Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:28th April 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Chakmas and Hajongs
- International Financial Services Centre Authority
- Hunger Crisis
- hydrogen fuel-based car
- Special liquidity facility for mutual funds
- Other important current affairs:
1.Chakmas and Hajongs :

The Rights and Risks Analysis Group has sought the Indian Prime Minister’s intervention in ensuring food for the Chakma and Hajong communities in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Chakmas and Hajongs have allegedly not been included in the Covid-19 Economic Relief Package announced by the central government in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic.
- Under the Relief Package, as part of the PM Gareeb Kalyan Ann Yojana: Each person who is covered under the National Food Security Act gets an additional five kg wheat or rice for free, in addition to the 5 kg of subsidized foodgrain already provided through the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- One kg of pulse per household is also provided for free, according to regional preferences.
- Their ration cards were illegally and arbitrarily seized by the state government in October 1991.
- As a result, they are forced to buy food items at normal or hiked prices while other vulnerable sections are paying ₹5 per kg as per the economic package.
- Since the members of the communities have become legal citizens of India, denial of food violates the Right to Life guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Chakmas and Hajongs
- These are ethnic people who lived in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, most of which are located in Bangladesh.
Chakmas are predominantly Buddhists, while Hajongs are Hindus. - They are found in northeast India, West Bengal, Bangladesh, and Myanmar
2. International Financial Services Centre Authority.:

The Government of India has established the International Financial Services Centre Authority. The headquarters of the authority is to be established in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- The Authority was established through a notification.
- The notification issued by the GoI brings into effect certain effects of IFSCA Act, 2019.
- The authority will regulate financial markets in the International Financial Service Centres in India.
- The main function of the authority is to regulate financial products such as contracts of insurance, deposits, securities of the financial institutions that have been approved by regulators.
- The regulators include RBI, SEBI, Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority, IRDAI.
International Financial Services Centres Authority
- The authority consists of 9 members that are appointed by the Government of India.
- The members are to have a term of three years.
- The members include Chairperson, two members from the Ministry of Finance, one each from RBI, SEBI, IRDAI and PFRDA and two members based on the recommendation of the search committee
- International Financial Service Centre will provide fundraising services to corporates, individuals and governments. It will also look into global tax management, wealth management, merger, risk management operations, etc.
3.Hunger Crisis”:

The United Nations recently has warned of “hunger pandemic” due to COVId-19. Apart from COVID-19, the other factors that are to contribute to the crisis include wars in Syria, the crisis in Lebanon and desert locusts destroying crops in East Africa.
- The COVID-19 outbreak according to the organization is to starve more than 130 million people.
- Also, the poor will be hit hard due to the decline in exports, tourism and the collapse in oil prices. Also, there is a huge decline in foreign aid.
- The UN says that around 300,000 people are expected to lose their lives due to lack of food for a period of three months.
- The World Food Programme is currently in need of 1.9 billion USD in order to stockpile food in countries that are at risk of starving. If not addressed, there are possibilities of severe famines.
- The WFP is the food assistance branch of the United Nations.
- It is the largest humanitarian organization that addresses hunger and promotes food security.
- It works to eradicate hunger and malnutrition. It was established in 1961.
4.Hydrogen Fuel Cell-based electric cars:
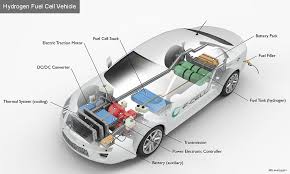
NTPC Ltd, India’s largest power producer and a central PSU under Ministry of Power have invited Global Expression of Interest (EoI) to provide 10 Hydrogen Fuel Cell (FC) based electric buses and an equal number of Hydrogen Fuel Cell-based electric cars in Leh and Delhi.
- The EoI has been issued by NTPC’s wholly-owned subsidiary, NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) Limited.
- The move to procure Hydrogen Fuel Cell-based vehicles is first of its kind project in the country, wherein a complete solution from green energy to the fuel cell vehicle would be developed.
- The initiative, which has been undertaken with the support of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, will also harness renewable energy for the generation of hydrogen and develop it’s storage and dispensation facilities as part of pilot projects at Leh and Delhi.
- The move to launch hydrogen-powered vehicles aims at decarbonizing mobility segment.
5. Special liquidity facility for mutual funds :

RBI has been decided to open a special liquidity facility for mutual funds of ₹ 50,000 crores to bail out Mutual Funds (MFs) hit by the turmoil in the debt fund segment that led to the closure of six credit risk funds by Franklin Templeton Mutual Fund.
- Under the SLF-MF, the RBI shall conduct repo operations of 90 days tenor at the fixed repo rate.
- The SLF-MF is on-tap and open-ended, and banks can submit their bids to avail funding on any day from Monday to Friday (excluding holidays).
- The scheme is available from April 27, 2020, till May 11, 2020, or up to utilization of the allocated amount, whichever is earlier.
- Funds availed under the SLF-MF shall be used by banks exclusively for meeting the liquidity requirements of MFs by extending loans, and undertaking the outright purchase of and/or repos against the collateral of investment-grade corporate bonds, commercial papers (CPs), debentures and certificates of Deposit (CDs) held by MFs.
- Liquidity support availed under the SLF-MF would be eligible to be classified as held to maturity (HTM) even in excess of 25 % of total investment permitted to be included in the HTM portfolio.
Other important current affairs:
1. Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Delhi have developed a web-based dashboard PRACRITI for predicting the spread of Covid-19 in India.
- PRACRITI is the acronym for the PRediction and Assessment of CoRona Infections and Transmission in India.
- Prediction of Covid-19 Cases: The dashboard gives detailed State-wise and district-wise predictions of Covid-19 cases in India for a three-week period.
- The data is updated on a weekly basis to accommodate various effects due to administrative interventions, the severity of the viral strain, change of weather patterns.
- It also accounts for the effect of different lockdown scenarios such as the effect of locking down district boundaries and implementing different levels of lockdown within a district.
- It also includes the effect of movement of population across district/state borders in the wake of Covid-19.
2. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research has started the trials of anti-leprosy drug trials against COVID-19. The drug trial is to be conducted with the help of Mycobacterium MW.
- The Mycobacterium MW is a heat-killed bacteria. It is to be tried on different COVID-19 patients.
- The drug trial was approved by the Drug Controller General of India.
- One particular strain of bacteria called the Mycobacterium MW is to be tried on several COVID-19 patients.
- The drug has already proved its effectivity against leprosy.
- The CSIR is also trying phytopharmaceuticals
3.The Asian Development Bank approved 1.5 billion USD loan to support the Indian Government in its actions against the spread of COVID-19 crisis.
- The fund is to be used in disease containments, social protection, and disease prevention.
4. The COVID Action Collab is an initiative by a group of experts.
- The main aim of the initiative is to address issues created by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It especially focuses on the poor and the vulnerable.
- The organization is now to test sewage for the presence of COVId-19 virus. Over 150 organizations have come together to make the initiative a success.
- The initiative was ideated by the Catalyst Group.
- The COVID-19 patients shed the virus through stools and urine.
- Currently, there are no significant steps taken to detect the virus in sewage.
- Also, there are no significant measures to segregate the wastes of COVID-19 infected persons.
- Even, in certain cities, persons that are home quarantined and infected with COVID-19 do not have separate waste collection system.
5. Students from IIT Bombay, Islamic University of Science and Technology, NIT Srinagar have come together to invent a low-cost ventilator called “Ruhdaar”.
- The cost of production of one ventilator is Rs 10,000.
- The design was initiated by the first-year student of IIT Bombay from Kashmir.
- He began to design the ventilator after learning that his home, the Kashmir Valley had only 97 ventilators in all.
6. Led by the World Health Organization, a long list of countries, industry groups, and non-governmental organizations committed to joining a project called Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator.
- Access to COVID-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator” is a Global Collaboration to Accelerate the Development, Production and Equitable Access to New COVID-19 diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines.
- A key goal is to level the global playing field so that any products will be available to rich and poor populations alike.
- The project, however, is still in the early stages. On May 4, countries and organizations are encouraged to start pledging contributions with an eye toward commitments worth about $8 billion in initial funding.
6. This year, the World Day for Safety and Health at Work will focus on addressing the outbreak of infectious diseases at work, in particular, on the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It is an annual international campaign to promote safe, healthy, and decent work.
- to ILO, a national occupational safety and health culture is one where –
- the right to a safe and healthy working environment is respected at all levels, governments, employers and workers actively participate in securing a safe and healthy working environment through a system of defined rights, responsibilities and duties, and where the highest priority is accorded to the principle of prevention.
- Observed on: 28 April (every year). 28 April is also the International Commemoration Day for Dead and Injured Workers organized worldwide by the trade union movement since 1996.
- Observed by: The International Labour Organization (ILO). This celebration is an integral part of the Global Strategy on Occupational Safety and Health of the ILO, as documented in the Conclusions of the International Labour Conference in 2003.
- Observed since: 2003.




