3D-Printed Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine : NASA
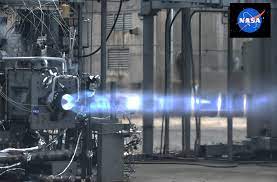
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, has achieved a significant milestone by successfully testing a novel 3D-printed Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE).
- The 251-second burn marks a significant achievement, showcasing the RDRE’s capability for extended propulsion needs.
- The RDRE is 3D-printed, demonstrating NASA’s advancements in additive manufacturing for cutting-edge propulsion systems.
- The test is a result of collaboration between NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, In Space LLC, and Purdue University.
- The partnerships aim to push the boundaries of propulsion technology.
- RDRE has the ability to enable a significant leap in design efficiency.
- The technology represents a step closer to creating lightweight propulsion systems that can send more mass and payload further into deep space, aligning with NASA’s Moon to Mars vision.




