Today Current Affairs: 9th February 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Einsteinium:
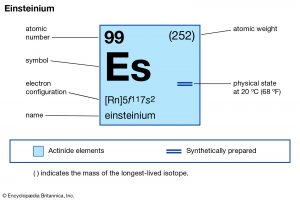
A team of scientists at the Berkeley Lab has reported some of the properties of element 99 in the periodic table called “Einsteinium”, named after Albert Einstein.
- With this new study published in the journal Nature last week, for the first time researchers have been able to characterize some of the properties of the element.
- It was discovered in 1952 in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb (the detonation of a thermonuclear device called “Ivy Mike” in the Pacific Ocean).
- The most common isotope of the element, einsteinium 253 has a half-life of 20 days.
- Because of its high radioactivity and short half-life of all einsteinium isotopes, even if the element was present on Earth during its formation, it has most certainly decayed.
- This is the reason that it cannot be found in nature and needs to be manufactured using very precise and intense processes.
Initiatives To Promote Farm Mechanization:

The government of India informed Parliament about the initiatives to Promote Farm Mechanization.
- A special dedicated scheme ‘Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)’ has been introduced by the Government of India in 2014-15.
- The scheme aims at making farm machines accessible and affordable for the small and marginal farmers (SMFs) through the establishment of Custom Hiring Centers(CHCs), creating Hubs for hi-tech & high-value farm equipment, and Farm Machinery Banks.
- Distribution of various subsidized agricultural equipment and machines to the individual farmers is also one of the activities under the scheme.
- For 2021-22 Rs. 1050 crore budget has been allocated for SMAM which is more than the previous year.
- Agricultural mechanization is crucial in the agriculture sector as it contributes towards improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the inputs used in the crop production thereby also increasing the productivity of crops.
- This also reduces drudgery associated with various farm operations.
Restriction Of The Industrial Trans Fatty Acid (TFA) In Food Products To 2 Percent From 2022:

The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has restricted the permissible amount of industrial Trans Fatty Acid (TFA) in food products to 2 percent from 2022.
- In December, the FSSAI had capped TFAs in oils and fats to 3% by 2021, and 2% by 2022 from the current levels of 5%.
- Food products that incorporate edible oils and fats as ingredients, including edible refined oils, vanaspati/partially hydrogenated oils, margarine, vegetable fat spreads, mixed fat spreads, bakery shortenings, fall under the ambit of the newly issued Regulations.
Industrial trans fatty acids:
- Trans fatty acids are created in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid, increase the shelf life of food items, and for use as an adulterant as they are cheap.
- They are present in baked, fried, and processed foods as well as adulterated ghee which becomes solid at room temperature.
- They are the most harmful form of fats as they clog arteries and cause hypertension, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Open Market Operations:

RBI announces ₹20,000 crore open market operations on February 10.
- Open market operations are the sale and purchase of government securities and treasury bills by RBI or the central bank of the country.
- The objective of OMO is to regulate the money supply in the economy.
- It is one of the quantitative monetary policy tools.
- RBI carries out the OMO through commercial banks and does not directly deal with the public.
Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga project:
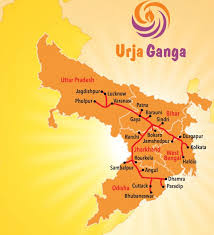
GAIL (India) Ltd has put West Bengal on the gas map of India after it completed laying a Rs 2,433-crore pipeline that will bring to the state cooking fuel that is cheaper than LPG and CNG that costs less than petrol and diesel, and fuel to produce urea for all its requirement.
- The 348-kilometer pipeline from Dobhi in Bihar to Durgapur in West Bengal is part of the Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga project.
- Inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his constituency Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh.
- A pipeline of length 2540 km is under construction from the states of Uttar Pradesh to Odisha.
Objectives:
- To provide piped cooking gas to the households of Varanasi within the next two years and to millions of others in neighboring states after one more year.
- To create 25 industrial clusters in these states which can utilize the gas as fuel and generate employment in these areas.
Lengthwise distribution: - The state of UP gets a gas line of length 338 km. Bihar state will get about 441 km long line.
- Jharkhand gets 500 KM long.
- West Bengal will have the pipeline of length 542 km and Odisha gets benefited from by 718 km pipeline
New Project In Sri Lanka By China:

A Chinese company has won a contract to set up hybrid wind and solar energy projects on three Sri Lankan islands off the northern Jaffna peninsula 45 km from Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu.
- Asian Development Bank (ADB) will fund the project, which will come up on Delft, Nainativu, and Analativu, three islands in the Palk Strait off the Jaffna peninsula.
- Delft, the largest of the three islands, is the closest to Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu, which lies to the island’s south west.
- Between the two is Kachchativu, the tiny island that India ceded to Sri Lanka in 1974.
- The waters around these islands are an area of contest and rivalry between Tamil Nadu and Jaffna fishers.
- The matter has been on the bilateral agenda for decades.
- India and Sri Lanka agreed to set up a Joint Working Group (JWG) on Fisheries in 2016 between the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare of India and Ministry of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources Development of Sri Lanka as the mechanism to help find a permanent solution to the fishermen issue.
Mission Innovation 2.0:

The Union Minister of Science & Technology addressed the Mission Innovation (MI) to mark the beginning of phase-2 of the mission or Mission Innovation 2.0.
- India played a leadership role in MI Steering Committee and is a member of the Analysis and Joint Research and Business & Investor Engagement sub-groups.
Mission Innovation:
- Mission Innovation was announced on 30th November 2015, on the sidelines of the Paris Climate Agreement to undertake ambitious measures to combat climate change.
- It is a global initiative of 24 countries and the European Union to accelerate global clean energy innovation.
Mission Innovation 2.0:
- To achieve the shared goal of accelerating innovation, all the members have agreed to develop a second phase (2.0) that includes:
- An enhanced Innovation Platform building on current activities to strengthen the global clean energy innovation ecosystem and to accelerate learning.
- New public-private innovation alliances – Missions – built around ambitious and inspirational goals backed by voluntary commitments that can lead to tipping points in the cost, scale, availability, and attractiveness of clean energy solutions.
Kuruba Community :

A massive rally was organized by the Kuruba community to urge the state government of Karnataka to recommend the Centre inclusion of the community in the Scheduled Tribe (ST) list.
- From Independence, the community enjoyed the ST status. In 1977, Justice LG Havanur, who headed the backward class commission, moved the Kurubas to the ‘most backward classes’ category from the ST list.
- However, the Commission brought in an area restriction stating that those living in Bidar, Yadgir, Kalaburagi and Madikeri with Kuruba synonyms can continue to avail the ST benefits.
About Kurubas:
- The Kurubas of Karnataka are a traditional sheep rearing community.
- Presently, the Kurubas constitute 9.3% of the state’s population and come under the backward classes category.
- Kurubas are the fourth largest caste in Karnataka after the Lingayats, Vokkaligas, and Muslims.
- Kurubas in other states are known by different names – as Dhangars in Maharashtra, Rabaris or Raikas in Gujarat, Dewasis in Rajasthan, and Gadarias in Haryana.
Demands by Lingayat Community: Three years earlier, the Lingayat community demanded a separate minority religion tag in Karnataka.
- The Lingayat sub-sect Panchamasali has also demanded its inclusion in the 2A category of backward classes – which currently provides 15% reservations to backward castes.
‘Kiran Helpline’:

As per the data of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, 70% of callers to the ‘Kiran Helpline’, launched in September 2020, were men. Most of the calls have been from young adults.
- The 24/7 toll-free helpline ‘Kiran’ provides support to people facing anxiety, stress, depression, suicidal thoughts and other mental health concerns.
Data Analysis:
- Gender & Mental Health: Out of the 13,550 new calls received, 70.5% were from males and 29.5% from females.
- Vulnerable Age Group: The majority of callers (75.5%) were in the age group of 15 to 40 years, while 18.1% in the 41 to 60 age group.
- Major Issues: Majorly the challenges faced by the callers were related to anxiety and depression; while few others included pandemic-related challenges, suicidal tendency, substance abuse, and others miscellaneous.
Issues Related to Male Mental Health:
- Traditional Gender Roles: Societal expectations and traditional gender roles play an important role in why men are less likely to discuss or seek help for their mental health problems.
- Ignoring Warning Signs: For men, the warning signs of mental disorders include irritability, trouble focusing, tiredness or listlessness, aches and pains, alcohol or drug abuse, and more.
- Lack of Proper Attention: Research on men’s health issues has been given relatively low priority. Due to a lack of funding and proper attention, the situation becomes more serious.
- Increase in Number of Suicides: In 2018, around 250 Indian men took their own lives per day – more than twice the number of women.
Hope: UAE’s First Mission To Mars

HOPE Mission- the first Arab interplanetary mission is expected to reach Mars’ orbit on Tuesday in what is considered the most critical part of the journey to unravel the secrets of weather on the Red Planet.
- The Hope mission is a Mars orbiter spacecraft, which will study the thin atmosphere of Mars.
- The mission is officially named the Emirates Mars Mission (EMM) and the orbiter has been named Hope or ‘Al Amal’.
- It is the first interplanetary mission for the Arab World.
- The Hope probe has a mission life of one Martian year, which is almost two Earth years.
- The three main objectives of the Hope probe are:
- to understand the climate dynamics and global weather map of Mars by studying the lower atmosphere of Mars.
- to explain how the weather of Mars affects the escape of hydrogen and oxygen, by correlating conditions in the lower and upper atmosphere.
- to understand the presence and variability of hydrogen and oxygen in the upper atmosphere, and why Mars is losing these gases to space.
Cultural Heritage Of India:

Minister of Culture and Tourism informed Parliament about the Measures taken by the Government to preserving and promoting the traditional cultural heritage of India.
- The Ministry of Culture formulated a scheme titled “Scheme for Safeguarding the Intangible Heritage and Diverse Cultural Traditions of India”, with the objective of promoting the rich Intangible Cultural Heritage of India.
- India has successfully inscribed 13 Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) elements in the UNESCO Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity under the 2003 Convention.
- As the first step towards the making of a National Inventory of ICH, the Ministry of Culture (MoC) has put up a list in April 2020 on its website called “National list for ICH”.
- The National list of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of India is an attempt to recognize the diversity of Indian Culture embedded in its Intangible Heritage.
- Following UNESCO’s 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage, this list has been classified into five broad domains in which Intangible Cultural Heritage is manifested:
- Oral traditions and expressions, including language as a vehicle of the Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Performing Arts
- Social practices, Rituals, and Festive events
- Knowledge and practices concerning Nature and the Universe
- Traditional Craftsmanship




