Kuiper Belt:
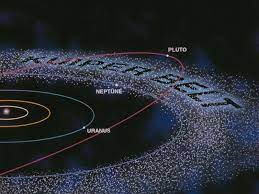
Astronomers have recently found compelling evidence suggesting the existence of an Earth-like planet in the distant Kuiper Belt of our solar system.
- Kuiper Belt also called the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt, is a flat ring of small icy bodies that revolve around the Sun beyond the orbit of the planet Neptune.
- It is named after Gerard Kuiper, a Dutch-American astronomer who hypothesised the existence of such a region in the 1950s.
- There are millions of these icy objects, collectively referred to as Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs) or trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), in this belt.
- The Kuiper Belt is a region of leftovers from the solar system’s early history.
- It is thought to be the source of most of the observed short-period comets, particularly those that orbit the Sun in less than 20 years.
- The Kuiper Belt is primarily composed of small icy bodies, such as dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets.
- Pluto, once considered the ninth planet in our solar system, is one of the most well-known Kuiper Belt objects.
- In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) reclassified Pluto as a dwarf planet, partly because of its location within the Kuiper Belt.




