Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 6th June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Sixth mass extinction:
- India’s Campaign Brochure for UNSC Seat:
- Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Rules of 2020:
- The Times Higher Education (THE) Asia University Ranking for 2020 was launched recently.:
- Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) :
- LiDAR:
- Pangong Tso
- Other important current affairs:
1. Sixth mass extinction:
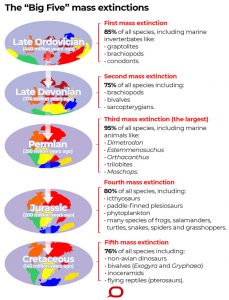
The ongoing sixth mass extinction may be one of the most serious environmental threats to the persistence of civilization, according to new research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS)
- This ongoing extinction of species, which coincides with the present Holocene epoch is known as Holocene extinction, Sixth extinction, or Anthropocene extinction.
- In the history of Earth, we’ve had five major extinction events in the history of life.
- The five mass extinctions that took place in the last 450 million years have led to the destruction of 70-95 % of the species of plants, animals, and microorganisms that existed earlier.
- The most recent was about 65 million years ago when an asteroid crashed into the Yucatán [Peninsula] and took out the dinosaurs, changing the climate dramatically.
- This ongoing extinction of species is a result of human activity.
- Earlier extinctions were caused by “catastrophic alterations” to the environment, such as massive volcanic eruptions, depletion of oceanic oxygen, or collision with an asteroid.
- The current rate of extinction of species is estimated at 100 to 1,000 times higher than natural background rates.
- This large number of extinctions spans numerous families of plants and animals, including mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and arthropods.
2.India’s Campaign Brochure for UNSC Seat:

India has released a campaign brochure ahead of the vote for the non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) in 2021-22.
- This will be the eighth time India will occupy a non-permanent UNSC seat, with its last term in 2011-2012.
India also seeks for permanent membership in the UNSC. - India along with other countries of G4 grouping (Japan, Brazil, and Germany) is asking for a spot for permanent membership in UNSC.
- Five permanent members: China, France, the Russian Federation, the UK, and the USA.
- India is guaranteed a place as it is the sole candidate for Asia-Pacific but needs two-thirds of the 193-member General Assembly to vote in its favor in a secret ballot scheduled for 17th June 2020 in New York (USA).
- International governance has been under increasing strain due to traditional and non-traditional security challenges. Terrorism is one of the most cited examples.
- Unreformed and under-representative global institutions and the Covid-19 pandemic with its economic impact has increased challenges for the UNSC.
- India will highlight international terrorism, United Nations reforms, and Security Council expansion, streamlining the peacekeeping operations and technology initiatives during its upcoming tenure.
3.Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Rules of 2020:

Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Rules of 2020 notified by the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- These rules seek to regulate the production, import, trade, ownership, and operation of unmanned aircraft systems or drones. They also create a framework for their use by businesses.
- Only authorized entities can sell the drone
- Entities authorized by the Director-General of Civil Aviation can operate it
- Permits for flying these also have to be sought online and a log has to be shared after the flight.
- The norms apply to all existing drones as well.
- Exception: Nano-drones weighing 250 grams or less can be operated without a drone pilot license.
- Insurance: No unmanned aircraft (UA) system shall be operated in India unless there is in existence a valid third party insurance policy to cover the liability that may arise on account of a mishap.
- Rule number 36 and 38 in the Ministry’s draft state that no unmanned aircraft shall carry any payload unless specified by the Director-General of DGCA.
- Neither shall a person “drop or project or cause or permit to be dropped or projected from a UAS (unmanned aircraft system) in motion anything,” except when specified.
- For owning and using a drone, one has to be at least 18 years old.
- In the case of companies, the requirement is that their main place of business has to be in India and the chairman, and at least two-thirds of directors have to be Indian citizens.
- Also, businesses operating drones have to be substantially owned and effectively controlled by Indian nationals.
4. The Times Higher Education (THE) Asia University Ranking for 2020 was launched recently.:
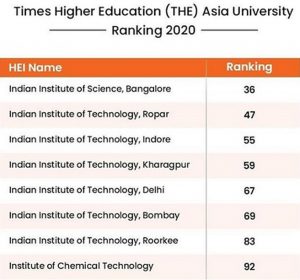
Times Higher Education (THE) is a weekly magazine based in London, reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
- The Times Higher Education (THE) Asia University Rankings 2020 use the same 13 performance indicators as THE World University Rankings.
- The universities are judged in four core areas:
- (1) Teaching,
- (2) Research,
- (3) Knowledge Transfer, and
- (4) International Outlook.
Key Findings:
- China is home to the continent’s top two universities for the first time this year, as Tsinghua University is ranked 1, and Peking University is ranked 2.
- With eight institutes in the top 100, India is the third most represented country in the Ranking.
- The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore retains its top position in the country by attaining the 36th spot globally.
- Eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) have also been featured in the top 100.
5. Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) :

In an effort to give a push to digital payments across the country, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is setting up a Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) of Rs 500 crore.
- This fund has been created to encourage acquirers to deploy point of sale (PoS) infrastructure, both physical and digital, in tier-3 to tier-6 centers and northeastern states.
- The RBI has made an initial contribution of Rs 250 crore covering half the fund. The remaining will come from the card-issuing banks and card networks operating in the country.
- The fund will be governed through an advisory council but it will be managed and administered by the RBI.
- Over the years, the payments ecosystem in the country has evolved with a wide range of options such as bank accounts, mobile phones, cards, etc.
- To provide further fillip to the digitisation of payment systems, it is necessary to give impetus to acceptance infrastructure across the country, more so in underserved areas.
- The fund is also in line with the measures proposed by the vision document on payment and settlement systems in India 2019-2021.
- The enhanced ability of PoS infrastructure is supposed to reduce the demand for cash over time.
- By 2021, there will be around 5 million active PoS by 2021.
6.LiDAR:
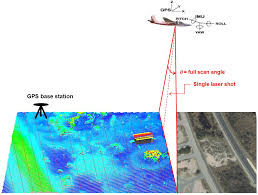
A U.K.-based team of archeologists has continued its research over the Tamar Valley through LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) despite lockdown due to Covid-19 in the country.
- LiDAR is commonly used by geologists and surveyors to make high-resolution maps.
- Tamar Valley is located in the south of England and is a rich archaeological landscape with many sites belonging to the Iron Age and the Roman era.
- The area is a World Heritage Site due to its historic mining activities.
- A World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for its special cultural or physical significance.
- The list of World Heritage Sites is maintained by the international ‘World Heritage Programme’, administered by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
LiDAR
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges & variable distances.
- These light pulses—combined with other data recorded by the airborne system— generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
- A LiDAR instrument principally consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver.
- Airplanes and helicopters are the most commonly used platforms for acquiring LiDAR data over broad areas.
- LiDAR is used for agriculture, hydrology and water management systems
and geology-related applications. - It is also used in archaeology.
7.Pangong Tso :

The Pangong Tso is the site of eye-to-eye confrontation between Indian and Chinese troops, following a scuffle in early May. Both sides have ramped up their troop presence but the “disengagement” process is also underway.
- Pangong Tso is a long narrow, deep, endorheic (landlocked) lake situated at a height of about 4,350 m in the Ladakh Himalayas.
- It is 134 km long and 5 km wide at its broadest point.
- In the Ladakhi language, Pangong means extensive concavity, and Tso is a lake in Tibetan.
- The brackish water lake freezes over in winter and becomes ideal for ice skating and polo.
- It is not a part of the Indus river basin area and geographically a separate landlocked river basin.
- The lake is not a Ramsar site yet. It is in the process of being identified under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance.
Line of Actual Control (LAC) and Pangong Tso lake
- The disputed boundary between India and China, also known as the Line of Actual Control (LAC), mostly passes on the land, but Pangong Tso is a unique case where it passes through the water as well.
- The points in the water at which the Indian claim ends and the Chinese claim begins are not agreed upon mutually.
- As things stand, 45 km-long western portion of the lake is under Indian control, while the rest is under China’s control.
- By itself, the lake does not have major tactical significance. But it lies in the path of the Chushul approach, one of the main approaches that China can use for an offensive into Indian-held territory.
- The barren mountains on the lake’s northern bank called the Chang Chenmo, jut out like a palm and the various protrusions are referred to as ‘fingers.’
- While India claims that the LAC starts at Finger 8, China claims that it starts at Finger 2, which is presently dominated by India. India physically controls area only up to Finger 4.
Other important current affairs:
1. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has announced that a giant asteroid called as 163348 (2002 NN4), is expected to pass Earth on 6th June 2020.
- However, it is approaching the Earth within the safe limit of distance.
- 163348 (2002 NN4): It was discovered in July 2002 and is expected to approach the earth in June 2020.
- The asteroid is estimated to be between 250-570 meters in diameter.
- The asteroid is a Near-Earth Object and classified as a Potentially Hazardous Asteroid (PHA).
- Near-Earth Objects (NEOs): NEOs are comets and asteroids pushed by the gravitational attraction of nearby planets into orbits that allow them to enter the Earth’s neighborhood.
2. A study by the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) has found that the radiative forcing of aerosols i.e. effect of anthropogenic aerosols is much higher over the high altitudes of western trans-Himalayas.
- ARIES, Nainital is an autonomous research institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The Trans-Himalayas Mountain Region is located to the north of the Great Himalayas which consists of Karakoram, Ladakh, Zaskar, and Kailash mountain ranges.
- It is also called the Tibet Himalayan Region because most of the part of these ranges lies in Tibet.
4. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has issued an advisory to streamline and formalize the process of importing live exotic animals.
- Many exotic species of birds, reptiles, and amphibians are imported into India for commercial purposes.
Key Points - Exotic Animals:
- The term exotic does not have a set definition but it usually refers to a wild animal or one that is more unusual and rare than normal domesticated pets like cats or dogs.
- These are those species that are not usually native to an area and are introduced to an area by humans.
- The advisory has defined them as those that are mentioned under the Appendices of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) but not under the Schedules of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The major reason for issuing the advisory is to regulate trade because the issue of zoonotic diseases is linked to wildlife.
- With this advisory, it will be known how many such exotic animals are there in the country.
5. Union Home Ministry has included indulging in Tablighi activities as a specific visa violation under the new amendments.
- It has added a new category—“restriction on engaging in Tabligh activities” in the “general policy guidelines relating to Indian visa.”
- The guidelines provide details of 24 categories of visas and the various conditions under which they could be granted online or by missions abroad.
- The $500 fine is also for other violations such as overstay of more than two years, visiting protected areas and cases involving both overstay and visa violations.
- As per the amended guidelines:
- Foreign nationals granted any type of visa and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders shall not be permitted to engage themselves in Tabligh work.
- There will be no restriction in visiting religious places and attending normal religious activities like attending religious discourses.
- However, preaching religious ideologies, making speeches in religious places, distribution of audio or visual display/pamphlets pertaining to religious ideologies, spreading conversion, etc. will not be allowed.
6. Retirement fund body, Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) said it has released Rs 868 crore pension along with Rs 105 crore arrear on account of the restoration of the commuted value of the pension.
- The government, had, in February this year notified the restoration of full pension after 15 years of retirement for pensioners who have commuted part of their pension at the time of retirement.
- This has resulted in a substantial increase in pension for those EPFO pensioners who retired before September 26, 2008, and had opted for partial commutation of pension.
- Commutation of pension will cost the government Rs 1500 crore.
- The higher pension benefit will be restored after 15 years from the date of receiving a commuted pension at the time of retirement.
- This means an individual who retired on April 1, 2005, would be eligible to receive the benefit of higher pension after 15 years i.e. from April 1, 2020.
8. Russian President Vladimir Putin declared a state of emergency after 20,000 tonnes of diesel oil to spilled into the Ambarnaya river, turning its surface crimson red.
- Ambarnaya is a shallow river in Siberia, Russia which flows in a northerly direction into Lake Pyasino. On leaving Lake Pyasino, the waters emerge as the Pyasina River.
- The Ambarnaya river is part of a network that flows into the environmentally sensitive Arctic Ocean.
- On May 29, 2020, an estimated 20,000 tonnes of Diesel oil leaked into the river following the collapse of a power plant owned by Norilsk Nickel.
- With a 12 km stretch of the river seriously affected, Russia’s president Vladimir Putin declared a state of emergency within Russia’s Krasnoyarsk Region, located in the Siberian peninsula.
9. The quantum of Foreign Portfolio Investments (FPIs) flows in the equity market reached a record high in the first week of June compared to any other month in the current calendar year of 2020.
- The foreign portfolio investors have bought shares worth about Rs. 21,000 crore in just five trading sessions in the first week of June 2020.
- This is the highest in any month of 2020, with the previous high registered in May at Rs. 14,569 crores.
- The FPI has been brought into sectors like automobiles, private banks, and pharmaceuticals.
- The sudden surge in FPIs is because of the Rights Issue of Reliance Industries Limited (RIL), stake sale in Kotak Mahindra Bank, and the slight increase in optimism in the Indian market.
- RIL’s Rights Issue is India’s largest Rights Issue at Rs. 53,124.20 crore.
- Uday Kotak sold shares worth around Rs. 6,800 crores of Kotak Mahindra Bank, which was bought by FPIs.
- However, the cumulative foreign flows in equities this year is still negative at Rs. 19,531 crores, since March and April saw huge outflows.
- March witnessed a record outflow of Rs. 61,973 crore, which was followed by selling worth Rs. 6,884 crore in April.
10.Nagar Van Scheme on the occasion of World Environment Day (5th June).
- The Nagar Van (Urban Forests) aims to develop 200 Urban Forests across the country in the next five years.
- Warje Urban Forest in Pune (Maharashtra) will be considered as a role model for the Scheme.
- The Scheme enforces people’s participation and collaboration between the Forest Department, Municipal bodies, NGOs, Corporates, and local citizens.
- These urban forests will primarily be on the existing forest land in the City or any other vacant land offered by local urban local bodies.
- The finances for the scheme will be paid for by the CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund (CAF) Act, 2016) funds.
- The CAF Act was enacted to manage the funds collected for compensatory afforestation which till then was managed by ad hoc Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- Compensatory afforestation means that every time forest land is diverted for non-forest purposes such as mining or industry, the user agency pays for planting forests over an equal area of non-forest land, or when such land is not available, twice the area of degraded forest land.
- As per the rules, 90% of the CAF money is to be given to the states while 10% is to be retained by the Centre.
11.iCommit’ initiative:
- Launched on the occasion of World Environment Day.
- The ‘#iCommit’ initiative is centered around the idea of building an energy resilient future.
- The calls upon all stakeholders and individuals to continue moving towards energy efficiency, renewable energy, and sustainability to create a robust and resilient energy system in the future.
- The initiative is driven by Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), under the administration of the Ministry of Power.
- It includes a diverse set of players such as Governments, Corporates, Multilateral and Bilateral Organisations, Thinks Tanks, and Individuals.
12. Healthy and Energy Efficient Buildings Initiative:
- Launched by Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), in partnership with the U.S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) MAITREE program.
- This initiative will address the challenges of retrofitting existing buildings and air conditioning systems so that they are both healthy and energy-efficient.
- Market Integration and Transformation Program for Energy Efficiency (MAITREE), under which this initiative has been launched, is a part of the US-India bilateral Partnership between the Ministry of Power and USAID and is aimed at accelerating the adoption of cost-effective energy efficiency as a standard practice within buildings, and specifically focuses on cooling.




