Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 7th October 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Nobel Prize in Physics 2020 :
- Krishna and Godavari River Water Dispute:
- “Sensors and Sensing for Precision Agriculture
- Indian Sign Language:
- Other important current affairs
1.Nobel Prize in Physics 2020 :

Nobel Prize in Physics 2020 has been awarded, with one half to Roger Penrose and the other half jointly to Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez for their discoveries about Blackhole.
- Roger Penrose used ingenious mathematical methods in his proof that black holes are a direct consequence of Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
- Einstein did not himself believe that black holes really exist, these super-heavyweight monsters that capture everything that enters them. Nothing can escape, not even light.
- Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez each lead a group of astronomers that, since the early 1990s, has focused on a region called Sagittarius A* at the centre of our galaxy.
- Their pioneering work has given us the most convincing evidence yet of a supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way.
2.Krishna and Godavari River Water Dispute:
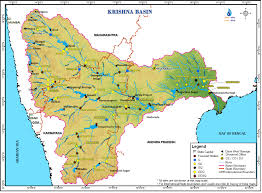
The Centre will determine the jurisdictions of the Krishna and Godavari river management boards (KRMB and GRMB), Union Jal Shakti Ministry (MoJS) announced at the Apex Council Meeting.
Highlights of issues:
- Jurisdiction of the KRMB and GRMB. Even after six years of their formation, their jurisdiction is still not notified because both the states have differing opinions on this issue.
- Submission of Detailed Project Reports (DPR) of new projects in river basins by the two governments for appraisal and sanction by the Apex Council.
- As per the APRA-2014, both KRMB and GRMB should technically appraise and clear them.
Establishing a mechanism to determine the share of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana in the Krishna and Godavari waters. - Shifting the headquarters of the Krishna River Management Board to Andhra Pradesh as mandated by APRA-2014.
Decisions:
- The Centre will go ahead with notifying the jurisdiction of both KRMB & GRMB because as per the APRA- 2014, no consensus is needed.
- Both States agreed to submit the DPRs of all the projects.
- With regards to sharing of river waters, the Telangana Chief Minister agreed to withdraw the case filed in Supreme Court, to allow the Centre to refer water sharing issues to the Krishna Godavari tribunal.
Apex Council:
- It has been constituted by the Central Government under the provisions of Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act (APRA), 2014.
- It supervises the functioning of the Godavari River Management Board and Krishna River Management Board.
- KRMB & GRMB are autonomous bodies established as per APRA-2014 under the administrative control of MoJS to manage and regulate the Waters of Krishna and Godavari Basin respectively in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- It comprises the Union Jal Shakti Minister and the Chief Ministers of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
Apex Council Meeting:
- It was the second meeting since 2016.
- Aim: To resolve the conflict between the two States over executing irrigation projects and sharing water from the Krishna and Godavari rivers.
Godavari River
- Godavari river rises from Trimbakeshwar near Nasik in Maharashtra and flows for a length of about 1465 km before outfalling into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Godavari basin extends over states of Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha in addition to smaller parts in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Tributaries: Pravara, Purna, Manjra, Penganga, Wardha, Wainganga, Pranhita (combined flow of Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha), Indravati, Maner and the Sabri.
Krishna River
- It originates near Mahabaleshwar (Satara) in Maharashtra. It is the second biggest river in peninsular India after the Godavari River.
- Drainage: It runs from four states Maharashtra (303 km), North Karnataka (480 km) and the rest of its 1300 km journey in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh before it empties into the Bay of Bengal.
- Tributaries: Tungabhadra, Mallaprabha, Koyna, Bhima, Ghataprabha, Yerla, Warna, Dindi, Musi and Dudhganga.
3.“Sensors and Sensing for Precision Agriculture” :

A session on “Sensors and Sensing for Precision Agriculture” was organised by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (ICAR-IARI).
Precision Agriculture
- Precision agriculture (PA) is an approach where inputs are utilised in precise amounts to get increased average yields, compared to traditional cultivation techniques such as agroforestry, intercropping, crop rotation, etc.
- Sustainable PA is this century’s most valuable innovation in farm management that is based on using Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs).
- It is based on sustainable agriculture and healthy food production and it consists of profitability and increasing production, economic efficiency and the reduction of side effects on the environment.
Benefits:
- Increases agriculture productivity.
- Prevents soil degradation.
- Reduces chemical application in crop production.
- Efficient use of water resources.
- Disseminates modern farm practices to improve the quality, quantity and reduced cost of production.
- Changes the socio-economic status of farmers.
4.Indian Sign Language:
The Indian Sign Language Research and Training Centre (ISLRTC) and the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to make NCERT textbooks accessible to hearing-impaired students in sign language.
- NCERT textbooks, teachers’ handbooks and other materials for Class I-XII of all subjects in Hindi and English medium would be converted into Indian Sign Language (ISL) in digital format.
- It is a step towards fulfilling the needs of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016, and New Education Policy, 2020.
- The signing of this MoU is based on the United Nations Children’s Fund – UNICEF’s initiative “Accessible Digital Textbooks for All”.
- So far, hearing-impaired children used to study only through verbal or written medium now they can study through Indian Sign Language which is the same all over the country.
- In the childhood days, the cognitive skills of children are developed and it is very necessary to provide them educational material as per their learning needs.
- It will not only enhance their vocabulary but also enhance their capabilities to understand concepts.
Indian Sign Language (ISL):
- Broadly, it’s a set of hand and facial gestures used to communicate, most often by the hearing and speech impaired.
- It has its own grammar, syntax, and regional “dialects”, essentially different gestures for the same word or sentiment.
- The main difference from spoken languages lies in the form: Sign languages are visual, spoken ones are auditory.
- Sign language is recognized as an official language in many countries across the world like the USA.
Other important current affairs:
1.The Rajasthan government has decided to build temporary shelters for migratory birds near the Sambhar Lake (near Jaipur) before 2020’s winter season.
- Every year, a large number of birds from the cold northern regions of Central Asia come to Sambhar Lake.
In 2019, more than 20,000 migratory birds died due to avian botulism in the lake. - Rajasthan High Court took suo motu cognisance of the mass death and asked the expert committee to carry out an investigation and make recommendations.
- The Court has constituted a seven-member expert committee to study the impact of salt-forming and identify any illegal salt mining in the lake.
- It has suggested the state government seek the center’s support for more funds for creating an infrastructure for the safety and security of birds.
3.Ministry of Electronics and Information and Technology (MeitY) has approved 16 eligible applicants under the PLI Scheme.
- Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing was notified on 1st April, 2020.
- It extends an incentive of 4% to 6% on incremental sales (over base year) of goods under target segments that are manufactured in India to eligible companies, for a period of five years subsequent to the base year (FY2019-20).
- Over the next 5 years, the approved companies under the PLI Scheme are expected to lead to total production of more than INR 10.5 lakh crore).
- The companies approved under the scheme are expected to promote exports significantly. Out of the total production of INR 10,50,000 crore in the next 5 years, around 60% will be contributed by exports of the order of INR 6,50,000 crore.
- The companies approved under the scheme will bring additional investment in electronics manufacturing to the tune of INR 11,000 crore.
4.The government has finally appointed three economists — PMEAC member Ashima Goyal, NCAER’s Shashanka Bhide and IIM-Ahmedabad professor Jayanth Varma — as new members of the RBI’s monetary policy committee (MPC) to decide on interest rates.
- The new members nominated have been given a four-year term.
- The other three ex-officio members of the MPC are Reserve Bank Governor Shaktikanta Das, Deputy Governor (in-charge of monetary policy) Michael Patra and executive director Janak Raj. The panel is chaired by RBI governor Shaktikanta Das.
- The six-member MPC has the mandate to maintain annual inflation at 4 percent, with an upper tolerance of 6 percent and a lower tolerance of 2 percent.
- The last meeting of the panel was held in August wherein the committee had decided to keep interest rates unchanged in a bid to tame inflation.




