Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 21st July 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Global Real Estate Transparency Index (GRETI) 2020.:
- Mahatma Jyotirao Phule crop loan waiver scheme
- plea bargaining:
- Kuwait’s draft residency bill
- Bubonic plague.:
- ChAdOx1 vaccine:
- “Retrofit of Air-conditioning to improve Indoor Air Quality for Safety and Efficiency” (RAISE)
- Other important current affairs:
1.Global Real Estate Transparency Index (GRETI) 2020.:

India is ranked 34th in Jones Lang LaSalle’s (JLL) biennial Global Real Estate Transparency Index (GRETI) 2020
- JLL has been tracking real estate transparency since 1999. This 11th edition of GRETI covers 99 countries and territories, and 163 city regions.
- The rankings have six Asia Pacific markets – Mainland China (32nd), Thailand (33rd), India (34th), Indonesia (40th), Philippines (44th), and Vietnam (56th) – among the top 10 biggest improvers globally.
- Mature markets such as Australia (3rd) and New Zealand (6th) have maintained their positions near the top of the global ranking.
- India has also edged into the top 20 for Sustainability Transparency through the active role of organizations like the Indian Green Building Council and Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA).
- Within the realty sector, key structural reforms made in the recent past include the Real Estate Regulation and Development Act 2016 (RERA), GST, Benami Transaction Prohibition (Amendment) Act, 2016, Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, digitization of land records, etc.
2.Mahatma Jyotirao Phule crop loan waiver scheme:

The Maharashtra government has claimed it has waived off loans of 83% out of total eligible farmers under the Mahatma Jyotirao Phule crop loan waiver scheme amounting to ₹17,646 crores.
- Scheme Announced in December 2019, it aims to write off crop loans up to Rs 2 lakh (taken between April 1, 2015, and March 31, 2019) which has not been repaid till September 30, 2019.
About Jyotirao Phule:

- Born in 1827 in the Satara district of Maharashtra.
- Phule was given the title of Mahatma on May 11, 1888, by Vithalrao Krishnaji Vandekar, a Maharashtrian social activist.
- His work is related mainly to the eradication of untouchability and caste system, emancipation and empowerment of women, reform of Hindu family life.
- Along with his wife, Savitribai Phule, he is regarded as a pioneer of women’s education in India.
- The couples were the first native Indians to open the first indigenously-run school for girls in India in August 1848 at Pune in Maharashtra.
- Later, the Phules started schools for children from the then untouchable castes such as Mahar and Mang.
- In 1863, he opened a home for pregnant Brahmin widows to give birth in a safe and secure place.
- He opened an orphanage home to avoid infanticide.
- In this regard, he is believed to be the first Hindu to start an orphanage for the unfortunate children.
- In 1868, Jyotirao decided to construct a common bathing tank outside his house to exhibit his embracing attitude towards all human beings and wished to dine with everyone, regardless of their caste.
- In 1873, Phule founded the Satyashodhak Samaj, or the Society of Seekers of Truth, for the rights of depressed classes, to denounce the caste system, and to spread rational thinking.
- His famous works: Tritiya Ratna (1855), Gulamgiri (1873), Shetkarayacha Aasud, or Cultivator’s Whipcord (1881), Satyashodhak Samajokt Mangalashtakasah Sarva Puja-vidhi (1887).
4. Plea bargaining:

Many members of the Tablighi Jamaat belonging to different countries have obtained release from court cases in recent days by means of plea bargaining.
- Plea bargaining refers to a person charged with a criminal offence negotiating with the prosecution for a lesser punishment than what is provided in law by pleading guilty to a less serious offence.
- It primarily involves pre-trial negotiations between the accused and the prosecutor.
- It may involve bargaining on the charge or in the quantum of sentence.
- Plea bargaining was introduced in 2006 as part of a set of amendments to the CrPC as Chapter XXI-A, containing Sections 265A to 265L.
- In India, a plea bargaining process can be initiated only by the accused;
- The accused will have to apply to the court for invoking the benefit of bargaining.
- The applicant should state that it is a voluntary preference and that he has understood the nature and extent of punishment provided in law for the offence.
- The court would then issue a notice to the prosecutor and the complainant or victim, if any, for a hearing.
- The voluntary nature of the application must be ascertained by the judge in an in-camera hearing at which the other side should not be present.
- Thereafter, the court may permit the prosecutor, the investigating officer and the victim to hold a meeting for a “satisfactory disposition of the case”.
- The outcome may involve payment of compensation and other expenses to the victim by the accused.
- Once mutual satisfaction is reached, the court shall formalise the arrangement by way of a report signed by all the parties and the presiding officer.
- The accused may be sentenced to a prison term that is half the minimum period fixed for the offence. If there is no minimum term prescribed, the sentence should run up to one-fourth of the maximum sentence stipulated in the law.
5. Kuwait’s draft residency bill:
Indian Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) has said that it is “closely monitoring” the status of Kuwait’s draft residency bill, which is aimed at expelling a bulk of foreigners from the country.
- The draft bill proposes to reduces the number of ex-pats in Kuwait from over 70% to 30% of the population. The purpose is to gradually decrease the number of ex-pats by bringing it down to 70% this year, 65% next year and so on.
- The bill specifies country-wise caps designating a quota for how many people of a certain nationality can be allowed to work in Kuwait.
- The Indian expatriate community, which is the largest ex-pat group in Kuwait, should not exceed 15% of the national population. It also calls for reducing the number of Egyptians, who form the second largest expatriate community, to 10% of Kuwait’s total population.
- Kuwait wants to balance the population proportion of Kuwaitis and ex-pats.
- As of now, the current population of Kuwait is 4.3 million, with Kuwaitis making up 1.3 million of the population, and ex-pats accounting for 3 million.
- A comprehensive draft law calling for a gradual reduction of ex-pats in Kuwait was announced to be submitted in the Assembly by the Speaker Marzouq Al-Ghanem, as per a media statement.
- The Indian community constitutes the largest expat community in Kuwait, totalling 1.45 million’.
- If the bill becomes a law, it will reduce the Indian presence in Kuwait and will prove to be a big blow to India’s remittance economy which is considerably dependent on Gulf nations.
- Kuwait is a top source of remittances for India. In 2018, India received nearly USD 4.8 billion from Kuwait as remittances.
6. Bubonic plague.:

A hospital in China’s Inner Mongolia reported a case of suspected bubonic plague.
- Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Yersinia pestis, a zoonotic bacteria, usually found in small mammals and their fleas.
- It is transmitted between animals through fleas. Humans can be infected through:
- the bite of infected vector fleas
- unprotected contact with infectious bodily fluids or contaminated materials
- the inhalation of respiratory droplets/small particles from a patient with pneumonic plague.
- Two main forms of plague infection, depending on the route of infection are –
- Bubonic plague is caused by the bite of an infected flea.
- Plague bacillus, Y. pestis enters at the bite and travels to the nearest lymph node where it replicates itself.
- The lymph node then becomes inflamed, tense and painful, and is called a ‘bubo’.
- Human to human transmission of bubonic plague is rare.
- Pneumonic plague, or lung-based plague, is the most virulent form of plague. Any person with pneumonic plague may transmit the disease via droplets to other humans.
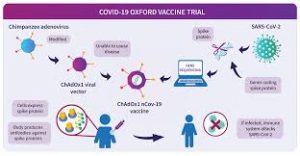
7.ChAdOx1 vaccine:
ChAdOx1 COVID-9 was jointly developed by British-Swedish company AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford.
- It has been found to be safe and induced an immune response in early-stage clinical trials.
- The vaccine belongs to a category called non-replicating viral vector vaccines.
- This vaccine is made from a genetically engineered virus that causes the common cold in chimpanzees.
- Scientists did this by transferring the genetic instructions of the coronavirus’ “spike protein” – the crucial tool it uses to invade human cells – to the vaccine.
- This was done so that the vaccine resembles the coronavirus and the immune system can learn how to attack it.
- The adenovirus, genetically modified so that it cannot replicate in humans, will enter the cell and release the code to make only the spike protein.
- The body’s immune system is expected to recognise the spike protein as a potentially harmful foreign substance and starts building antibodies against it.
- Once immunity is built, the antibodies will attack the real virus if it tries to infect the body.
- When someone is infected with the Covid-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2), the reason it spreads in the body easily is because of the spikes on its surface.
- These spikes, known as the ‘spike protein’, allow the virus to penetrate cells and, thereafter, multiply.
- Globally, Oxford and AstraZeneca have already begun phase III trials in Brazil, targeting 5,000 volunteers. A similar trial in South Africa is also expected to be underway.
8.“Retrofit of Air-conditioning to improve Indoor Air Quality for Safety and Efficiency” (RAISE) :

“Retrofit of Air-conditioning to improve Indoor Air Quality for Safety and Efficiency” (RAISE) national program has been launched.
- It is a joint initiative of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) and the S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) MAITREE Program.
Need for and significance of the programme:
- Poor air quality has been a concern in India for quite some time and has become more important in light of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- As people return to their offices and public spaces, maintaining good indoor air quality is essential for occupant comfort, well-being, productivity and overall public health.
- RAISE initiative can potentially alleviate the issue of bad air quality in workspaces across the nation and pioneer ways to make them healthier and greener.
- Market Integration and Transformation Program for Energy Efficiency (MAITREE) program:
- It is a part of the US-India bilateral Partnership between the Ministry of Power and USAID and is aimed at accelerating the adoption of cost-effective energy efficiency as a standard practice within buildings, and specifically focuses on cooling.
Other important current affairs:
1. India’s largest commercial shipbuilder Cochin Shipyard Ltd (CSL) has signed contracts for the construction of two autonomous electric ferries for Norway-based ASKO Maritime, with an option to build two more identical vessels.
- This Autonomous Electrical vessel project, partially funded by the Norwegian Government, is aimed at emission-free transport of goods across the Oslo fjord. The 67 meter-long vessels will initially be delivered as a full-electric transport ferry, powered by 1,846 kWh capacity battery.
- ASKO Maritime AS, the subsidiary group of NorgesGruppen ASA, is one of the largest players in the Norwegian retail segment.
- CSL is already constructing 23 hybrid electric boats for Kochi Water Metro.
2.MegaLab, the world’s largest genetic testing lab being built by the IIT Alumni Council, announced a Rs 500-crore incubator to intensify offensive against Covid in the Mumbai University campus.
- The MegaIncumbator will be the world’s first and largest engineered bio-molecule focused incubator to involve start-ups, other existing incubators and accelerators, and will come up at a 2.5 million sq ft space at the Kalina campus of Mumbai University.
- MegaLab Mumbai’ will start operations this month.
- The IIT Alumni Council is the largest body of alumni, students and faculty from all the 23 Indian Institutes of Technology and partnering Technical Institutes of Excellence and was formed in 2019 to carry out projects of social importance.
3, India is no longer involved in the Farzad-B gas field exploration project where ONGC’s foreign arm OVL had originally signed an agreement for exploration in 2002, investing approximately $100 million thus far
- Farzad B gas field is an offshore natural gas field located in Persian Gulf under the control of Iranian sovereignty.
- It was opened in 2008 and India had been negotiating the rights to oil and gas from the field till the US sanctions on Iran jeopardised India’s plans.
- Government of India cited policy changes by the Iranian government, Iran’s precarious finances, and the U.S. sanctions situation as the reasons for the decisions on Indian infrastructure projects in Iran, which would be undertaken through local companies instead.
5. A report by the State Bank of India (SBI) has recommended direct monetisation as a possible way of funding the Centre’s deficit at lower rates, without increasing inflation and affecting debt sustainability.
- Direct Monetisation: It simply means that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directly funds the Central government’s deficit against government bonds or securities.
- Until 1997, the government used to sell securities directly to the RBI. This allowed the government to technically print equivalent amounts of currency to meet its budget deficit.
- However, this practice was stopped over its inflationary impact and in favour of fiscal prudence.
- This is different from the “indirect” monetisation that RBI does when it conducts the Open Market Operations (OMOs) and/or purchases bonds in the secondary market.
6. The government has operationalized the first Mega Food Park (MFP) of Mizoram i.e. Zoram Mega Food Park.
- It has been set up under the ‘Mega Food Park Scheme’.
- Zoram MFP:
- It is located in Khamrang village in Kolasib District, Mizoram.
- It is spread over 55 acres of land and is set up at a cost of Rs. 75. 20 crores.
- It is not only expected to benefit the people of Mizoram but also that of adjoining districts in Assam.
- Assam already has an MFP in its Nalbari district- North East Mega Food Park.
- It will boost the North-East Region’s potential to become the organic destination of the world due to its rich agricultural and horticultural produce.
- Sikkim has already been declared as an organic state.
- Mega Food Park Scheme:
- Launched in: 2008-09 under the purview of the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- Aim: To provide a mechanism to link agricultural production to the market by bringing together farmers, processors and retailers so as to ensure maximizing value addition, minimizing wastage, increasing farmers income and creating employment opportunities particularly in the rural sector.
7. Indian Naval ships conducted a Passage Exercise (PASSEX) with the U.S. Navy’s USS Nimitz carrier strike group near the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- A passage exercise is normally undertaken whenever an opportunity arises, in contrast to pre-planned maritime
- Recently, the Indian Navy had also conducted similar PASSEXs with the Japanese Navy and the French Navy.
- PASSEX:
- Four frontline Indian naval ships which included INS Shivalik, INS Sahyadri, INS Kamorta and INS Rana, teamed up with carrier USS Nimitz and three other U.S. ships to conduct the exercise.
- USS Nimitz is the U.S. Navy’s largest aircraft carrier.
- Aim: To improve the cooperation between the U.S. and Indian maritime forces and to maximize training and interoperability, which also include air defence.
8. The Delhi High Court has sought responses from the Delhi government on a petition that said statements of child witnesses lodged at child welfare centres should be recorded through video conferencing and not physically in courts.
- The petition has been filed by Bachpan Bachao Andolan (BBA) in view of the outbreak of Covid-19.It is India’s largest movement campaigning for the rights of children.
- It was started in 1980 by Nobel Laureate Kailash Satyarthi.
- Mission: Identity, release, rehabilitate and educate children in servitude through prevention, direct intervention, mass mobilisation and legal action to create a child-friendly society.
- Functions: As a Non-Government Organisation (NGO), it has centred its focus on ending bonded labour, child labour and human trafficking, as well as demanding the right to education for all children.
- It organises Baal Panchayat on the occasion of World Day against Child Labour i.e. 12th June.
- It has so far freed more than 88,000 children from servitude, including bonded labourers.
- Nobel Prize: In 2014, Kailash Satyarthi was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize jointly with Malala Yousafzai for their contribution towards child education
9. National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA), has constituted a Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) under the Chairmanship of R Narayanaswamy, Professor, Indian Institute of Management, Bengaluru.
- Composition: Seven members, including the Chairman.
- Functions: Aid and advise the Executive Body of the NFRA on issues related to the drafts of accounting standards and auditing standards. Provide inputs from the perspectives of users, preparers and auditors of financial statements.
- National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) was constituted on 1st October 2018 under section 132 (1) of the Companies Act, 2013.
- In the wake of accounting scams, a need was felt to establish an independent regulator for enforcement of auditing standards and ensuring the quality of audits so as to enhance investor and public confidence in financial disclosures of companies.
10. The new Consumer Protection Act, 2019 came into force on 20th July 2020 and it will empower consumers and help them in protecting their rights through its various notified rules and provisions.
- The new act will be swift and less time consuming compared to the older Consumer Protection Act, 1986 in which single-point access to justice was given making it a time-consuming exercise.
- The old act provided for a three-tier consumer dispute redressal machinery at the National (National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission), State and District levels.




