ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation):
The recent La Niña event in the tropical Pacific Ocean has officially ended, with the climate system now transitioning to ENSO-neutral conditions as confirmed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
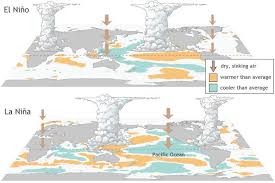
- ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation): ENSO is a significant climate phenomenon that involves changes in sea-surface temperatures (SST) in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It affects various global weather patterns, including wind behavior, atmospheric pressure, and rainfall distribution.
- El Niño: Warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures, associated with unusual global warming patterns.
- La Niña: Cooler-than-usual sea surface temperatures, often linked with colder atmospheric patterns and stronger trade winds.
- ENSO-Neutral: Neither El Niño nor La Niña dominates the climate system, making forecasts less certain, but often acting as a transitional phase between the two extreme conditions.
- ENSO-Neutral Phase is typically seen as a transition period between El Niño and La Niña.
- In March 2025, NOAA scientists observed that SST anomalies in the Niño-3.4 region had reached -0.01°C, much warmer than the La Niña threshold of -0.5°C.
- The cool waters that had characterized La Niña in previous months have now faded.




