Today Current Affairs: 10th February 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Motion Of Thanks:

As many as 50 speakers from 25 political parties participated in the debate in Rajya Sabha on the Motion of Thanks lasting over three days.
- The President makes an address to a joint sitting of Parliament at the start of the Budget session, which is prepared by the government and lists its achievements.
- The address is followed by a motion of thanks moved in each House by ruling party MPs. During the session, political parties discuss the motion of thanks also suggesting amendments.
- Notices of amendments to Motion of Thanks on the President’s Address can be tabled after the President has delivered his Address.
- Amendments may refer to matters contained in the Address as well as to matters, in the opinion of the member, the Address has failed to mention.
- Amendments can be moved to the Motion of Thanks in such form as may be considered appropriate by the Speaker.
- The only limitations are that members cannot refer to matters which are not the direct responsibility of the Central Government and that the name of the President cannot be brought in during the debate since the Government and not the President is responsible for the contents of the Address.
Provisions governing them:
- President’s Address and Motion of Thanks are governed by Articles 86 (1) and 87 (1) of the Constitution and Rules 16 to 24 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
UN Human Rights Council:

The U.S. has announced plans to reengage with the UN Human Rights Council that former President Donald Trump withdrew from almost three years ago.
- UNHRC was reconstituted from its predecessor organization, the UN Commission on Human Rights to help overcome the “credibility deficit” of the previous organization.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The UNHRC has 47 members serving at any time with elections held to fill up seats every year, based on allocations to regions across the world to ensure geographical representation.
- Each elected member serves for a term of three years.
- Countries are disallowed from occupying a seat for more than two consecutive terms.
Functions:
- The UNHRC passes non-binding resolutions on human rights issues through a periodic review of all 193 UN member states called the Universal Periodic Review (UPR).
- It oversees the expert investigation of violations in specific countries (Special Procedures).
Eco-Sensitive Zone Around Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary:
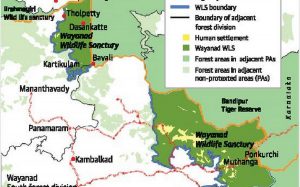
The draft notification of the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) on an Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) which runs around the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS) has triggered protests in Wayanad (Kerala).
Draft Notification:
- The 118.5 sq km area has been earmarked as an Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ), of which 99.5 sq km is outside the sanctuary and the remaining 19 sq km comprises revenue villages within the sanctuary.
- There will be restrictions on several human activities in ESZ, including a ban on all new and existing mining, stone quarrying and crushing units, and new industries causing pollution.
- It also includes a ban on the establishment of major hydroelectric projects and the setting up of new sawmills, brick kilns, and commercial use of firewood within ESZ.
- Besides, no new commercial hotels and resorts shall be permitted within 1km of the boundary of the protected area or up to the extent of ESZ, whichever is nearer.
- It also bars the felling of trees in private lands without prior permission of the competent authority in the state government.
Modifications In Pre And Post Matric Scholarship Schemes:

Department of Social Justice & Empowerment informed Lok Sabha about the Modifications in Pre and Post Matric Scholarship Schemes.
The scheme-wise important changes introduced are as follows:
Pre-Matric Scholarship for SC students:
- The funding pattern under the scheme was revised from the concept of committed liability to a fixed sharing pattern of 60:40 between Centre and the States (90:10 in case of North Eastern States) or Notional Allocation whichever is lower.
- The Annual Family Income limit was increased from Rs. 2.00 lakh to Rs 2.5 lakh in 2018 and rates of maintenance allowances were also increased.
Post-Matric Scholarship for Scheduled Castes (SC) students:
- During the year 2020-21, the Union Cabinet has approved the revision and continuation of the scheme from the year 2020-21 to 2025-26 which includes, inter-alia, revision of funding pattern to a sharing ratio of 60:40 between the Centre and the States (90:10 in case of NE States)
Pre-Matric Scholarship for Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and Post Matric Scholarship for OBCs:
- The income limit has been changed under Pre Matric Scholarship of OBC and Post Matric Scholarship for OBCs as per details given below:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship for OBC: increased from Rs.1.00 lakh to Rs. 2.50lakh per annum.
- Post Matric Scholarship for OBC: increased from Rs.1.50 lakh to Rs.2.50lakh per annum.
National Monsoon Mission:

Minister of Earth Science informed Rajya Sabha about National Monsoon Mission.
- Under the Monsoon Mission, Ministry has developed state-of-the-art weather and climate prediction models, which are now in operational use.
- These models include models for short-range to medium range (1-10 days), extended-range (10days to 30 days), and seasonal (up to one season).
Targets of Monsoon Mission:
- Development of a seamless prediction system using monsoon mission model, on different time scales, like Seasonal (for whole Monsoon season), Extended range (up to 4 weeks), Short-range prediction (up-to 5days).
- Initiate and coordinate the working partnership between Indian and foreign institutes to develop a system for the prediction of extremes and climate applications
- Develop and implement a system for climate applications having social impacts (such as agriculture, flood forecast, extreme events forecast, wind energy, etc.)
- Advanced data assimilation system for preparing high-quality data for model predictions.
National AYUSH Mission (NAM):

Central Government is implementing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of National AYUSH Mission (NAM) through States/UTs for development and promotion of AYUSH systems of medicine including Ayurvedic system.
The Mission inter-alia makes the following provisions for the promotion of AYUSH systems including the Ayurvedic system:
- Co-location of AYUSH facilities at Primary Health Centers (PHCs), Community Health Centers (CHCs) and Districts Hospitals (DHs).
- Up-gradation of exclusive State Government AYUSH Hospitals and Dispensaries.
- Setting up of up to 50 bedded integrated AYUSH Hospital.
- Upgradation of State Government Under-Graduate and Post-Graduate Educational Institutions.
- Setting up of new State Government AYUSH Educational Institutions in the States where it is not available in Government Sector.
- Strengthening of State Government/State Government Co-operatives/Public Sector Undertakings for manufacturing of quality medicines in AYUSH Systems.
- Strengthening of State Drug Testing Laboratories for ASU &H Drugs for stringent quality control.
- Support for the cultivation of Medicinal Plant including processing and post-harvest management to ensure supply of quality raw material for AYUSH medicine and other products.
Major Ports Authorities Bill – 2020:

The “Major Ports Authorities Bill, 2020” was passed in the Rajya Sabha on February 10, 2020. The bill was passed using the ballot votes.
Significance of the Bill:
- The Union minister of state for ports, shipping, and waterways, Mansukh Mandaviya, highlighted that the bill will encourage good competition within the major private ports.
- The bill also boosts port land usage and it will amplify competition in port tariffs.
Provisions of the bill:
- The bill aims to provide more autonomy in decision-making.
- It will provide autonomy to the 12 major ports of India, Namely’
- The bill will also professionalize the governance of the port with the formation of boards.
- The bill will replace the Major Port Trusts Act, 1963.
- It comprises of the provisions of creating a Board of Major Port Authority for each major port that in turn will replace the existing Port Trusts.
Uttarakhand Glacier Burst:

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the first images of the glacier burst that happened in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand. The glacial burst has so far caused 32 lives. After the incident, more than a hundred people are still missing.
- The satellite images show that flash floods were reported in Rishi Ganga and Dhauli Ganga river catchment areas.
- The flash floods were caused due by a major snow avalanche closer to the Raini village of Chamoli district.
- The images show that power plants located at Raini and Tapovan have gone through the maximum damage in the glacial burst.
- One image shows the deposition of debris in Dhauli Ganga.
- Another image shows the damage that occurred to the dam infrastructures at Tapovan and Raini.
- These images were captured by the ISRO’s advanced earth imaging and mapping satellite CARTOSAT-3.
Glacial burst:
- Scientists are still investigating the reason for the glacial burst or the avalanche or the release of the accumulated water. Bu the experts are pointing that climate change can be blamed.
- This is so because the warming temperatures are resulting in the shrinking of glaciers across the world.
Formation And Promotion Of 10,000 Farmer Produce Organizations (FPOs):

The Government of India has launched a new Central Sector Scheme called the “Formation and Promotion of 10,000 Farmer Produce Organizations (FPOs)”.
Highlights:
- The scheme has been launched with a clear strategy and committed resources in order to form and promote 10,000 new FPOs across India.
- For the making of FPOs, Rs 6865 crore have been allocated.
- The scheme has been launched because the agriculture sector plays a crucial role in economic development and Nation building.
- The country is also at the forefront in the development of agriculture across the world.
- Further, India wants to double its agricultural export by 2022.
- But, more than 86% of farmers in India are small and marginal. They need the facilities of improved technology, better input, credit, and more markets in order to incentivize them. It would help them to produce a better quality commodity.
- Thus, if these small, marginal, and landless farmers are aggregated into FPOs, it would help them to enhance the economic strength & market linkages of farmers. This in turn will help in enhancing their income.
About FPOs Scheme:
- This is a Central Sector Scheme that receives funding from the Government of India.
- FPOs will be developed in production clusters.
- In the FPOs, agricultural and horticultural produces will be grown and cultivated to leverage the economies of scale.
- It will also improve the market access for members.
- Further, the “One District One Product” cluster will be created to promote specialization.
- Under this scheme, the formation & Promotion of FPOs will be done with the help of Implementing Agencies (IAs).
The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change:

The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change has published its new research in Lancet Planetary Health Journal recently. The report has highlighted the benefits of the adoption of the Paris Agreement to health.
- It highlights that the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are inconsistent with the Paris Agreement.
- The Paris Agreement aims to limit the warming to below 2°C.
- The report also focuses on the crucial and overlooked incentive to tackle climate change.
- The study was carried in countries that represent 50 percent of the world’s population namely, China, Germany, Brazil, India, Indonesia, South Africa, Nigeria, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- These countries also account for 70 percent of the world’s emissions.
Key findings of the report
- The signatories of the Paris agreement are updating and revising their NDCs in the backdrop of COP26 of 2021.
- However, the NDCs are not that strong globally to achieve the Paris agreement. Thus, there is a risk of global temperature rise of more than 3°C.
- The report further highlights that the adoption of the policies which are inconsistent with the aim of the Paris Agreement and with the prioritization of health can help in saving around,
- 4 million lives as a result of better diet
- 6 million lives as a result of cleaner air, and
- 1 million lives as a result of increased exercise.
- The report mentioned that, though the direct benefits of carbon mitigation are in the long-term the health co-benefits of the climate policies have immediate positive benefits.
- It says, If India follows the commitments of the Paris agreement, then it can save 4.3 lakh lives as a result of cleaner air and 17.41 lakh lives as a result of better diet.
Index-linked Insurance Policies (ILIPs):

A committee was set up by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) on the request of some insurers. The committee has recommended introducing index-linked insurance policies (ILIPs).
Index-linked insurance policies (ILIPs):
- The returns coming from the ILIPs will be linked to benchmark indices.
- ILIPs are the Insurance products linked with the benchmark indices.
- It includes a 10-year Sovereign Bond Index, Sensex or Nifty, etc.
- The ILIPs linked with the government bonds are less risky while those linked with the equity-based indices will go through the fluctuation in returns in accordance with the stock market performance.
- ILIPs are the alternative or complementary option to the current conventional guaranteed products such as annuities and savings products.
- It can also be used as unit-linked insurance plans (ULIPs) with respect to the volatile markets and stressed interest rates.
- The ILIPs can be regarded as a life insurance policy under Section 10(10D) and taxability of the Insurance Policy Act.
Excessive Use Of Fertilizer:

Union Minister of Agriculture informed Lok Sabha about the Excessive Use of Fertilizer.
- Investigations carried out under the All India Coordinated Research Project on ‘Long Term Fertilizer Experiments’ over five decades at fixed sites have indicated that continuous use of nitrogenous fertilizer alone had a deleterious effect on soil health and crop productivity showing deficiencies of other major and micronutrients.
- The consumptions of chemical fertilizers in the country during 2017-18, 2018-19, 2019-20 and 2020-21 (upto kharif 2020) are 54.38, 56.21, 59.88, and 33.85 million tonnes of fertilizer products (Urea, Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP), Murate of Potash (MOP), Complexes and Single Super Phosphate (SSP), respectively.
- The Government has launched a National Mission on Soil Health Card to promote soil test based balanced and judicious fertilizer application in the country.
- Similarly, organic farming is being promoted under Parampragat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) and Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North East Region (MOVCD-NER) in the country.
- Training and demonstrations are organized through ICAR institutions including Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), and agricultural universities to educate farmers on all these aspects.




