intelligent Transportation Systems Endeavor for Indian Cities (InTranSE) during the year 2009-2012 (Phase-I) that witnessed IIT Bombay, IIT Madras, IIM Calcutta and C-DAC Thiruvananthapuram collaboratively developing, implementing, demonstrating and knowledge transfer of ITS products and solutions.
- The InTranSE Phase-II program (2019-2021) is aiming at undertaking R&D projects collaboratively with IIT Bombay, IIT Madras, IISc Bangalore and C-DAC Thiruvananthapuram
- It will achieve traffic efficiency by minimising traffic problems, prompting efficient infrastructure usage, enriching users with prior information about traffic and reducing travel time as well as enhancing the safety and comfort of commuters.
Corbett Tiger Reserve : Five People Killed In Two Months

Five people have been killed near Uttarakhand’s Corbett Tiger Reserve in the past two months.
- Corbett Tiger Reserve is located on the foothills of the Himalayas in Uttarakhand.
- By and large, the reserve is spread over the Bhabar and lower Shivalik regions with a deep-water table.
- Corbett was the first national park in India and was established in 1936.
- It was named Hailey National Park then. In 1957, the park was rechristened Corbett National Park in memory of the late Jim Corbett, a great naturalist and eminent conservationist.
- The habitat is characterised by open meadows (chaurs) interspersed with sal and moist, mixed deciduous forests.
- The grasslands are locally known as ‘Chaur’, which are an outcome of abandoned settlements or past clearings.
Candida auris : Deadly Fungal Infection
A deadly fungal infection called Candida auris has been spreading rapidly in the United States recently.
- Candida auris (C. auris) is an emerging multidrug-resistant yeast (fungus) that represents a global health threat.
- It is capable of causing invasive infections in the human body. It can cause severe illness in people with weakened immune systems.
- Scientists first discovered C. auris in Japan in 2009. Since then, it has spread quickly to other countries.
- It is primarily contracted in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes.
- It can also live on the skin or other body parts without making a person sick.
- This is called being “colonised.”
- The fungus can either colonise a specific region of the body, such as the skin, rectum, or mouth, without causing symptoms or it can cause severe invasive infections by entering the bloodstream or wounds.
- It can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment, or from physical contact with a person who is infected or colonised.
- It can cause infections in different parts of the body, such as the bloodstream, open wounds, and ears.
- The symptoms depend on the location and severity of the C. auris infection.
- Symptoms may be similar to those of an infection caused by bacteria. There is not a common set of symptoms specific to C. auris infections.
- Most C. auris infections are treatable with antifungal drugs.
The Economics Of The Food System Transformation : Report

The Food System Economics Commission has published a report titled-” The Economics of the Food System Transformation”, highlighting that a sustainable transformation of existing food systems is urgently required at an estimated total cost of USD 500 billion per year.
- The Food System Economics Commission (FSEC) is a private consortium of scientists across nationalities and academic fields, aimed at identifying the challenges to food system security and the policy changes required to overcome them.
Highlights of the Report:
- Globally, current food systems cost significantly more than they contribute to development.
- A sustainable transformation of existing food systems is urgently required at an estimated total cost of $500 billion per year.
- This cost is equivalent to only 0.2–0.4% of global GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and is small relative to the multi-trillion dollar benefits it could bring.
- The current global food system is characterised by hidden environmental, health, and social costs exceeding 10 trillion USD in 2020.
- Under the existing scenario, food systems will continue to drive a third of global Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, which will contribute to 2.7 degrees Celsius of warming by the end of the century compared to pre-industrial periods.
- Food production will become increasingly vulnerable to climate change, with the likelihood of extreme events dramatically increasing.
- The report contrasts two pathways up to 2050: Current Trends (CT) and Food System Transformation (FST).
- The CT pathway shows continued food insecurity, obesity increase, and negative environmental impacts by 2050.
- Transforming food systems can contribute significantly to economies and address health and climate challenges.
- Global convergence towards healthy diets could contribute as much as 70% of the total economic benefits of pursuing the FST pathway.
- Food systems under FST could become net carbon sinks by 2040, helping limit global warming to below 1.5°C.
- Positive developments include extensive reforestation, reducing extreme weather events, protecting land, halving nitrogen surplus, and reversing biodiversity loss.
Ramsar Sites :Increased
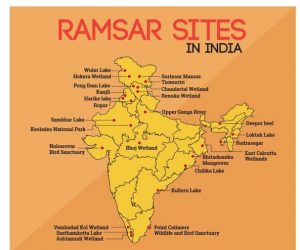
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change announced that on the eve of World Wetlands Day, 2024, India has increased its tally of Ramsar sites to 80 from the existing 75 by designating five more wetlands as Ramsar sites.
- Three of these sites, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve, Aghanashini Estuary and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve are located in Karnataka whereas two, Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest are in Tamilnadu.
- Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar Sites (16 sites) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10 sites).
- Ramsar Convention is an intergovernmental treaty, adopted on 2nd February 1971, in the Iranian city of Ramsar, on the southern shore of the Caspian Sea.
- In India, it came into force on 1st February 1982, under which wetlands of international importance are declared as Ramsar sites.
Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka):
- It is a human-made village irrigation tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 244.04 acres adjoining the Ankasamudra village.
Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka):
- It is spread over an area of 4801 ha, and is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields) and salt production.
Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (Karnataka):
- It is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely Common pochard (Aythya ferina) and River tern (Sterna aurantia) and four near-threatened species namely Oriental Darter (Anhinga melanogaster), Black-headed Ibis (Threskiornis melanocephalus), Woolly- necked Stork (Ciconia episcopus) and Painted Stork (Mycteria leucocephala).
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India. It has been declared globally as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA).
Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu):
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating agricultural crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- About 198 species of birds have been recorded here; some of the important visitors being the Bar headed Goose, Pin-tailed duck, Garganey, Northern Shoveler, Common Pochard, Eurasian Wigeon, Common teal and Cotton teal.
Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu):
- It derives its name from the Tamil word, “Solai”, which means a ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
Exercise Vayu Shakti-24:

The Indian Air Force will be conducting Exercise Vayu Shakti-24 on 17th February 2024 at the Pokhran Air to Ground Range, near Jaisalmer.
- Exercise Vayu Shakti is set to deliver a compelling display of the Indian Air Force’s offensive and defensive prowess, seamlessly operating both day and night.
- Additionally, the exercise will highlight collaborative manoeuvres with the Indian Army, showcasing their joint operational capabilities.
- The exercise will showcase IAF’s prowess in precision, long-range weapon delivery, and effective operations from various air bases, including special missions with transport, helicopter fleets, Garuds, and Indian Army elements.
- This year, 121 aircraft, including Tejas, Prachand, Dhruv, Rafale, Mirage-2000, Sukhoi-30 MKI, Jaguar, Hawk, C-130J, Chinook, Apache, and Mi-17, will participate in the exercise, showcasing the capabilities of indigenous Surface to Air Weapon systems Akash and Samar in tracking and shooting down intruding aircraft.
NITISH Device : Bihar State Disaster Management Authority

The Bihar State Disaster Management Authority has launched the Novel Initiative Technological Intervention for Safety of Humanlives (NITISH) device, an innovative pendant-shaped technology designed to provide timely alerts to farmers and the public, specifically targeting lightning, floods, heatwaves, and coldwaves.
- The initiative was triggered by recurring deaths among farmers due to lightning and flash floods, emphasizing the device’s role in saving lives.
- The NITISH Device is introduced in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Patna.
- The device is connected to the Bihar Meteorological Service Centre, ensuring real-time and accurate weather-related alerts.
- The NITISH device will sound an alert to its users half an hour before lightning or flooding.
- The pendant will get charged from body heat.
- The device will sound an alert in three ways: it will send voice messages; its colour will change from green to red; and the device will keep warming till its user switches it off.
- Considering the challenges faced by farmers, the device is waterproof, ensuring durability and functionality in various weather conditions.
World Wetlands Day 2024 : 2nd February

India celebrated World Wetlands Day 2024 at Sirpur Lake, a Ramsar site in Indore.
- The theme of World Wetlands Day 2024 was ‘Wetlands and Human Wellbeing,’ emphasizing the critical role wetlands play in flood protection, clean water, biodiversity, and recreational opportunities.
- India increased its tally of Ramsar sites to 80 by designating five more wetlands as Ramsar sites recently.
- Wetlands are low-lying areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally.
- They are transition zones between land and water, where the flow of water, the cycling of nutrients, and the energy of the sun meet.




