Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:30th April 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Annual Special 301 Report
- Supreme Court of India gave its judgment on the admission criteria of minority institutions.:
- National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP):
- Impact of China’s dams on the Mekong River
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):
- Aero India
- other important current affairs.
1. Annual Special 301 Report.:

India continues to be on the ‘Priority Watch List’ of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) for lack of adequate intellectual property (IP) rights protection and enforcement, the USTR said in its Annual Special 301 Report.
- India remained one of the most challenging economies for IP enforcement and protection. While India made “meaningful progress” to enhance IP protection and enforcement in some areas over the past year, it did not resolve recent and long-standing challenges and created new ones.
- These long-standing concerns were about:
- innovators being able to receive, maintain and enforce patents particularly in the pharmaceutical sector;
- concerns over copyright laws not incentivising the creation and commercialisation of content; and
- an outdated trade secrets framework.
- The report also mentioned high customs duties on medical devices and Information and Communications Technology.
Special 301 Report:
- The Special 301 Report is prepared annually by the Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) that identifies trade barriers to United States companies and products due to the intellectual property laws, such as copyright, patents, and trademarks, in other countries.
- The Special 301 Report is published pursuant to Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974 as amended by Section 1303 of the Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988.
- The Special 301 Report was first published in 1989.
2. Supreme Court of India gave its judgment on the admission criteria of minority institutions.:

- Recently, the Supreme Court of India gave its judgement on the admission criteria of minority institutions.
- It held that the National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET) is mandatory for admission to all the medical colleges and the right of minority institutions is not absolute and is amenable to regulation.
- Few colleges challenged the notifications issued by the Medical Council of India (MCI) and the Dental Council of India (DCI) under Sections 10D of the Indian Medical Council Act of 1956 and the Dentists Act of 1948 for uniform entrance examinations.
- The management of such minority-run medical institutions held that uniformly bringing them under the ambit of NEET would be a violation of their fundamental right to occupation, trade and business [Article 19(1)(g)] and would violate their fundamental rights of religious freedom and to manage their religious affairs (Article 25-28) and to administer their institutions (Article 30).
- Few petitioners claimed that rules notified by Andhra Pradesh government are violative of rights of minority educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the Constitution.
Highlights of the Judgement:
- The SC held that the fundamental and religious rights of minorities and rights available under Article 30 are not violated by provisions carved out in Section 10D of the MCI and Dentists Act.
- The right to freedom of trade or business is not absolute.
- It is subject to reasonable restriction in the interest of the students’ community to promote merit, recognition of excellence, and to curb the malpractices.
- A uniform entrance test qualifies the test of proportionality and is reasonable.
- The NEET is mandatory for admission to medical colleges run by religious and linguistic minority communities and it would apply for both aided and unaided medical colleges administered by minorities.
- NEET was started to check several malpractices in the medical education, to prevent capitation fee by admitting students which are lower in merit and to prevent exploitation, profiteering, and commercialisation of education.
- Uniform entrance exams will ensure improvement in future public health by encouraging merit which will further enhance the Directive Principles enshrined in the Constitution.
- The SC also upheld rules framed by the Andhra Pradesh government making Secondary School Certificate (SSC)/Transfer Certificate (TC) the basis for a candidate’s claim of minority status for admission to B.Ed courses.
- The rules also require minority institutions to allot vacant seats under management quota to non-minority students on merit.
3.National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP):

The Task Force on National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) submitted its Final Report on NIP for FY 2019-25 to the Union Minister for Finance.
- The Final Report of NIP Task Force is projecting total infrastructure investment of Rs 111 lakh crore during the period FY 2020-25.
- Out of Rs. 111 lakh crore,
- projects worth Rs 44 lakh crore (40% of NIP) are under implementation,
- projects worth Rs 33 lakh crore (30%) are at the conceptual stage,
- projects worth Rs 22 lakh crore (20%) are under development.
- Information regarding the project stage is unavailable for projects worth Rs 11 lakh crore (10%).
- Sectors such as energy (24%), roads (18%), urban (17%) and railways (12%) amount to around 71% of the projected infrastructure investments in India.
- The Centre (39%) and States (40%) are expected to have an almost equal share in implementing the NIP in India, followed by the private sector (21%).
- The Task Force has recommended that three Committees be setup:
- a Committee to monitor NIP progress and eliminate delays;
- a Steering Committee in each Infrastructure ministry level for following up implementation; and
- a Steering Committee in DEA for raising financial resources for the NIP.
- The NIP project database would be hosted on India Investment Grid (IIG) shortly to provide visibility to the NIP and help in its financing with prospective investors; domestic and foreign, able to access updated project-level information.
4.Impact of China’s dams on the Mekong River:
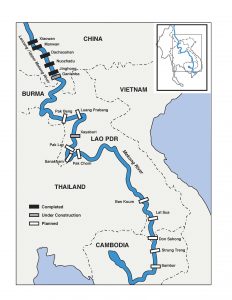
Recently, a US-funded study has highlighted the possible impact of China’s dams on the Mekong River (known as the Lancang River in China) and countries downstream.
- The study was published by the Sustainable Infrastructure Partnership in Bangkok and the Lower Mekong Initiative.
- The Lower Mekong Initiative is a US partnership with all the downstream countries of Mekong besides Myanmar.
- The Mekong flows from China to Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam.
Findings of the Study:
- It also raised questions on other Chinese dams on rivers which originate in China like the Brahmaputra and their similar impact on neighbouring countries like India.
- China’s southwestern Yunnan province had above-average rainfall from May to October 2019.
- However, there was a severe lack of water in the lower Mekong in 2019 in comparison to 1992, based on satellite data.
- The Mekong River Commission has emphasised on the need for more scientific evidence to establish whether dams caused a 2019 drought.
- The Mekong River Commission comprises Cambodia, Laos, Thailand and Vietnam,
- According to the study, six dams built since the commissioning of the Nuozhadu dam in 2012 had altered the natural flow of the river.
- China’s Stand: It has called the study groundless and highlighted the drought faced by Yunnan because Lancang only accounts for 13.5% of Mekong’s flows.
- China has maintained that the dams, it is building, are run of the river dams which store water for power generation.
- India’s Stand: According to Indian experts, the study is not conclusive because it only considers the water flowing into the lower basin at one station in Thailand.
- It did not consider other dams and water-use along the course of the river.
- The lower basin is not entirely dependent on flows from China, but also receives water from tributaries in all other countries it flows in, which the study did not account for.
5.Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) region is expected to post a 2.7 per cent economic decline in 2020 due to the impact of Covid-19.
- This will be the most significant fall since the near-zero growth rate logged in 2009 during the global financial crisis.
- The region’s unemployment rate is projected to rise to 5.4 per cent in 2020 from 3.8 per cent in 2019, or an additional 23.5 million workers being unemployed in 2020.
- An economic rebound is a forecast for 2021, with the anticipated growth of 6.3 per cent, higher than the projected global economic growth of 5.8 per cent.
- This rebound, however, depends on the effectiveness of containment mechanisms to avoid a second wave of the Covid-19 pandemic as well as measures to stimulate the economy.
APEC:
- The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to leverage the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific.
- Aim: to create greater prosperity for the people of the region by promoting balanced, inclusive, sustainable, innovative and secure growth and by accelerating regional economic integration.
6.Aero India:

Recently, the Ministry of Defence has announced that the 13th edition of Aero India will be held from February 3 to 7, 2021 at Air Force Station Yelahanka (Karnataka).
- Aero India is a biennial international military and civil airshow.
- It is a premier event that draws international and Indian military and civil aircraft makers, their support industries, military brass and government dignitaries, and business visitors.
- The Yelahanka air base, about 30 km from the city centre Bengaluru has been hosting the air show in February since it was started in 1996.
- The 2021 Aero India will be organised by the Defence Exhibition Organisation, Ministry of Defence.
In 2019 it was organised by Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL).
Defence Exhibition Organisation
- It is an autonomous organisation of the Indian Government established in 1981.
- The organisation was established to promote the export potential of the Indian defence industry.
- The agency is responsible for organising international exhibitions such as DEFEXPO and Indian participation at overseas exhibitions.
Other important current affairs:
1. Recently, the International Labour Organization (ILO) has warned that nearly half of the entire global workforce is in immediate danger of having their livelihoods destroyed by the coronavirus pandemic.
- Informal workers at risk: Due to Covid-19 lockdown, three-quarters of workers (some 1.6 billion people) engaged in the informal economy have suffered massive damage to their capacity to earn a living.
- Further, without alternative income, these workers and their families would have no means to survive.
- The global workforce is 3.3 billion people, of which more than two billion people work in the informal economy.
- Hard-hit Sectors: The worst-affected sectors would be accommodation and food services, manufacturing, wholesale and retail trade, and real estate and business activities.
2. India has appointed diplomat T S Tirumurti, currently serving as Secretary in the Ministry of External Affairs, as its Permanent Representative to the United Nations.
- Permanent Missions to the United Nations: According to Article 1 (7) of the Vienna Convention on the Representation of States in their Relations with International Organizations of a Universal Character, a “Permanent Mission” is a: “ mission of permanent character, representing the State, sent by a State member of an international organization to the Organization”.
- The Permanent Mission is the diplomatic mission that every member state deputies to the United Nations.
- It is headed by a Permanent Representative, who is also referred to as the “UN ambassador”
3. Doctors have picked up a slight rise in the number of children of all ages needing intensive care treatment for a condition called “multi-system inflammatory state”.
- The rise has happened over the past three weeks in London and elsewhere in the UK.
- The multi-system inflammatory state is a severe immune response that can affect the body in multiple ways, most importantly by making the blood vessels leaky, a condition called Kawasaki disease.
- This leads to low blood pressure and a build-up of fluid in the lungs and organs.
- It is extremely serious. Patients need urgent intensive care to support the heart, lungs and sometimes other organs such as the kidneys.
4..International Jazz Day 2020:
- International Jazz Day 2020 is being celebrated on April 30
- International Jazz Day is an International Day declared by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization in 2011 “to highlight jazz and its diplomatic role of uniting people in all corners of the globe.”
- It is celebrated annually on April 30.
- The idea came from jazz pianist and UNESCO Goodwill Ambassador Herbie Hancock. Jazz Day is chaired by Hancock and the UNESCO Director-General.
- The celebration is recognized on the calendars of both UNESCO and the United Nations.
- Jazz is a music genre that originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the African-American communities of New Orleans, United States. Jazz is seen by many as “America’s classical music” and is hailed as “one of America’s original art forms”.




