Scabies : Infectious Skin Disease
Malawi has seen a resurgence of the infectious skin disease scabies in an outbreak that is being linked to the climate crisis.
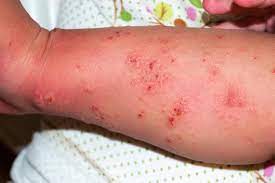
- Scabies is a parasitic infestation caused by a mite known as Sarcoptes scabiei.
- This causes an itchy rash to form on the skin.
- Untreated, these microscopic mites can live on the skin for months.
- They reproduce on the surface of the skin and then burrow into it to lay eggs.
- Scabies is often found in the skin folds. But scabies can appear on many parts of the body.
- It is contagious and can spread quickly from person-to-person through close skin contact (e.g. living in the same residence) with an infested individual.
- Symptoms: Scabies symptoms include
- severe itch, often worse at night;
- itchy lines (linear burrows) and bumps (papules) on the fingers, wrists, arms, legs, and belt area;
- larger rash in infants and small children, including on the palms, soles of the feet, ankles, and scalp.
- A more severe type of scabies, called crusted scabies, makes the skin crusty and scaly and affects large areas of the body.
- Treatment: Scabies is easily treated. Medicated skin creams or pills kill the mites that cause scabies and their eggs. However, the itching may not stop for many weeks after treatment.




