Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 26th November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster (APC) :
- Bru Resettlement:
- 33rd PRAGATI meeting.:
- Cyclone Nivar:
- MPLAD scheme:
- Other important current affairs:
1. Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster (APC) :

The Union Minister of Food Processing Industries has attended the Independent Management Advisory Committee (IMAC) meeting to consider the proposals received under the Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster (APC) of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY).
- IMAC approved 7 proposals with a total project cost of Rs. 234.68 crore including grants-in-aid of Rs. 60.87 crore in Meghalaya, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Maharashtra.
- These projects will leverage private investment of Rs. 173.81 crore and are expected to generate employment for 7750 persons.
Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster:
- It was approved in May 2017 under the PMKSY, to incentivise the setting up of APCs in the country.
- Aims: To develop modern infrastructure and common facilities to encourage a group of entrepreneurs to set up food processing units based on cluster approach by linking groups of producers/farmers to the processors and markets.
- These clusters will help in reducing the wastage of the surplus produce and add value to the horticultural/agricultural produce which will result in an increase of income of the farmers and create employment at the local level.
Under the scheme, each APC has two basic components:
- Basic Enabling Infrastructure like roads, water supply, power supply, drainage, etc.
- Core Infrastructure/Common Facilities like warehouses, cold storages, tetra pack, sorting, grading, etc.
Requirements for Setup:
- At least 5 food processing units with a minimum investment of Rs. 25 crore and at least 10 acres of land is required for at least 50 years.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana
- In 2016, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) introduced an umbrella Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters (SAMPADA), which was proposed to be implemented with an allocation of Rs. 6,000 crores for the period of 2016-20.
- In 2017, it was renamed as the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY).
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- Objectives:
- To supplement agriculture.
- To create processing and preservation capacities.
- To modernize and expand existing food processing units with a view to increasing the level of processing.
- To add value leading to the reduction of wastage.
- Seven component schemes under PMKSY:
- Mega Food Parks.
- Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure.
- Infrastructure for APC.
- Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages.
- Creation/Expansion of Food Processing and Preservation Capacities.
- Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure.
- Human Resources and Institutions.
- Under PMKSY, capital subsidy in the form of grants-in-aid ranging from 35% to 75% of the eligible project cost subject to a maximum specified limit is provided to investors under the various schemes for undertaking infrastructure, logistic projects, and setting up of food processing units in the country.
2.Bru Resettlement:

Parts of north Tripura have witnessed violent protests over the proposed resettlement of Bru tribals.
- Bru or Reang is a community indigenous to Northeast India, living mostly in Tripura, Mizoram and Assam.
- In Tripura, they are recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group.
- In Mizoram, they have been targeted by groups that do not consider them indigenous to the state.
- In 1997, following ethnic clashes, nearly 37,000 Brus fled Mamit, Kolasib and Lunglei districts of Mizoram and were accommodated in relief camps in Tripura.
- Since then, 5,000 have returned to Mizoram in eight phases of repatriation, while 32,000 still live in six relief camps in North Tripura.
- In January 2020, a quadrilateral agreement was signed by the Centre, the two state governments and Bru representatives to allow the remaining 32,000 to permanently settle in Tripura.
2020 Agreement:
- After the agreement was made in January 2020, the state has planned 12 resettlement spots across six districts with 300 families each.
- The Centre has announced a special development project with funding of Rs. 600 crore.
- Each resettled family will get an estimated 0.03 acres of land for building a home, Rs. 1.5 lakh as housing assistance, and Rs. 4 lakh as a one-time cash benefit for sustenance, a monthly allowance of Rs. 5,000 and free rations for two years from the date of resettlement.
Reason for the Protest:
- The 2020 agreement led to protests from Bengali and Mizo groups in Tripura.
- They claim that settling thousands of migrants permanently in the Kanchanpur sub-division of the North Tripura district would lead to demographic imbalance, exert pressure on local resources and potentially lead to law and order problems.
- They alleged that 650 Bengali families from around Kanchanpur and 81 Mizo families from Jampui Hill range, who fled due to “atrocities” by Brus, were yet to be resettled two decades on.
Conditions of the Brus:
- They are in fear and uncertainty as they suffer an economic blockade due to these protests.
- They haven’t received foodgrains as per their relief package this month and if the protest continues, their condition will deteriorate further.
3.33rd PRAGATI meeting.:

The Prime Minister (PM) has chaired the 33rd PRAGATI meeting.
- Interaction through PRAGATI is held once every month on Fourth Wednesday, known as PRAGATI Day.
Highlights of the Meeting:
- The PM asked states to develop a state-specific export strategy, and reviewed development projects worth Rs. 1.41 lakh crore spread across 10 states and union territories.
- Grievances related to Covid-19 and to the PM Awas Yojana (Gramin) were also taken up.
- PM SVANidhi, agriculture reforms and development of districts as export hubs were reviewed.
PRAGATI:
- Launched in 2015, PRAGATI is the multimodal platform for Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation involving central and state governments.
- It has been designed by the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) team with the help of the National Informatics Center (NIC).
- It enables the PM to discuss the issues with the concerned central and state officials with full information and latest visuals of the ground-level situation.
- It is a three-tier system (PMO, Union Government Secretaries, and Chief Secretaries of the States).
- Objective:
- Grievance Redressal
- Program Implementation
- Project Monitoring
- The PRAGATI platform uniquely bundles the three latest technologies: Digital data management, video-conferencing, and geo-spatial technology.
- Significance: It promotes cooperative federalism as it brings together the Secretaries of the Government of India and the Chief Secretaries of the States.
- It is a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
- It is an innovative project in e-governance and good governance.
- Concerns: The direct interaction of the PM with the state secretaries without involving the political executives of the states is undermining the state political executive.
- It is also said that this is leading to a concentration of power in the extra-constitutional office of PMO.
4.Cyclone Nivar:
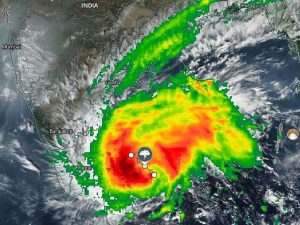
- The tropical cyclone Nivar has made landfall along the Tamil Nadu-Puducherry coast.
- Landfall refers to the phenomenon of a cyclone’s outer wall moving over the coastline and beyond.
- A tropical cyclone is an intense circular storm that originates over warm tropical oceans and is characterized by low atmospheric pressure, high winds, and heavy rain.
- A characteristic feature of tropical cyclones is the eye, a central region of clear skies, warm temperatures, and low atmospheric pressure.
- Storms of this type are called hurricanes in the North Atlantic and eastern Pacific and typhoons in SouthEast Asia and China.
- They are called tropical cyclones in the southwest Pacific and Indian Ocean region and Willy-willies in north-western Australia.
- Storms rotate anticlockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere.
Cyclone Nivar:
- It is the fourth cyclone that has taken shape in the North Indian Ocean region this year. The first three cyclones were Cyclone Gati (made landfall in Somalia in November), Cyclone Amphan (eastern India witnessed it in May), and Cyclone Nisarga (in Maharashtra).
- Nivar will be the second cyclone to hit Tamil Nadu in two years after Cyclone Gaja in 2018.
- The storm has been named Cyclone Nivar, based on the guidelines of the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO). Nivara has been selected from the list of names given by Iran.
- According to WMO guidelines, countries in every region are supposed to give names for cyclones.
- The North Indian Ocean Region covers tropical cyclones formed over Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea.
- The 13 members, which come under the region, are Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Yemen.
- A total of 169 cyclones were named by these countries for this year, with 13 names from each country.
- It has weakened from a very severe cyclonic storm to a severe cyclonic storm with a wind speed of 100-110 km per hour.
5.MPLAD scheme:

Centre within its rights to suspend MPLADS, says Bombay high court:
- The Union government was within its powers to suspend the MPLAD scheme and divert such funds to combat Covid-19.
- Besides, this (Covid-19) is a disaster so the government will have to resort to Disaster Management Act. It is within its powers to invoke the Act.
- The Union government had resorted to Disaster Management Act to suspend the member of Parliament local area development (MPLAD) scheme in April this year.
- A petition was filed against this in the Court.
About MPLAD scheme:
- Launched in December 1993.
- Seeks to provide a mechanism for the Members of Parliament to recommend works of developmental nature for creation of durable community assets and for provision of basic facilities including community infrastructure, based on locally felt needs.
- The MPLADS is a Plan Scheme fully funded by Government of India.
- The annual MPLADS fund entitlement per MP constituency is Rs. 5 crore.
- MPs are to recommend every year, works costing at least 15 per cent of the MPLADS entitlement for the year for areas inhabited by Scheduled Caste population and 7.5 per cent for areas inhabited by S.T. population.
- In order to encourage trusts and societies for the betterment of tribal people, a ceiling of Rs. 75 lakh is stipulated for building assets by trusts and societies subject to conditions prescribed in the scheme guidelines.
- Release of Funds: Funds are released in the form of grants-in-aid directly to the district authorities.
- The funds released under the scheme are non-lapsable.
- The liability of funds not released in a particular year is carried forward to the subsequent years, subject to eligibility.
- The MPs have a recommendatory role under the scheme.
- The district authority is empowered to examine the eligibility of works, sanction funds and select the implementing agencies, prioritise works, supervise overall execution, and monitor the scheme at the ground level.
- At least 10% of the projects under implementation in the district are to be inspected every year by the district authority.
Other important current affairs:
1.To drive infrastructure creation in the country, the Union Cabinet on Wednesday approved the infusion of ₹6,000 crore equity in the National Infrastructure Investment Fund’s (NIIF’s) debt platform in the next two years.
- Out of the proposed amount, ₹2,000 crores will be infused in the current financial year.
- NIIF Debt Platform is sponsored by National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), comprising of Aseem Infrastructure Finance Limited (AIFL) and NIIF Infrastructure Finance Limited (NIIF-IFL).
- The NIIF Strategic Opportunities Fund has set up a Debt Platform comprising an NBFC Infra Debt Fund and an NBFC Infra Finance Company.
- NIIF through its Strategic Opportunities Fund (‘NIIF SOF’) owns a majority position in both the companies and has already invested ~ Rs.1,899 crore across the Platform.
- The Strategic Opportunities Fund (SOF fund) through which the NIIF investment has been made will continue to support the two companies apart from investing in other suitable investment opportunities.
2.Union Cabinet on Wednesday approved ₹2,480 crore foreign direct investment (FDI) in ATC Telecom Infra Pvt Ltd. ATC Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd is looking to acquire 12.32% stake in ATC Telecom Infra Pvt Ltd through the FDI route.
- ATC Telecom Infrastructure Private Limited is engaged in the business of providing telecom infrastructure services to telecom operators.
- Founded in 2006, ATC Asia Pacific Pte Ltd’s business includes holding or owning securities of companies other than banks.
- FDI up to 100% is allowed in Telecom Services Sector wherein 49% under automatic route and beyond 49% through government route subject to observance of licensing and security conditions by the licensee as well as investors as notified by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) from time to time.
3.Two American MQ9B Sea Guardian unarmed drones have been inducted by the Indian Navy.
- The drones would be on lease with India for one year.
- It is the maritime variant of the Predator MQ9 Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV).
- It has a maximum endurance of 40 hours and a maximum flying altitude of 40,000 feet.
- It has a 3600 maritime surveillance radar and an optional multimode maritime surface search radar.
- It can be used in operations such as Anti-Surface Warfare, Anti-Submarine Warfare, Humanitarian Assistance/Disaster Relief, Search and Rescue, Law Enforcement (Drug Trafficking, Illegal Immigration and Piracy), etc.
5.Samvidhan Diwas on 26th November:
- The nation is celebrating the Constitution Day, also known as Samvidhan Diwas on 26th November to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India.
- The Constitution Day is observed annually on November 26 to mark the anniversary of the adoption of Indian Constitution on November 26, 1949 by the Constituent Assembly of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950.
- The Government of India declared 26 November as Constitution Day in 2015 by a gazette notification. The year of 2015 was the 125th birth anniversary of Ambedkar, who played a key role in the drafting of the constitution. Previously this day was celebrated as National Law Day.
6.The Uttar Pradesh government has extended the Essential Services Maintenance Act in the State, banning strikes in all departments and corporations under it for a period of another six months.
- The Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA) is an act of Parliament of India.
- Objective: It was established to ensure the delivery of certain services, which if obstructed would affect the normal life of the people.
- These include services like public transport (bus services), health services (doctors and hospitals).
- ESMA gives police right to arrest without a warrant anybody violating the Act’s provisions.
- The ESMA is a law made by the Parliament of India under List No. 33 in Concurrent List of 7th Schedule of Constitution of India.
7.Mega Food Park inaugurated in Punjab.
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries is implementing Mega Food Park Scheme in the country since 2008.
- It aims at providing a mechanism to link agricultural production to the market by bringing together farmers, processors and retailers.
- Significance: These food parks give a major boost to the food processing sector by adding value and reducing food wastage at each stage of the supply chain with particular focus on perishables.
- Funding: A maximum grant of Rs 50 crore is given for setting up a MFP, in minimum 50 acres of contiguous land with only 50% contribution to the total project cost.
8.Bhutan has announced that it had established diplomatic relations with Germany, increasing the restricted number of capitals that Thimphu has formal ties with to 53 states and the EU.
- This is the kingdom’s first diplomatic foray in seven years.
- Since 1949, when Bhutan first signed a friendship agreement with India, which kept the two countries closely engaged on all foreign policy issues, Bhutan has been historically cautious about establishing ties with other countries.
- Until 2007, when Bhutan conducted its first election, it had formal relations with just 22 countries, most donor countries such as Japan, Australia, and several Nordic countries. It also made a firm decision not to open ties with any of the permanent five members of the UN Security Council, despite many requests from them and in particular from the U.S. and China.
- After the election of Prime Minister Jigme Thinley in 2008, however, the Bhutanese government rapidly increased its diplomatic forays, signing agreements with 31 countries in five years.




