Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 28th December 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- The giant Antarctic iceberg A68a:
- Governor’s Role in Calling an Assembly Session:
- Inner-Line Permit in Manipur:
- Monpa Handmade Paper of Arunachal Pradesh:
- Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY SEHAT:
- 1761 Battle of Panipat:
- Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate vaccine:
- Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor:
- Other important current affairs
1.The giant Antarctic iceberg A68a:

The giant Antarctic iceberg A68a has become a cause for concern for South Georgia Island.
- The giant iceberg A68, the biggest block of free-floating ice from Antarctica with an area of about 5,800 sq. km, has been drifting in the Atlantic Ocean since 2017.
- This year, due to an ocean current, the iceberg was propelled into the South Atlantic Ocean and since then it has been drifting towards the remote sub-Antarctic island of South Georgia, which is a British Overseas Territory (BOT).
- This has prompted fears about the impact the iceberg could have on the island’s abundant wildlife.
- Icebergs travel with ocean currents and either get caught up in shallow waters or ground themselves.
- Recently, US National Ice Center (USNIC) confirmed that two new icebergs calved from A68a and were large enough to be named and tracked. They are called A68E and A68F.
- South Georgia is an island in the southern Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). The main settlement is Grytviken.
- The US National Ice Center (USNIC) is responsible for naming icebergs, which are named according to the Antarctic quadrant in which they are spotted.
2.Governor’s Role in Calling an Assembly Session:

Kerala Governor has turned down a request by Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan to summon a special sitting of the Assembly to debate the new three central farm laws. This raises questions on the role of a Governor and the contours of the powers he or she has under the Constitution.
- According to Article 174 of the Constitution “The Governor shall from time to time summon the House or each House of the Legislature of the State to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit” .
- The provision also puts on the Governor the responsibility of ensuring that the House is summoned at least once every six months.
- Although it is the Governor’s prerogative to summon the House, according to Article 163, the Governor is required to act on the “aid and advice” of the Cabinet.
- So when the Governor summons the House under Article 174, this is not of his or her own will but on the aid and advice of the Cabinet.
- There are a few instances where the Governor can summon the House despite the refusal of the Chief Minister who heads the Cabinet.
- When the Chief Minister appears to have lost the majority and the legislative members of the House propose a no-confidence motion against the Chief Minister, then the Governor can decide on his or her own on summoning the House.
- But the actions of the Governor, when using his discretionary powers can be challenged in court.
- A number of rulings by the Supreme Court has settled the position that the Governor cannot refuse the request of a Cabinet that enjoys majority in the House unless it is patently unconstitutional.
3.Inner-Line Permit in Manipur:

The Union Home Minister has highlighted the importance of Inner-Line Permit (ILP) system in Manipur while inaugurating several development projects in Manipur.
- The projects include Thoubal Multipurpose Project (Thoubal Dam), Integrated Command and Control Center at Imphal, etc.
- Thoubal multipurpose project was first considered by the Planning Commission in 1980 and the original cost of the project was Rs. 47.25 crores.
- A scheme for it was launched in 2004 but nothing happened till 2014 and the project remained on paper.
- It is located on river Thoubal, a tributary of Manipur river and will irrigate 35,104 hectares.
- ILP was a long-standing demand of the people of Manipur and denying it would have been an injustice to the indigenous people.
- Hence, Manipur, along with Dimapur district of Nagaland, was brought under the purview of the ILP System in December 2019.
- Dimapur was the only place in Nagaland which was not under the ILP system because the district is a commercial hub and has a mixed population (often referred to as ‘Mini India’).
- Pressure groups in the northeast view this permit as a shield against the entry of illegal immigrants.
Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur and Mizoram were exempted from the provisions of the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) 2019 due to the ILP. - The provisions on citizenship for illegal migrants would not apply to tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram or Tripura as included in the Sixth Schedule to the Constitution and the area covered under the ILP system.
- In December 2019, the Meghalaya Assembly adopted a resolution for implementing the ILP regime in the state and urged the centre to include it in the ILP system.
Inner Line Permit System:
- Implemented under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR) 1873, the ILP is an official travel document that allows inward travel of an Indian citizen into a protected/restricted area for a limited period.
- This Act was enacted during the British era to protect the Crown’s own commercial interests by preventing ‘British subjects’ (Indians) from trading within these regions.
- In 1950, the Indian government replaced ‘British subjects’ with ‘Citizen of India’.
- An imaginary line known as the inner-line was created to divide between the two communities so that neither party could go beyond the line without a permit from the appropriate authorities.
- Under Section 2 of the Regulation of 1873, the ILP was only applicable to the three North-Eastern States viz. Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
- On 11th December 2020, the President signed the order extending ILP to Manipur, which became the fourth state where the ILP regime is applicable.
- It is a special permit obligatorily required by “outsiders” from other regions of the country to enter the notified states.
- It is issued by the concerned State Government and can be issued for travel purposes solely.
- Foreigners need a Protected Area Permit (PAP) to visit tourist places which are different from ILPs needed by domestic tourists.
- Under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order 1958, all areas falling between the ‘Inner Line’, as defined in the said order, and the International Border of the State have been declared as a Protected Area.
- A foreign national is normally not allowed to visit a Protected/Restricted Area unless it is established to the satisfaction of the Government that there are extraordinary reasons to justify such a visit.
4.Monpa Handmade Paper of Arunachal Pradesh:

The 1000-year old heritage art – the Monpa Handmade Paper of Arunachal Pradesh – which was driven to extinction, has come to life once again, with the committed efforts of Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC).
- The art of making Monpa handmade paper originated over 1000 years ago. Gradually the art became an integral part of local custom and culture in Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Once produced in every household in Tawang, this handmade paper was a major source of livelihood for the locals.
- The fine-textured handmade paper, which is called Mon Shugu in the local dialect, is integral to the vibrant culture of the local tribes in Tawang.
- The paper has great historic and religious significance as it is the paper used for writing Buddhist scriptures and hymns in monasteries.
- The Monpa handmade paper, will be made from the bark of a local tree called Shugu Sheng, which has medicinal values too.
- However, the handmade paper industry almost disappeared in the last 100 years; prompting KVIC to plan the revival of this ancient art. KVIC recently commissioned a Monpa handmade paper making unit in Tawang which aims at reviving the art.
5.Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY SEHAT:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY SEHAT to extend coverage to all residents of Jammu & Kashmir.
AB-PMJAY SEHAT Scheme:
- The Scheme provides free of cost insurance cover. It provides financial cover upto Rs. 5 lakh per family on a floater basis to all residents of the UT of J&K.
- Floater basis, means that it can be used by one or all members of the family. The whole family is insured under one plan.
- The scheme would work in convergence with Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY).
Benefits:
- Full coverage to residents of J&K:
- At present, about 6 lakh families of the UT are getting the benefit of the Ayushman Bharat Scheme. After the health plan, all 21 lakh families will get the same benefit.
- Portability of treatment:
- Treatment will not be limited to government and private hospitals in Jammu and Kashmir only. Rather, various hospitals are connected under this scheme in the country.
- The hospitals empanelled under PM-AY scheme shall provide services under this scheme as well.
- Universal Health Coverage:
- The scheme will ensure Universal Health Coverage and focus on providing financial risk protection and ensuring quality and affordable essential health services to all individuals and communities.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC) includes the full spectrum of essential, quality health services, from health promotion to prevention, treatment, rehabilitation, and palliative care.
- UHC enables everyone to access the services, protecting people from the financial consequences of paying for health services out of their own pockets and reducing the risk that people will be pushed to poverty.
Ayushman Bharat PMJAY Yojana:
- The PMJAY, world’s largest health insurance/assurance scheme fully financed by the government, provides a cover of Rs. 5,00,000 per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation across public and private empanelled hospitals in India.
- Pre-hospitalisation and Post-hospitalisation expenses such as diagnostics and medicines are also included in the scheme.
6.1761 Battle of Panipat:

Manoj Dani, an independent U.S.-based researcher of art history, has assimilated rare paintings pertaining to the battle and its key players in a work titled Battle of Panipat: In Light of Rediscovered Paintings.
- The book contains rare paintings from the Bibliothèque nationale de France (BnF), the British Library, the National Museum in Delhi, Bonhams of U.K. and the Pune-based Bharat Itihas Sanshodak Mandal (BISM).
- There are a myriad of myths surrounding Panipat. Far from a well-established narrative of this pivotal event, we have only scratched the surface of this crucial episode, and that whatever we know is only from a handful or selected sources of dubious veracity.
- The paintings depict key players such as Ahmad Shah Abdali, Sadashivrao Bhau, Najib Khan Rohilla, Dattaji Shinde, Vishwas Rao, Suraj Mal Jat and other Maratha, Afghan, Rohilla and Jat chiefs.
- The book deftly weaves analysis from original archival sources, casting a revealing light on the shifting alliances of 18th century Indian politics.
Background:
- Two other major battles had been fought on the Panipat plains:
- The First Battle of Panipat, in 1526, laid the foundation of the Mughal Empire in India after its first ruler, Babur, ended the Delhi Sultanate, which at the time was led by the Lodi dynasty.
- The Second Battle of Panipat, in 1556, cemented Mughal rule when Akbar fought off a threat from the king Hemu ‘Vikramaditya’.
About the Third Battle of Panipat, fought in 1761:
- Fought between Maratha forces and invading armies of Afghan general Ahmed Shah Abdali of Durrani Empire in 1761.
- Abdali was supported by two Indian allies— the Rohillas Najib-ud-daulah, Afghans of the Doab region and Shuja-ud-Daula- the Nawab of Awadh.
7.Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate vaccine:
The first indigenous vaccine against pneumonia, developed by the Serum Institute of India (SII), will be launched.
- In July, India’s drug regulator had granted market approval for the Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate vaccine.
- Infectious agents may include bacteria, viruses and fungi.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in children, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) is the second most common cause of bacterial pneumonia.
- The respiratory syncytial virus is the most common viral cause of pneumonia.
- Air sacs in an infected individual’s lungs (alveoli) become inflamed due to deposits of fluid and pus, making it painful and difficult for them to breathe.
About pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23):
- It protects against pneumococcal infections.
- PPSV23 protects against 23 types of pneumococcal bacteria.
8.Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor:
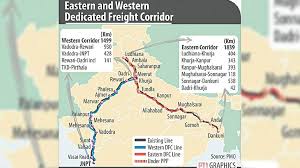
PM to inaugurate the New Bhaupur- New Khurja section and the Operation Control Centre of Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor.
About the eastern corridor:
- Length: 1856 km.
- Consists of two distinct segments: an electrified double-track segment & an electrified single-track segment.
- Starts from Sahnewal near Ludhiana (Punjab) and will pass through the states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand to terminate at Dankuni in West Bengal.
- Constructed by Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited (DFCCIL), that has been set up as a special purpose vehicle to build and operate Dedicated Freight Corridors.
- Eastern Corridor is projected to cater to a number of traffic streams-coal for the power plants in the northern region of U.P., Delhi, Haryana, Punjab and parts of Rajasthan from the Eastern coal fields, finished steel, food grains, cement, fertilizers, lime stone from Rajasthan to steel plants in the east and general goods.
Other important current affairs:
1.A team of scientists has created a nanomicelle that can be used for effective drug delivery to treat various cancers including breast, colon and lung cancer.
- Nanotechnology or nanotech is the technology that involves the manipulation of matter on atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scales. This includes particles of a scale of 1 to 100 nanometers.
- Nanomicelles are formed when amphiphilic molecules assemble themselves to create a globular structure that is only around 5 to 100nm in diameter.
- Different agents are used to create nanomicelles, however, they are usually made through surfactant molecules that may be non-ionic, ionic, and cationic detergents. Some nanomicelles may also be developed from a mixture of lipids and detergents.
- Use in Drug Delivery:
- They are amphiphilic, i.e. have a hydrophilic outer shell and a hydrophobic interior. This dual property makes them a perfect carrier for delivering drug molecules.
- The hydrophilic shell makes the micelle water soluble that allows for intravenous delivery while the hydrophobic core carries a payload of drug for therapy.
- Once injected intravenously, these nanomicelles can easily escape the circulation and enter the tumours where the blood vessels are found to be leaky. These leaky blood vessels are absent in the healthy organs.
2.The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) is going to launch ‘Main Bhi Digital (me too digital)’ drive for the street vendors to enable them to accept and make payments digitally.
- The drive has been encouraged by the success of the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PMSVANidhi) scheme, launched in the wake of the Covid-19 lockdown, to provide vendors microcredit.
- Main Bhi Digital Drive: As part of the new drive, between 4th January to 22nd January 2021, over 10 lakh street vendors across the country who have availed of the Rs. 10,000 loan will be trained in using digital payments.
- The vendors would be able to not just receive payments digitally but also pay for material they procure from sellers using unique QR codes.
- The mobile phones of the vendors will be equipped with the software needed for the transactions, and training provided to them on safe and secure payments.
3.Eminent dance scholar and critic Sunil Kothari passed away at the age of 87.
- He was conferred with the fourth highest civilian award, Padma Shri, in 2001.
- He authored 20 books on Indian classical dances and wrote extensively on Bharatanatyam, Kathak and Manipuri dance forms.
- His scholarly work, “Sattriya: Classical Dance of Assam”, helped in creating a better understanding of the dance form in the national and global circuit.
- His other notable contributions include New Directions in Indian Dance and Kuchipudi Indian Classical Dance Art.
- He was elected as a Fellow of Sangeet Natak Akademi.
4.USA’s plan to have the first nuclear reactor on the moon by the end of 2026 — for which the US Department of Energy in collaboration with Nasa intends to solicit industry design proposals in early 2021 — got an impetus with a recent White House directive.
- On December 16, outgoing President Donald Trump, issued the “National Strategy for Space Nuclear Power and Propulsion”.
- Under it, he asked Nasa to “initiate fission surface power project for lunar surface demonstration by 2027 with scalability to a power range of 40 kilowatt-electric and higher to support a sustained lunar presence and exploration of Mars”.
- NASA aims to establish a flight hardware system that is ready for integrating with the lunar lander by 2026-end. The fission power system — as the nuclear reactor is called — will benefit future robotic and human exploration missions to the moon as well as Mars.
- The availability of safe, efficient, and readily available power is critical to these missions and a fission surface power system meets those requirements.
- The fission surface power system will be fully manufactured and assembled on earth and integrated on a lander as a payload.
- The system — consisting of four major subsystems including a nuclear reactor, an electric power conversion unit, heat rejection array, and power management and distribution subsystem — will be designed to operate for up to 10 years.
5.Union Home Minister Amit Shah launched several development projects in Manipur.
- He inaugurated the e-office and Thoubal Multipurpose Project (Thoubal Dam) in Imphal through virtual mode which will irrigate 35,104 hectares.
- He also laid the foundation stone of projects, including the Churachandpur Medical College, IT-SEZ at Mantripukhri, Manipur Bhawan in New Delhi and the Integrated Command and Control Center at Imphal.
- Shri Shah said earlier projects were abandoned after performing ground-breaking ceremonies and work is now being done under the leadership of Modi ji, to inaugurate all projects whose foundation stones were laid by previous governments.
6.To avoid an adverse reaction to the cold wave, the IMD shared a list of recommendations, one of which was avoiding alcohol.
- According to the IMD, severe cold wave conditions are likely in parts of Haryana, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi and Rajasthan from December 29 onwards.
- The maximum temperature is also forecast to fall by 3 to 5 degrees Celsius after December 28.
- Alcohol can decrease the core temperature of the body and increase the risk of hypothermia during cold exposure.
- A retrospective study in 2004 showed that alcohol consumption is associated with 68 per cent of accidental hypothermia cases.
- Alcohol is a vasodilator, which means that it causes blood vessels to relax and dilate or open.
- So after consuming alcohol, the volume of blood brought to the skin’s surface increases, making you feel warmer as a result.
- This is also what causes an intoxicated person to look flushed.
- As the body begins to believe that it is warm, you also start to sweat — a reaction that automatically reduces overall body temperature.
- Drinking copious amounts of alcohol may affect your bodies ability to detect the cold properly, which is in place to protect you from frostbite and hypothermia.
- However, experts say drinking moderately in temperate environments does not significantly affect the core temperature of the body.
7.Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has introduced Rule 86B in Goods and Services Tax (GST) rules which restricts use of input tax credit (ITC) for discharging GST liability to 99 per cent.
- As per the new rule, Businesses with monthly turnover of over ₹50 lakh will have to mandatorily pay at least 1 per cent of their GST liability in cash.
- Exceptions under the new rule:
- This restriction will not apply where the managing director or any partner have paid more than ₹1 lakh as income tax or the registered person has received a refund amount of more than ₹1 lakh in the preceding financial year on account of unutilised input tax credit.
- The idea remains to prevent misutilisation of credit by businesses taking fake credits.
- There are fears that the mandatory cash payment would adversely affect small businesses, increase their working capital requirement and make GST a more complex indirect tax system.




