Today Current Affairs: 8th September 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Food Emergency In Sri Lanka:

Sri Lankan President, has declared an economic emergency to contain rising food prices, a depreciating currency, and rapidly depleting forex reserves.
- The emergency was declared under the Public Security Ordinance on the supply of essential goods.
Factors Responsible for Sri Lankan Economic Crisis:
- Underperforming Tourism Industry: The tourism industry, which represents over 10% of the country’s Gross Domestic Product and brings in foreign exchange, has been hit hard by the coronavirus pandemic.
- As a result, forex reserves have dropped from over $7.5 billion in 2019 to around $2.8 billion in July 2021.
- Depreciating Currency: With the supply of foreign exchange drying up, the amount of money that Sri Lankans have had to shell out to purchase the foreign exchange necessary to import goods has risen.
- Due to this, the value of the Sri Lankan rupee has depreciated by around 8% so far this year.
- Rising Inflation: Sri Lanka depends heavily on imports to meet even its basic food supplies, such as sugar, dairy products, wheat, medical supplies.
- So the price of food items has risen in tandem with the depreciating rupee.
- Diminishing Inflow of Foregin Currency: The pandemic has affected all major sources of foreign exchange earnings like exports, worker remittances, etc.
- Food Shortage: Sri Lankan Government’s recent decision to ban import of chemical fertilizers and adopt an “organic only” approach.
- This overnight shift to organic fertilizers could impact food production severely.
V. O. Chidambaram Pillai:

The Prime Minister paid tribute to V. O. Chidambaram Pillai, the legendary freedom fighter on his 150th birth anniversary.
- He was popularly known as Kappalottiya Tamilan (The Tamil Helmsman) and Sekkizuththa Semmal (scholarly gentry who suffered at the oil press).
- Vallinayagam Olaganathan Chidambaram Pillai (VOC) was born 5th September 1872 to an eminent lawyer Olaganathan Pillai and Paramyee Ammai in Ottapidaram, Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
- By 1906, VOC won the support of merchants and industrialists in Tuticorin and Tirunelveli for the idea of establishing a Swadeshi merchant shipping outfit by the name of the Swadeshi Steam Navigation Company (SSNCo).
- He established many institutions like Swadeshi Prachar Sabha, Dharmasanga Nesavu Salai, National Godown, Madras Agro-Industrial Society Ltd and Desabimana Sangam.
- VOC and Siva were aided in their efforts by a number of Tirunelveli-based lawyers, who formed an organisation called the Swadeshi Sangam, or ‘National Volunteers’.
- The nationalist movement acquired a secondary character with the beginning of the Tuticorin Coral Mills strike (1908).
- Even prior to Gandhiji’s Champaran Satyagraha (1917), VOC took up the cause of the working class in Tamil Nadu, and thus he is a forerunner to Gandhiji in this respect.
- VOC, along with other leaders, resolved to take out a mammoth procession on the morning of 9th March 1908 to celebrate the release of Bipin Chandra Pal from jail and to hoist the flag of Swaraj.
Common Services Centres (CSC):

The Common Services Centres (CSC) has received approvals to manage and operate Passport Seva Kendra kiosks in rural areas.
- CSC is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY).
- The CSC is a strategic cornerstone of the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP), approved by the Government in May 2006, as part of its commitment in the National Common Minimum Programme to introduce e-governance on a massive scale.
- The objective of CSCs is to provide high quality and cost-effective video, voice and data content and services, in the areas of e-governance, education, health, telemedicine, entertainment as well as other private services.
- The Scheme creates a conducive environment for the private sector and NGOs to play an active role in implementation of the CSC Scheme, thereby becoming a partner of the government in development of rural India.
- The PPP (Public Private Partnership) model of the CSC scheme envisages a 3-tier structure consisting of the:
- CSC operator (called Village Level Entrepreneur or VLE);
- Service Centre Agency (SCA), that will be responsible for a division of 500-1000 CSCs; and
- State Designated Agency (SDA) identified by the State Government responsible for managing the implementation in the entire State.
CSC and Digital India:
- Digital India is a flagship programme of India with a vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
CSCs enable the three vision areas of the Digital India programme:- Digital infrastructure as Utility to Every Citizen.
- Governance and services on demand.
- Digital empowerment of citizens.
CSC 2.0:
- It was launched in 2015, expanding the programme’s outreach to all gram panchayats in the country.
- At least one CSC is envisaged in each of the 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats.
- CSC 2.0 is a service delivery oriented entrepreneurship model with a large bouquet of services made available for the citizens through optimum utilization of infrastructure already created in the form of State Wide Area Network (SWAN), State Service Delivery Gateway (SSDG), e-District, State Data Centre (SDC), and (National Optical Fiber Network (NOFN)/BharatNet.
8th National Level Exhibition And Project Competition (NLEPC) For The INSPIRE Awards – MANAK

The 8th National Level Exhibition and Project Competition (NLEPC) for the INSPIRE Awards – MANAK (Million Minds Augmenting National Aspiration and Knowledge), has commenced.
- It is aligned with the ‘Start-up India’ initiative and is being executed by DST (Department of Science and Technology) with National Innovation Foundation – India (NIF), an autonomous body of DST.
- Under the scheme the students are invited from all government or private schools throughout the country, irrespective of their educational boards (national and state).
- It covers the students in the age group of 10-15 years and studying in classes 6 to 10, to pursue Science and a career in Research.
- An award of Rs.10,000 is disbursed into bank accounts of winning students under Direct Benefit Transfer scheme.
- It does not believe in conducting competitive exams for identification of talent at any level. It believes in and relies on the efficacy of the existing educational structure for identification of talent.
- Aim: To motivate students to become future innovators and critical thinkers.
- Objectives:
- To target one million original ideas/innovations rooted in science and societal applications to foster a culture of creativity and innovative thinking among school children.
- To address the societal needs through science and technology and nurture them to become sensitive and responsible citizens and innovation leaders of tomorrow.
INSPIRE Scheme:
- The INSPIRE (Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research) scheme is one of the flagship programmes of the Ministry of Science and Technology & Earth Sciences.
- Its objective is to communicate to the youth population of the country the creative pursuit of science and attract talent to the study of science at an early stage and build the required critical human resource pool for strengthening and expanding the Science & Technology system and Research & Development base.
- The Government of India has successfully implemented the INSPIRE scheme since 2010. The scheme covers students in the age group of 10-32 years and has five components.
- The INSPIRE Awards- MANAK is one of its components.
DefExpo-2022

The 12th edition of DefExpo will be held in Gandhinagar, Gujarat in March 2022.
- DefExpo is a flagship biennial event of the Ministry of Defence, showcasing the land, naval, air as well as homeland security systems.
- The aim of the DefExpo 2022 is to build upon the vision to achieve Atmanirbharta’ in defence and reach the $5bn defence exports target by 2024.
- The 11th edition of DefExpo was held at Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh) in 2020.
Defence Sector Reforms Under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan:
- Revision of FDI Limit: The FDI limit in defence manufacturing under automatic route is raised from 49% to 74%.
- Project Management Unit (PMU): The government is expected to begin time-bound defence procurement and faster decision making by setting up a Project Management Unit (for contract management purposes).
- Reduction in Defence Import Bill: The government will notify a list of weapons/platforms banned for imports and thus such items can only be purchased from the domestic market. Separate budget provision for domestic capital procurement.
- Corporatisation of the Ordnance Factory Board: It will include a public listing of some units, ensuring a more efficient interface of the manufacturer with the designer and end-user.
Assam Cattle Preservation Act, 2021:

Various pressure groups in Assam groups recently held a rally against the Assam Cattle Preservation Act, 2021, stating that the law was an assault on the farm economy in the name of religion.
- It is aimed at regulating slaughter, consumption and transportation of cattle.
Highlights of the law:
- Slaughter of cow, calf and heifer is prohibited.
- Transportation of cattle from or through Assam is prohibited.
- Sale of beef or beef products is prohibited in areas predominantly inhabited by Hindu, Jains, Sikhs, and other non-beef eating communities.
- Sale of beef or beef products is prohibited within a 5-km radius of any temple, satra or other Hindu religious institutions.
- Punishment under the Assam Cattle Preservation Bill, 2021 for violation:
- Those found violating the rules shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term not less than three years and up to eight years or a fine that may vary between Rs 3 lakh and Rs 5 lakh or both.
- If someone convicted is found guilty of the same or a related offence the second time, the punishment will be doubled.
What Are The Prophylactic Medicines?
Ayush Ministry kickstarts campaign to distribute prophylactic medicines.
- The kit of Ayurveda prophylactic medicines for Covid-19 contains Sanshamani Vati, which is also known as Guduchi or Giloy Ghan Vati and Ashwagandha Ghan Vati.
- The kit and the guidelines have been prepared by the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Medicines (CCRAS).
- In the next one year, the immunity booster medicines and the guidelines to combat Covid-19 will be distributed to 75 lakh people across the country.
- Special focus will be on geriatric (people of 60 years and above age) population and the front-line workers.
- Distribution of Ayush prophylactic medicines will help citizens to boost immunity against the coronavirus.
Prophylactic Medicines:
- Prophylactic means a preventive measure.
- The word comes from the Greek for “an advance guard,” an apt term for a measure taken to fend off a disease or another unwanted consequence.
- A prophylactic is a medication or a treatment designed and used to prevent a disease from occurring. For example, prophylactic antibiotics may be used after a bout of rheumatic fever to prevent the subsequent development of Sydenham’s chorea.
6th Eastern Economic Forum (EEF)

Prime Minister Narendra Modi delivered a video-address during the plenary session of the 6th Eastern Economic Forum (EEF) held in Vladivostok, Russia recently.
- It may be recalled that the PM was the Chief Guest for the 5th EEF in 2019.
About the ‘EEF’:
- The Eastern Economic Forum was established by decree of the President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin in 2015.
- It supports the economic development of Russia’s Far East and to expand international cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It takes place each year in Vladivostok, a city in Russia.
- It serves as a platform for the discussion of key issues in the world economy, regional integration, and the development of new industrial and technological sectors, as well as of the global challenges facing Russia and other nations.
- Over the years, it has emerged as an international platform for discussing the strategy for developing political, economic and cultural ties between Russia and Asia Pacific.
- The Forum business programme includes a number of business dialogues with leading partner countries in the Asia-Pacific region, and with ASEAN, a key integration organization of dynamically developing nations in Southeast Asia.
- The Far East is the easternmost part of Russia.
- It borders two oceans, the Pacific and the Arctic, and five countries (China, Japan, Mongolia, the United States and the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)).
- The Far Eastern Federal District covers more than a third of the country’s territory.
- The Far East is rich in natural resources like diamonds, stannary, borax materials, 50 gold, tungsten, and fish and seafood.
- About 1/3 of all coal reserves and hydro-engineering resources of the country are here.
- Forests of the region comprise about 30% of the total forest area of Russia.
Inspiration 4: SpaceX’s First All-Civilian Space Mission:

Entrepreneur Elon Musk’s SpaceX recently announced that ‘Inspiration4’, its first all-civilian, non-governmental spaceflight, is on track for launch on September 15.
- The Crew Dragon spacecraft is set to be launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Centre in Florida in the US.
- It will take a group of four private citizens into space for three days.
- All four seats on the spacecraft have been purchased by US billionaire Jared Isaacman, founder of the fintech company Shift4 Payments.
- This is a part of an effort to raise millions for the Tennessee-based St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, a paediatric treatment and research facility that focuses on children’s catastrophic diseases, particularly leukaemia and other cancers.
What is Inspiration 4?
- The mission involves circling the Earth for three days, and then splashing down into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Inspiration4 will orbit the Earth at 575km, higher than the International Space Station (408km) and the Hubble space telescope (547km).
- This will be the farthest distance travelled by a crewed mission since 2009, when astronauts last went to repair the Hubble.
- The Dragon module that the group will be using has also been modified for the mission.
National Farmers Database:

The Centre has created a National Farmers’ Database with records of 5.5 crore farmers, which it hopes to increase to 8 crore farmers by December by linking it to State land record databases, according to Agriculture Minister Narendra Singh Tomar.
- Farmers’ database is key to advances in digital agriculture. Agriculture has to be linked with digital technology, scientific research and knowledge.
- The national database was created by taking data from existing national schemes such as PM-KISAN, soil health cards and the insurance scheme PM Fasal Bima Yojna.
- So far, 5.5 crore farmers had been identified in this manner.
- The Minister urged the States to create their own databases using the national database’s federated structure and also allow linkages to the land records maintained by the States.
- With the help of State governments, a total of eight crore farmers would be included by the end of the year. He also urged to study the Karnataka model for digital agriculture presented at the conference.
- In July, Mr. Tomar told the Lok Sabha that the database could be used “for targeted service delivery with higher efficiency and in a focussed and time-bound manner” and that it was the core for the proposed Agristack digital agriculture ecosystem.
- Already, companies such as Microsoft, Amazon and Patanjali had been asked to develop technology solutions for farmers using data from the database.
- Activists have raised privacy and consent concerns about using farmers’ data in such a way.
What Is A Satellite Phone?:

Since earlier this week, the Internet has been abuzz with news that the next-generation iPhone could have satellite connectivity, thus enabling it to make calls without a cellular network.
- It all started when top Apple analyst Ming-Chi Kuo said the Apple’s next-generation iPhone 13 will feature a low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite communication mode.
- Low earth orbit (LEO) satellites operate 311 miles (roughly 500 kilometers) above the Earth’s surface. There are hundreds of satellites that move around at this height.
- Because they are closer to the earth’s surface, unlike traditional satellites that are stationed higher at roughly 36,000 km, the time needed for data to be sent and returned is shorter.
- A satellite phone, or satphone as it is commonly called, works by connecting to a telecommunications satellite in space.
- They are capable of receiving and making calls anywhere in the world, even in the remotest parts be it the Himalayas or an uninhabited island in the Pacific.
- The concept of a satellite phone is not new. In fact, the first satellite phone was launched by Motorola in 1989.
Account Aggregator:
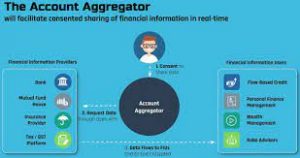
On September 2 eight of India’s major banks joined the Account Aggregator (AA) network that will enable customers to easily access and share their financial data.
- The framework, which has been under discussion since 2016 and in the testing phase for some time, will now be open to all customers.
- An Account Aggregator is a non-banking financial company engaged in the business of providing, under a contract, the service of retrieving or collecting financial information pertaining to its customer.
- It is also engaged in consolidating, organising and presenting such information to the customer or any other financial information user as may be specified by the bank.
- The licence for AAs is issued by the RBI, and the financial sector will have many AAs.
- The AA framework allows customers to avail various financial services from a host of providers on a single portal based on a consent method, under which the consumers can choose what financial data to share and with which entity.
- It reduces the need for individuals to wait in long bank queues, use Internet banking portals, share their passwords, or seek out physical notarisation to access and share their financial documents.




