Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 15th July 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- PRAGYATA:
- Kazi 106F:
- Tatya Tope
- Sree Padmanabha Swamy Temple in Thiruvananthapuram.
- .Nagorno-Karabakh region in the South Caucasus
- .Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019:
- Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA):
- Other important current affairs
1.PRAGYATA:

The Union HRD Ministry has announced PRAGYATA guidelines for online classes operationalized by schools amid the COVID pandemic.
- Recently, the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) has released guidelines on digital education titled ‘PRAGYATA’.
- The guidelines have been prepared by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
- These are only advisory in nature and state governments can formulate their own rules, based on local needs.
- The guidelines include eight steps of online/digital learning i.e. Plan- Review- Arrange- Guide- Yak (talk)- Assign- Track- Appreciate.
Digital Access:
- Over 25 crore students across the country have been out of school since mid-March 2020. (owing to Covid-19 pandemic).
- The guidelines acknowledge that these students live in households which fall into different categories:
- Those who have computers or smartphones with 4G internet access.
- Those with smartphones but limited or no internet access.
- Those with television with cable or DTH.
- Those with a radio set or a basic mobile phone with FM radio.
- And those with no communication devices at all.
- It emphasized the aim of digital classrooms is not to try and recreate Face-to-Face (F2F) classrooms over the internet.
- It advises schools to first survey the digital infrastructure available with teachers as well as students, the levels of parental involvement before making decisions about the mode of teaching.
- Therefore, schools must also make arrangements to reach students who do not have access to any digital infrastructure at home.
Duration:
- For kindergarten, nursery and pre-school, only 30 minutes of screen time per day for interacting with parents is recommended.
- Schools can hold live online classes for a maximum of 1.5 hours per day for Classes 1-8, and 3 hours per day for Classes 9-12.
2.‘Kazi 106F:

‘Kazi 106F’, described as the country’s only Golden Tiger, has emerged as the social media sensation right after its picture tweeted by an IFS officer went viral.
- Kazi 106 F, the tigress, resides in world heritage Kaziranga National Park of Assam. It is also known as ‘Tabby tiger’ or ‘Strawberry tiger’.
- The skin of tigers is orange-yellow with black stripes and a whitish abdominal region.
- The yellowish background is controlled by a set of ‘agouti genes’ and their alleles and the black color stripes are controlled by ‘tabby genes’ and their alleles. Suppression of any of these genes may lead to color variation in the tiger.
- Agouti genes interact with the pigment cells to produce yellow to red or brown to black expression. This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti here same is happening in our tigress – Kazi 106 F
3.Tatya Tope :

Maharashtra government recently informed the Bombay High Court that more than ₹2.5 crore had already been spent on the construction of a national monument of the general Tatya Tope at Yeola in Nashik district.
- The Central government has sanctioned funds to the extent of 75% of the estimated cost while the rest will be borne by the State.
- A PIL was filed in the court seeking a direction to authorities to change the place sanctioned for the monument from Yeola taluka to a plot in Angangaon village in Yevla tehsil of the same district, which belongs to the Irrigation department.
- However, the Court has declined to provide an interim relief on the belated approach and said 50% of the construction work of the monument had already been completed.
About Tatya Tope:
- Also known as Ramachandra Pandurang Tope, he was one of the most notable Indian freedom fighters and a general in the Rebellion of 1857.
- Born in 1814 in Nashik, Maharashtra, Tatya Tope was the only son of Pandurang Rao Tope and his wife Rukhmabai
- Tatya Tope was an intimate friend and the right hand of Nana Sahib, the adopted son of Peshwa
- In May 1857, Tatya Tope won the battle over the Indian troops of the East India Company at Kanpur
- He forced General Windham to retreat from the city of Gwalior.
- He collaborated with Rani Lakshmi Bai of Jhansi to seize Gwalior.
- Tatya Tope was defeated by Sir Colin Campbell (later Baron Clyde) on December 6, 1857.
- He was hanged on April 18, 1859, in General Meade’s camp at Shivpuri.
4.Sree Padmanabha Swamy Temple in Thiruvananthapuram.

Reversing the 2011 Kerala High Court decision, the Supreme Court has upheld the right of the Travancore royal family to manage the property of deity at Sree Padmanabha Swamy Temple in Thiruvananthapuram.
- The Temple has been in the news since 2011 after the discovery of treasure worth over Rs. 1 lakh crore in its underground vaults.
- The central legal question was whether Utradam Thirunal Marthanda Varma, the younger brother of Chithira Thirunal Balarama Varma, the last Ruler of Travancore, could claim to be the “Ruler of Travancore” after the death of the ruler in 1991.
- The court examined this claim within the limited meaning of that term according to the Travancore-Cochin Hindu Religious Institutions Act, 1950 to claim ownership, control, and management of the ancient Sree Padmanabha Swamy Temple.
The judgment:
- The Supreme Court (SC) has reversed the 2011 Kerala High Court decision, which had directed the Kerala government to set up a trust to control the management and assets of the temple.
- The court said that, as per customary law, the shebait rights (right to manage the financial affairs of the deity) survive with the members of the family even after the death of the last ruler.
- The court defined ‘shebait’ as the “custodian of the idol, its earthly spokesman, its authorized representative entitled to deal with all its temporal affairs and to manage its property”.
Directions:
- Accepting the royals’ submission that the temple is a “public temple”, the court issued a slew of directions for its transparent administration in the future.
- It directed the setting up of an administrative committee with the Thiruvananthapuram District Judge as its chairperson.
- The other members would be a nominee of the trustee (royal family), the chief thanthri of the temple, a nominee of the State, and a member nominated by the Union Ministry of Culture.
- This committee would take care of the daily administration of the temple.
- It also ordered a second committee to be constituted to advise the administrative committee on policy matters.
- This would be chaired by a retired High Court judge nominated by the Chief Justice of the Kerala High Court.
5.Nagorno-Karabakh region in the South Caucasus. :
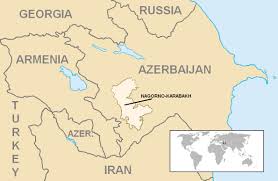
For approximately four decades, territorial disputes and ethnic conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan in Central Asia have impacted the Nagorno-Karabakh region in the South Caucasus. Recently, tensions escalated at the border between the two countries.
- Nagorno-Karabakh, also known as Artsakh, is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh.
- Nagorno-Karabakh is a disputed territory, internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan, but mostly governed by the Republic of Artsakh, a de facto independent state with an Armenian ethnic majority established on the basis of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic.
- Azerbaijan has not exercised political authority over the region since the advent of the Karabakh movement in 1988. Since the end of the Nagorno-Karabakh War in 1994, representatives of the governments of Armenia and Azerbaijan have been holding peace talks on the region’s disputed status.
6.Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019:

After facing flak from the transgender community, the Centre has done away with the requirement of a medical examination for trans persons applying for a certificate of identity in its latest draft rules framed under the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019.
Overview of the draft ‘Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020’:
- All educational institutions are to have a committee that transgender persons can approach in case of any harassment or discrimination.
- The “appropriate government” is also required to take adequate steps to “prohibit discrimination in any government or private organization or establishment.”
- States will be responsible for the “timely prosecution of individuals” charged under Section 18 of the Act which proscribes offenses against the transgender community and penalties therein.
- The offenses would be punishable with imprisonment for six months up to two years, with a fine.
- State governments will have to set up a Transgender Protection Cell under the District Magistrate and DGP to monitor cases of offenses against transgender persons and implement Section 18.
- The law was a consequence of the directions of the Supreme Court of India in the National Legal Services Authority vs. Union of India case judgment, mandating the Central and State governments to ensure legal recognition of all transgender persons and proactive measures instituted for their welfare.
- It calls for establishing a National Council for Transgender persons (NCT).
7.Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA):

At the upcoming Virtual “EU- India Summit”, Leaders expected to give a kickstart to negotiations on the Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) as the EU-India FTA is known, which have failed to be resumed despite several commitments by the leaders, including at the last E.U.-India summit in 2017.
- Negotiators are still “quite far apart” due to what Europe perceives as India’s “protectionist stance”.
- Besides, Make in India program has been accelerated by the COVID-19 crisis and recent pronouncements that India wants to go ‘Self-reliant’ have added to the situation.
India- EU trade:
- Trade with India formed under 3% of the E.U.’s global trade, which is “far below” what was expected of the relationship.
- Conversely, the E.U. is India’s largest trading partner and investor, and accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
About BTIA:
- In June 2007, India and the EU began negotiations on a broad-based Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) in Brussels, Belgium.
- These negotiations are pursuant to the commitment made by political leaders at the 7th India-EU Summit held in Helsinki on 13th October 2006 to move towards negotiations for a broad-based trade and investment agreement on the basis of the report of India-EU High-Level Technical Group.
Other important current affairs:
1. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) Mars Mission or ‘Hope’ is scheduled for launch on 16th July 2020.
- It is one of three missions launching to Mars this month. The USA and China, both have surface rovers in the late stages of preparation.
- Hope Mission:
- It is the first interplanetary mission for the Arab World.
- The ‘Hope Orbiter’ will be lifted on an H-IIA rocket from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, a machinery maker in Japan.
- It will be launched from Tanegashima Island in Japan.
- The UAE does not have its own rocket industry.
- Once launched, it is expected to arrive in orbit around Mars in February 2021 (the year of 50th anniversary of UAE’s founding).
- It costs about USD 200 million and will carry three instruments: an infrared spectrometer, an ultraviolet spectrometer, and a camera.
2. Recently, scientists at the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI) have developed a simple, low-cost, environment-friendly, and sustainable supercapacitor device.
- ARCI is an autonomous organization of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of IndiaSupercapacitor Device:
- The supercapacitor is developed from industrial waste cotton-based electrode & natural seawater electrolyte.
- Industrial waste cotton was converted into highly porous carbon fibers by the activation process and then utilized to make high-performance supercapacitor electrodes.
- Natural seawater was explored as an environment-friendly, cost-effective and alternative aqueous electrolyte.
3. Recent studies have shown that people unexposed to and not infected with Covid-19 (caused by SARS-CoV-2 or Novel Coronavirus) may still exhibit T cell responses specific to other coronaviruses.
- A huge number of adults are exposed to four different coronaviruses that cause common cold and studies have shown that 20-50% of healthy people display SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells.
- The healthy people studied were those tested prior to the pandemic or have not been infected with novel coronavirus.
- Memory T cells protect against previously encountered pathogens.
- It is thought that SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell responses seen in healthy people might arise from memory T cells derived from exposure to ‘common cold’ coronaviruses.
- However, it is not known that the presence of pre-existing immunity from memory T cells offers clinical relevance when exposed to SARS-CoV-2.
- Measuring pre-existing immunity and correlating it with infection and severity of the disease is the only way to find out its role in protection against SARS-CoV-2.
- However, the relationship between the infections by and immunity from common cold coronavirus and age is not well established.
- That is why it is unclear why children do not show severe symptoms, while older people do.
- These considerations underline how multiple variables may be involved in potential pre-existing partial immunity to Covid-19.
4. According to the latest census report prepared by the Madhya Pradesh forest department, the number of dolphins in the Chambal river has been reduced by 13% in 4 years.
- There are just 68 dolphins left in the 435-kilometer-long Chambal river sanctuary which passes through three states i.e. Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- Gangetic Dolphins are the sanctuary’s main attraction.
- The decreasing trend is continuing from 2016 when there were 78 dolphins.
- The maximum carrying capacity of dolphins in Chambal is 125.
- The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available.
- The dolphins were spotted for the first time in 1985 in the Chambal river (a tributary of Yamuna) near Etawah, Uttar Pradesh.
- At that time, the number was more than 110.
5. On July 11, 25 years on, commemoration services were held at the Srebrenica-Potocari Memorial and Cemetery in remembrance of the victims of the Srebrenica massacre, the ethnic cleansing of Bosnian Muslims.
- In July 1995, approximately 8,000 Muslims, mostly men, and boys were killed in Srebrenica, a town in Bosnia and Herzegovina in south-eastern Europe, by Bosnian Serb forces led by Commander Ratko Mladić.
- These killings were later classified as genocide by international tribunals investigating the massacre.
- The disintegration of Yugoslavia in 1991 threw the south-eastern and central Europe in chaos and led to violent inter-ethnic wars in the region over the next few years. In many ways, the violence perpetrated against Bosniaks or Bosnian Muslims during the Srebrenica massacre was a result of this regional conflict.
6. World Youth Skills Day 2020 is being held on July 15 under the theme “Skills for a Resilient Youth in the Era of COVID-19 and Beyond”.
- Designated by the General assembly in 2014, the World Youth Skills Day is an opportunity for technical and vocational education and training (TVET) institutions to acknowledge the importance of equipping young people with skills for employment.
- The vision of the Incheon Declaration: Education 2030 is fully captured by Sustainable Development Goal 4 “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”.




