Today Current Affairs: 13th May 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
National Programme On Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage:

The Union Cabinet has approved the proposal of the Department of Heavy Industry for implementation of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme ‘National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage’.
- The move aims to achieve a manufacturing capacity of 50 GigaWatt Hour of ACC and five Giga Watt Hour of Niche ACC with an outlay of 18,100 crores.
- ACCs are the new generation of advanced storage technologies that can store electric energy either as electrochemical or as chemical energy and convert it back to electric energy as and when required.
- It will also give a big push to electric mobility, benefiting three-wheelers, four-wheelers, and heavy vehicles.
- India is currently importing Battery Storage Equipment worth 20 thousand crore rupees and the scheme will be helpful in making the country self-reliant (Atmanirbhar).
2021 World Food Prize:

Dr. Shakuntala Haraksingh Thilsted, a global nutrition expert of Indian descent has won the prestigious 2021 World Food Prize for her groundbreaking research in developing holistic, nutrition-sensitive approaches to aquaculture and food systems.
Shakuntala Haraksingh Thilsted:
- Thilsted’s trailblazing research on small native fish species in Bangladesh led to the development of nutrition-sensitive approaches to aquatic food systems at all levels, from the farm to food processing to final consumers, resulting in improved diets for millions of the most vulnerable people in Asia and Africa.
- Thilsted, who is a native of Trinidad and Tobago and a citizen of Denmark, was born in 1949 in the Caribbean island of Trinidad in the small village of Reform. Most of the inhabitants, including her family, were descendants of Indian Hindu migrants brought to Trinidad to engage in agricultural labour.
World Food Prize:
- The World Food Prize recognizes the achievements of individuals who have advanced human development by improving the quality, quantity, or availability of food in the world.
- It recognizes contributions in any field involved in the world food supply such as plant, animal and soil science; nutrition; rural development; marketing; food processing and packaging; water and the environment; physical infrastructure; policy analysis, etc.
- The prize is open to every individual without regard to race, religion, nationality, or political beliefs.
- Presented by: World Food Prize Foundation, with various sponsor companies.
- The prize was conceived by Dr. Norman E. Borlaug, winner of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in global agriculture.
- The Prize was created in 1986 and was first awarded in 1987 with M. S. Swaminathan of India being the first recipient.
- Ceremony: The annual award is presented each October on or around UN World Food Day (October 16).
- Cash prize: In addition to the cash award of $250,000, the Laureate receives a sculpture designed by the noted artist and designer, Saul Bass.
The International Nurses And Midwives Day:

The International Nurses and Midwives Day is celebrated on May 12 every year
- The celebration of International Nurses Day started in 1965 by the International Council of Nurses(ICN).
- This day is the birth anniversary of the famous Florence Nightingale.
- She was an English nurse, social reformer, and statistician. During the Crimean war, she gained fame while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses, being the pillar of modern nursing. She brought a reputation for nursing and became an icon in Victorian culture.
- The theme for this year’s International Nurses Day is Nurses: A Voice to Lead-A Vision for Future Healthcare.
NITI Aayog’s Ambitious Project For Great Nicobar Island:

The Environment Appraisal Committee (EAC) – Infrastructure I of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has flagged serious concerns about NITI Aayog’s ambitious project for Great Nicobar Island.
- The committee has, however, removed the first hurdle faced by the project. It has “recommended” it “for grant of terms of reference (TOR)” for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies, which in the first instance will include baseline studies over three months.
- Documents uploaded recently on the MoEFCC’s Parivesh portal show that the 15-member committee headed by marine biologist and former director, Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS), Deepak Apte, made the decision.
- The proposal includes an international container transhipment terminal, a greenfield international airport, a power plant, and a township complex spread over 166 sq. km. (mainly pristine coastal systems and tropical forests), and is estimated to cost ₹75,000 crores.
- This includes Galathea Bay, the site of the port and the centrepiece of the NITI Aayog proposal.
- Galathea Bay is an iconic nesting site in India of the enigmatic Giant Leatherback, the world’s largest marine turtle.
- A number of species are restricted to just the Galathea region.
- These include the critically endangered Nicobar shrew, the Great Nicobar crake, the Nicobar frog, the Nicobar cat snake, a new skink (Lipinia sp), a new lizard (Dibamus sp,) and a snake of the Lycodon sp that is yet to be described.
Increased Child Marriages In Lockdown:

Some activists and organizations of Karnataka have raised the issue of increased child marriages in Lockdown with the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- According to a report published in December 2020 by ChildLine India, the pandemic and the subsequent lockdown have proved to be new drivers of child marriages in rural Madhya Pradesh.
Child Marriage:
- It is defined as a marriage of a girl or boy before the age of 18 and refers to both formal marriages and informal unions in which children under the age of 18 live with a partner as if married.
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) estimates suggest that each year, at least 1.5 million girls under 18 get married in India, which makes it home to the largest number of child brides in the world – accounting for a third of the global total.
- A recent study by The Lancet shows that up to 2.5 million more girls (below the age of 18) around the world are at risk of marriage in the next 5 years because of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Reason for Increased Child Marriages during Lockdowns:
- Lack of Alert Mechanism:
- Pandemic Induced Pressures: Economic pressures due to the pandemic have pushed poor parents to marry off girls early.
- With no schools, the safety of children, particularly girls, was a major reason for the increase in violence against children and child marriages.
The mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture:

The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has provided an enhanced allocation of Rs. 2250 Crore for the year 2021-22 for ‘Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Horticulture is the branch of plant agriculture dealing with garden crops, generally fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. M.H. Marigowda is considered the Father of Indian Horticulture.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- MIDH is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare is implementing MIDH with effect from 2014-15.
- MIDH is implemented under Green Revolution – Krishonnati Yojana.
- Under MIDH, the Government of India (GoI) contributes 60% of the total outlay for developmental programs in all the states except states in the North East and the Himalayas, 40% share is contributed by State Governments.
- In the case of the North Eastern States and the Himalayan States, GoI contributes 90%.
MIDH Sub-Schemes:
National Horticulture Mission (NHM):
- It is being implemented by State Horticulture Missions (SHM) in selected districts of 18 States and 6 Union Territories.
Horticulture Mission for North East & Himalayan States (HMNEH):
- HMNEH is being implemented for the overall development of Horticulture in North East and Himalayan states.
National Horticulture Board (NHB):
- NHB is implementing various schemes under MIDH in all States and UTs.
Coconut Development Board (CDB):
- CDB is implementing various schemes under MIDH in all Coconut growing states in the country.
Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH):
- CIH was established at Medi Zip Hima, Nagaland in 2006-07 for providing technical backstopping through capacity building and training of farmers and Field functionaries in the North Eastern Region.
- Achievements of MIDH:
- During the year 2019-20, the country recorded its highest ever horticulture production of 320.77 million tonnes.
- MIDH has played a significant role in increasing the area under horticulture crops.
- Area and production during the years 2014-15 to 2019-20 has increased by 9% and 14% respectively.
- It has contributed significantly towards improving the quality of produce and productivity of farmland.
- The initiative of MIDH has not only resulted in India’s self-sufficiency in the horticulture sector but also contributed towards achieving sustainable development goals of zero hunger, good health, and wellbeing, no poverty, gender equality, etc.
Aerial Passenger Ropeway System Between Dehradun And Mussoorie:

The Union Cabinet gave its approval to the transfer of land of Indo-Tibetan Border Police, ITBP to the Government of Uttarakhand for the development of Aerial Passenger Ropeway System between Dehradun and Mussoorie.
- The proposed Ropeway is a mono-cable ropeway of 5580 meters length between Purkul Gaon, Dehradun and Library, Mussoorie being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 285 crore.
- It will have a carrying capacity of 1,000 persons per hour per direction. This will considerably reduce the traffic flow on the road route from Dehradun to Mussoorie.
- Besides, this will generate direct employment of 350 and indirect employment of more than 1,500 people. Once completed, the ropeway will be a huge attraction for tourists which in turn will provide a boost to the tourism industry in the state and create additional employment opportunities in the tourism sector.
Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP):
- The Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) is India’s primary border patrol organization with its border with China’s Tibet Autonomous Region. It was raised in 1962 in the wake of the Sino-Indian War of 1962.
- The “Indo-Tibetan Border Police Force Act, 1992″ provides for the constitution and regulation” of the ITBP “for ensuring the security of the borders of India and for matters connected therewith”.
Covid-19: Make It The Last Pandemic: IPPPR:

An independent global panel, the Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response (IPPPR) in its report named “Covid-19: Make it the Last Pandemic concluded that the catastrophic scale of the Covid-19 pandemic could have been prevented.
- The report was requested by World Health Organization (WHO) member states in May 2020.
Reasons for Inflated Covid Catastrophe:
- Bad Decisions:
- A series of bad decisions meant Covid-19 went on to kill at least 3.3 million people so far and devastate the global economy.
- Poor strategic choices, unwillingness to tackle inequalities and an uncoordinated system created a toxic cocktail which allowed the pandemic to turn into a catastrophic human crisis.
- Failure of Institutions:
- Institutions failed to protect people and science-denying leaders eroded public trust in health interventions.
- The threat of a pandemic had been overlooked and countries were woefully unprepared to deal with one.
- Lack of Urgency:
- Early responses to the outbreak detected in Wuhan, China in December 2019 lacked urgency, with February 2020 a costly “lost month” as countries failed to heed the alarm.
- Delay:
- The emergence of Covid-19 was characterized by a mixture of some early and rapid action, but also by delay, hesitation, and denial.
- WHO could have declared the situation a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), its highest level of alarm in January 2020.
Article 311 Of The Constitution:

A police officer was dismissed from the service by Mumbai Police Commissioner under Article 311(2)(b) of the Constitution without a departmental enquiry.
- Article 311 (1) says that no government employee either of an all India service or a state government shall be dismissed or removed by an authority subordinate to the own that appointed him/her.
- Article 311 (2) says that no civil servant shall be dismissed or removed or reduced in rank except after an inquiry in which s/he has been informed of the charges and given a reasonable opportunity of being heard in respect of those charges.
- People Protected under Article 311: The members of
- Civil service of the Union,
- All India Service, and
- Civil service of any State,
- People who hold a civil post under the Union or any State.
- The protective safeguards given under Article 311 are applicable only to civil servants, i.e. public officers. They are not available to defense personnel.
- Exceptions to Article 311 (2):
- 2 (a) – Where a person is dismissed or removed or reduced in rank on the ground of conduct which has led to his conviction on a criminal charge; or
- 2 (b) – Where the authority empowered to dismiss or remove a person or to reduce him in rank is satisfied that for some reason, to be recorded by that authority in writing, it is not reasonably practicable to hold such inquiry; or
- 2 (c) – Where the President or the Governor, as the case may be, is satisfied that in the interest of the security of the State, it is not expedient to hold such inquiry.
Israel-Palestine:
Israeli armed forces attacked Al-Aqsa Mosque in the Haram esh-Sharif in Jerusalem, ahead of a march by Zionist nationalists commemorating Israel’s capture of the eastern half of the city in 1967.
- The threatened eviction of dozens of Palestinian families in the East Jerusalem neighborhood of Sheikh Jarrah escalated the crisis further.
- Zionism is a worldwide Jewish movement that resulted in the establishment and development of the state of Israel and that now supports the state of Israel as a Jewish homeland
Al-Aqsa Mosque:
- It is one of the holiest structures in the Islamic faith. It sits inside a 35-acre site known by Muslims as Haram al-Sharif, or the Noble Sanctuary, and by Jews as the Temple Mount.
- The site is part of the Old City of Jerusalem, sacred to Christians, Jews and Muslims.
- It is believed to have been completed early in the eighth century and faces the Dome of the Rock, the golden-domed Islamic shrine that is a widely recognized symbol of Jerusalem.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, UNESCO, has classified the Old City of Jerusalem and its walls as a World Heritage Site.
Conflict over Jerusalem:
- Jerusalem has been at the center of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. According to the original 1947 United Nations (UN) partition plan, Jerusalem was proposed to be an international city.
- But in the first Arab Israel war of 1948, the Israelis captured the western half of the city, and Jordan took the eastern part, including the Old City that houses Haram al-Sharif.
- Israel captured East Jerusalem from Jordan in the Six-Day War 1967 and annexed it later.
- Since its annexation, Israel has expanded settlements in East Jerusalem.
- Israel sees the whole city as its “unified, eternal capital”, whereas the Palestinian leadership across the political spectrum have maintained that they would not accept any compromise formula for the future Palestinian state unless East Jerusalem is its capital.
Sheikh Jarrah Issue:
- Hundreds of thousands of Palestinians were forced out of their homes when the State of Israel was created in historical Palestine in 1948.
- Twenty-eight of those Palestinian families moved to Sheikh Jarrah in East Jerusalem to settle there.
- In 1956, when East Jerusalem was ruled by Jordan, the Jordanian Ministry of Construction and Development and the UN Relief and Works Agency facilitated the construction of houses for these families in Sheikh Jarrah. But Israel would capture East Jerusalem from Jordan in 1967.
- By the early 1970s, Jewish agencies started demanding the families leave the land.
- Earlier this year (2021), the Central Court in East Jerusalem upheld a decision to evict four Palestinian families from their homes in Sheikh Jarrah in favor of Jewish settlers.
- The issue remains unresolved and potentially inflammable.
India’s Stand on Israel-Palestine Issue:
- India recognised Israel in 1950 but it is also the first non-Arab country to recognize Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian.
- India is also one of the first countries to recognize the statehood of Palestine in 1988.
- In 2014, India favored UNHRC’s resolution to probe Israel’s human rights violations in Gaza. Despite supporting the probe, India abstained from voting against Israel in UNHRC in 2015.
- As a part of Link West Policy, India has de-hyphenated its relationship with Israel and Palestine in 2018 to treat both the countries as mutually independent and exclusive.
- In June 2019, India voted in favor of a decision introduced by Israel in the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) that objected to granting consultative status to a Palestinian non-governmental organization.
- So far India has tried to maintain the image of its historical moral supporter for Palestinian self-determination, and at the same time to engage in the military, economic, and other strategic relations with Israel.
Indian Researchers Have Sequenced 624 Pangolin Scales:
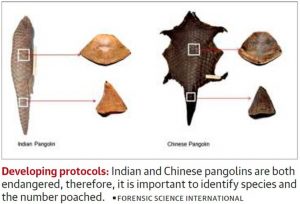
Indian Researchers have sequenced 624 pangolin scales, thereby categorizing the Indian and Chinese pangolins.
- Pangolins, despite being listed in Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 continues to be the world’s most trafficked mammal.
- The primary demand for its scales in the making of traditional East Asian medicines has led to an estimated illegal trade worth $2.5 billion every year.
- To enforce the appropriate national and international laws and to track the decline of the species, researchers of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), Kolkata, have now developed tools to tell apart the scales of Indian pangolin (Manis crassicaudata) and Chinese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla).
- They characterized the morphological features and investigated genetic variations between the two species by sequencing 624 scales of pangolins and comparing the sequences with all eight pangolin species.
- Based on the size, shape, weight, and ridge counts on the scales, the team was able to categorize the two species of Indian and Chinese pangolins.
- Though the Chinese pangolin is distributed mostly in Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, the north-eastern part of our country is also its home.
Institute Of Chartered Accountants Of India (ICAI) And Qatar Financial Centre Authority (QFCA):

The Union Cabinet has approved the signing of MoU between the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) and the Qatar Financial Centre Authority (QFCA).
- The MoU would enhance cooperation between the Institutes to work together to strengthen the Accounting profession and entrepreneurship base in Qatar.
- This MoU will benefit the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India and Qatar Financial Centre Authority.
- ICAI has an active Chapter in Doha, Qatar which was established in the year 1981 and is the oldest among the 36 overseas Chapters of the ICAI. Qatar (Doha) Chapter is amongst the most vibrant Chapters of ICAI.
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament of India, The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949′, to regulate the profession of Chartered Accountancy in India.
- Qatar Financial Centre Authority (QFCA) an independent legal entity established pursuant to Law No. (7) of 2005, is responsible for the development and promotion of the QFC as a world-class on-shore financial and business centre in the State of Qatar.




