Today Current Affairs: 17th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Section 66A Of The Information Technology Act, 2000.:

The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has requested States and Union Territories (UTs)to direct all police stations under their jurisdiction not to register cases under the repealed Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- It has also asked the States and UTs to sensitize law enforcement agencies for the compliance of the order issued by the Supreme Court on 24.03.2015.
- The MHA has also requested that if any case has been booked in States and UTs under section 66A of the IT Act, 2000, such cases should be immediately withdrawn.
- The Supreme Court in its judgment on 24.03.2015 in the matter of Shreya Singhal Vs. Union of India, had struck down Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- This made Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 null and void with effect from the date of the order, therefore 24.03.2015 and hence no action could be taken under this section.
National Programme For Dairy Development (NPDD).:

In order to further boost growth in livestock sector and thereby making animal husbandry more remunerative, Government has realigned the National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD).
- The realigned National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) will have two components.
- Component ‘A’ of NPDD will be implemented with emphasis on milk procurement, processing, marketing and quality of milk and milk products.
- The scheme is targeted towards installation of about 8900 bulk milk coolers, which is likely to cover about 26,700 villages.
- Component ‘B’ of NPDD will avail financial assistance from Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and will create or strengthen infrastructure in 4500 villages, 8.96 LLPD chilling and 7 LLPD processing capacity with incremental procurement of about 14.20 LLPD from 1.5 Lakh additional milk producers.
PRASHAD Scheme:

PM Modi inaugurated various development projects in Varanasi which includesTourist Facilitation Centre under the Project “Development of Varanasi Under PRASHAD Scheme – Phase II” and operation of Cruise Boat from Assi Ghat to RajGhat under the Project “Development of River Cruise in Varanasi under PRASHAD Scheme”.
- The ‘National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive’ (PRASHAD) is a Central Sector Scheme fully financed by the Government of India launched by the Ministry of Tourism in the year 2014-15.
- Its objective is integrated development of identified pilgrimage and heritage destinations.
- The project “Development of Varanasi Under PRASHAD Scheme – Phase II” was approved by the Ministry of Tourism with the cost of Rs. 44.69 crores in Feb. 2018.
Violence In South Africa:

Riots and looting in South Africa have left more than 70 people dead, hurt thousands of businesses and damaged major infrastructure.
- It is the worst civil unrest since the end of white minority rule in 1994.
Reason for Recent Violence:
- Protests began over calls for release of former president Jacob Zuma, who served the country from 2009-18 and is facing corruption charges.
- Former Cabinet ministers, high-ranking government officials and executives of state-owned enterprises have implicated Jacob Zuma in corruption.
- Many feel that his successor as president, Cyril Ramaphosa, has failed to provide decisive leadership – either to calm anger over Zuma’s imprisonment or to reassure South Africans that they will be safe.
- While the violence may have been spurred on by the imprisonment of Jacob Zuma, it’s being fanned by underlying problems in the country amid a raging pandemic and failing economy.
- In 2020, the country had witnessed its sharpest decline in annual Gross Domestic Product since 1946.
- Unemployment stood at a record high of 32.6% in the first three months of 2021.
- The government has condemned the violence and has stated that there is no justification for the violence. A lot of criminals or opportunistic individuals are trying to enrich themselves during this period.
- It has deployed its army to support the South African police, however, the rioting and looting haven’t stopped.
Adjournment Motion:

The Shiromani Akali Dal (Political Party) has decided to move an Adjournment Motion in the Lok Sabha against the government on the three controversial farm laws.
- Motions and resolutions are procedural devices to raise a discussion in the House on a matter of general public interest.
- Adjournment motion is introduced only in the Lok Sabha to draw the attention of the House to a definite matter of urgent public importance.
- It involves an element of censure against the government, therefore Rajya Sabha is not permitted to make use of this device.
- It is regarded as an extraordinary device as it interrupts the normal business of the House. It needs the support of 50 members to be admitted.
- The discussion on this motion should last for not less than two hours and thirty minutes.
- However, the right to move a motion for an adjournment of the business of the House is subject to the following restrictions. i.e. it should:
- Raise a matter which is definite, factual, urgent and of public importance.
- Not cover more than one matter.
- Be restricted to a specific matter of recent occurrence.
- Not raise a question of privilege.
- Not revive discussion on a matter that has been discussed in the same session.
- Not deal with any matter that is under adjudication of court.
- Not raise any question that can be raised on a distinct motion.
Amazon Forests:

According to a recent study, Amazon Forests have started emitting Carbon dioxide (CO2) instead of absorbing it.
- Growing trees and plants have taken up about a quarter of all fossil fuel emissions since 1960, with the Amazon playing a major role as the largest tropical forest.
Findings:
- A significant amount of deforestation (over the course of 40 years) in eastern and southeastern Brazil has turned the forest into a source of CO2 that has the ability to warm the planet.
- It might have also affected a long-term decrease in rainfall and increase in temperatures during the dry season.
- Not only the Amazon rainforests, some forests in Southeast Asia have also turned into carbon sources in the last few years as a result of formation of plantations and fires.
- Forest fires have doubled since 2013. One reason that they happen is when farmers burn their land to clear it for the next crop.
- Most of the emissions are caused by fires.
- A part of the Amazon emitting carbon even without fires was particularly worrying. This was most likely the result of each year’s deforestation and fires making adjacent forests more susceptible the next year.
Amazon Rainforests:
- These are large tropical rainforests occupying the drainage basin of the Amazon River and its tributaries in northern South America.
- Tropical forests are closed-canopy forests growing within 28 degrees north or south of the equator.
- They are very wet places, receiving more than 200 cm rainfall per year, either seasonally or throughout the year.
- Temperatures are uniformly high – between 20°C and 35°C.
- Such forests are found in Asia, Australia, Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and on many of the Pacific Islands.
- The Amazon rainforests cover about 80% of the Amazon basin and they are home to nearly a fifth of the world’s land species and is also home to about 30 million people including hundreds of indigenous groups and several isolated tribes.
Special Livestock Sector Package:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved implementation of a special livestock sector package (Rs. 9,800 crore).
- The aim is to boost growth in the livestock sector and thereby make animal husbandry more remunerative to farmers engaged in Animal Husbandry Sector.
- It includes the share of investments by State Governments, State Cooperatives, Financial institutions, External funding agencies and other stakeholders.
- The package has been designed by revising and realigning various components of the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying’ Schemes for the next five years, starting 2021-22.
- All the schemes of the Department will be merged into three broad categories as:
- Development Programmes: It includes Rashtriya Gokul Mission, National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD), National Livestock Mission (NLM) and Livestock Census and Integrated Sample Survey (LC & ISS) as sub-schemes.
- Disease Control Programme: It is renamed as Livestock Health and Disease Control (LH & DC) which includes the present Livestock Health and Disease Control (LH & DC) scheme and National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP).
- Infrastructure Development Fund: The Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development fund (AHIDF) and the Dairy Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF) are merged and the present scheme for support to Dairy Cooperatives and Farmer Producer Organizations engaged in Dairy activities is also included in this third category.
Significance of the Sector:
- A large number of farmers depend upon animal husbandry for their livelihood. It supports the livelihood of almost 55% of the rural population.
- Also, India is the highest livestock owner of the world.
- As per the 20th Livestock Census, the total Livestock population is 535.78 million in the country showing an increase of 4.6% over Livestock Census-2012.
Anti-Defection Law::

Lok Sabha Secretariat has issued notices to three MPs, after their parties petitioned Speaker Om Birla, seeking their disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law.
- They have been asked to give their comments within 15 days of receipt of letters.
Anti-defection law:
- In 1985 the Tenth Schedule, popularly known as the anti-defection law, was added to the Constitution by the 52nd Amendment Act.
- The purpose of the Amendment was to bring stability to governments by deterring MPs and MLAs from changing their political parties on whose ticket they were elected.
- The penalty for shifting political loyalties is the loss of parliamentary membership and a bar on becoming a minister.
- If a member of a house belonging to a political party:
- Voluntarily gives up the membership of his political party, or
- Votes, or does not vote in the legislature, contrary to the directions of his political party. However, if the member has taken prior permission, or is condoned by the party within 15 days from such voting or abstention, the member shall not be disqualified.
- If an independent candidate joins a political party after the election.
- If a nominated member joins a party six months after he becomes a member of the legislature.
India’s Textile Sector:

The Union Minister of Textiles held an in-depth review of initiatives undertaken by the Ministry of Textiles for giving a boost to the textiles sector.
- Textiles & garments industry is labour intensive sector that employs 45 mn people in India is second only to the agriculture sector in terms of employment.
- India’s textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy, and is a storehouse and carrier of traditional skills, heritage and culture.
- It can be divided into two segments-
- The unorganised sector is small scale and uses traditional tools and methods. It consists of handloom, handicrafts and sericulture (production of silk).
- The organised sector uses modern machinery and techniques and consists of the spinning, apparel and garments segment.
- It contributes 2.3% to Indian Gross Domestic Product, 7% of Industrial Output, 12% to the export earnings of India and employs more than 21% of total employment.
- India is the 6th largest producer of Technical Textiles with 6% Global Share, largest producer of cotton & jute in the world.
- Technical textiles are functional fabrics that have applications across various industries including automobiles, civil engineering and construction, agriculture, healthcare, industrial safety, personal protection etc.
- India is also the second largest producer of silk in the world and 95% of the world’s hand woven fabric comes from India.
World Youth Skill Day:

Every year, 15th July is observed as the World Youth Skills Day.
- It was designated by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2014.
- Aim:
- To equip young people around the world with essential skills for employment, work, and entrepreneurship.
- To achieve the Incheon Declaration: Education 2030, “which devotes considerable attention to technical and vocational skills development, specifically regarding access to affordable quality technical and vocational education and training (TVET) institutions.’’
- This vision is fully captured by Sustainable Development Goal-4, which aims to “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”.
- To eliminate gender disparity.
- Theme for 2021:
- ‘Reimagining Youth Skills Post-Pandemic’.
State of Youth Employment and Schools during Covid-19:
- According to the estimates of UNESCO, schools were shut down for over 30 weeks in 50% of the countries between March 2020 and May 2021.
- Respondents to a survey of the TVET, which was jointly collected by UNESCO, the ILO and the World Bank, revealed that distance learning was the most common way of imparting skills.
- Youth employment fell 8.7% last year, compared with 3.7% for adults.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Powered Grievance Management Application:
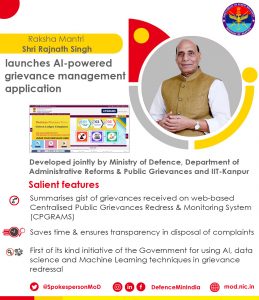
Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh launched an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered grievance management application in New Delhi on July 15, 2021, developed by Ministry of Defence with the help of IIT-Kanpur.
- This is the first AI based system developed to improve grievance redressal in the Government.
- The AI tool developed as part of the initiative has capability to understand the content of the complaint based on the contents therein. As a result, it can identify repeat complaints or spam automatically.
- Based on the meaning of the complaint, it can categorise complaints of different categories.
The Drone Rules, 2021:

Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) has released the updated – The Drone Rules, 2021 for public consultation. The Drone Rules, 2021 will replace the UAS Rules 2021 (released on 12 March 2021).
Key takeaways from the Draft Drone Rules, 2021 include:
- Approvals abolished: unique authorisation number, unique prototype identification number, certificate of conformance, certificate of maintenance, import clearance, etc.
- Number of forms reduced from 25 to 6.
- Fee reduced to nominal levels. No linkage with the size of the drone.
- Safety features like ‘No permission – no take-off’ (NPNT), real-time tracking beacon, geo-fencing etc. to be notified in future. A six-month lead time will be provided for compliance.
- Digital sky platform shall be developed as a business-friendly single-window online system.
- Interactive airspace map with green, yellow, and red zones will be displayed on the digital sky platform. Yellow zone reduced from 45 km to 12 km from the airport perimeter.
- No flight permission required upto 400 feet in green zones and upto 200 feet in the area between 8 and 12 km from the airport perimeter.
- No pilot licence required for micro drones (for non-commercial use), nano drone and for R&D organisations.
- No restriction on drone operations by foreign-owned companies registered in India.
- Coverage of drones under Drone Rules, 2021 increased from 300 kg to 500 kg. This will cover drone taxis also.
- Maximum penalty under Drone Rules, 2021 reduced to INR 1 lakh. This shall, however, not apply to penalties in respect of violation of other laws.
- Drone corridors will be developed for cargo deliveries.
- Drone promotion council to be set up to facilitate a business-friendly regulatory regime.




