First Direct Detection Of Dark Energy:
An international team of researchers made the first direct detection of dark energy. The experiment named XENON1T, is the world’s most sensitive dark matter experiment and was operated deep underground at the INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Italy.
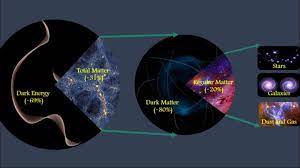
- Dark energy is the mysterious form of energy that makes up about 68% of the universe, and has intrigued physicists and astronomers for decades.
About the Experiment:
- The XENON1T is a dark matter research project, operated at the Italian Gran Sasso National Laboratory.
- It is a deep underground research facility featuring increasingly ambitious experiments aiming to detect dark matter particles.
- The experiments aim to detect particles in the form of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) by looking for rare interactions via nuclear recoils in a liquid xenon target chamber.
Other Dark Matter and Energy Experiments:
- LUX-Zeplin – a next generation dark matter experiment located at the Sanford Underground Research Facility, US.
- PandaX-xT – project at China Jinping Underground Laboratory.
Dark Matter And Dark Energy:
- While dark matter attracts and holds galaxies together, dark energy repels and causes the expansion of our universe.
- Despite both components being invisible, a lot more is known about dark matter, since its existence was suggested as early as the 1920s, while dark energy wasn’t discovered until 1998.
About Dark Energy:
- The Big Bang occurred nearly 15 billion years ago and expanded. Earlier, astronomers believed that eventually the expansion of the Universe will slow down because of gravity and it will recollapse.
- However, data from the Hubble Telescope suggested that the Universe’s expansion is accelerating.
- The astronomers theorize that the faster expansion rate is due to a mysterious, dark force or energy that is pulling galaxies apart.




