Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 25th June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Annual Tuberculosis (TB) Report 2020.:
- Extension to OBC Sub-Categorisation Commission
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Sub-ordinate Debt (CGSSD)
- Global Education Monitoring Report 2020: UNESCO:
- Seabed 2030 Project.:
- Pakistan to remain on FATF grey list:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY):
- Other important current affairs
1. Annual Tuberculosis (TB) Report 2020.:
Recently, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has launched the annual Tuberculosis (TB) Report 2020.
- India is committed to eliminating tuberculosis from the country by 2025, five years ahead of the global target by the World Health Organisation (WHO) i.e. 2030.
- To align with the ambitious goal, the programme has been renamed from the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) to National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- State TB Index: On the basis of the score in State TB Index, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh were the top three best-performing states for tuberculosis control under the category of states with 50 lakh population.
- Tripura and Nagaland were best-performing in the category of states having less than 50 lakh population.
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu were selected as the best performing Union Territories.
- It also revealed that Tobacco consumption is rising among Indian TB patients.
8% of TB cases can be attributable to tobacco usage. - People living with HIV are the most vulnerable among all those TB patient groups which have other comorbidities (rate of death). Hence, the World Health Organization lays social emphasis (through awareness programs) on them.
- India accounts for 9% of all HIV-associated TB deaths in the world, the second-highest number globally.
- A total of 92,000 HIV-associated TB patients were recorded on an annual basis.
- Awareness among TB patients about their HIV status has gone up to 81% from 67%.
- Diabetes Associated TB: The other such group is patients suffering from diabetes. According to the report, 20% of all TB cases in India also suffer from diabetes.
- In 2019, among the notified TB patients under the Revised National TB Control Programme, 64 % were screened for Diabetes.
According to the report, India notified the highest number of 24.04 lakh tuberculosis cases last year (2018) as against an estimated 26.9 lakh cases by WHO, indicating that around three lakh patients missed out from the national TB programme.
- Low Fatality: It stated that 79,144 deaths due to tuberculosis were reported in 2019, which is much lower than the WHO estimate of 4.4 lakh fatalities.
- Treatment Success Rate: It is around 70-73% in the last two years. From 2014-2016, it was between 76 and 77%.
Initiatives by India
- The Nikshay Ecosystem: It is the National TB information system which is a one-stop solution to manage information of patients and monitor program activity and performance throughout the country.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY): This scheme is aimed at providing financial support to TB patients for their nutrition.
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign: Launched In September 2019 it is showcasing the highest level of commitment for the elimination of TB.
- The Saksham Project: It is a project of the Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS) that has been providing psycho-social counseling to DR-TB patients.
Tuberculosis
- TB is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs.
- TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with TB cough, sneeze, or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air.
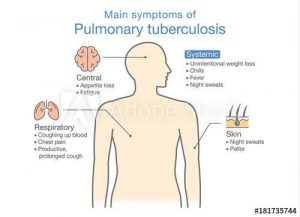
- Symptoms: Cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever, and night sweats.
2.Extension to OBC Sub-Categorisation Commission(Article 340 of the Indian Constitution):

Cabinet approves Extension of term of the commission constituted under Article 340 of the constitution to examine the issue of Sub-categorization within other Backward Classes in the Central List.
- Article 340 of the Indian Constitution lays down conditions for the appointment of a Commission to investigate the conditions of the backward classes.
- The President may by order appoint a Commission consisting of such persons as he thinks fit to investigate the conditions of socially and educationally backward classes within the territory of India.
- Article 14 of the Constitution guarantees equality before the law. That means un-equals cannot be treated equally. Measures are required to be taken for the upliftment of un-equals to bring them on par with the advanced classes.
- Article 16 (4) provides that the State can make any provision for the reservation of appointments or posts in favor of any backward class of citizens who, in the opinion of the state, are not adequately represented in the services under the State.
Sub- categorization:
- National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) proposed the sub-categorization of Other Backward Classes (OBCs) back in 2015.
- In October 2017, President Ram Nath Kovind, in the exercise of the powers conferred by Article 340 of the Constitution, appointed a commission to examine the issue of sub-categorization of OBCs, chaired by retired Justice G. Rohini, to ensure social justice in an efficient manner by prioritizing the Extremely Backward Classes (EBCs).
- Sub categorization of the OBCs will ensure that the more backward among the OBC communities can also access the benefits of reservation for educational institutions and government jobs.
- At present, there is no sub-categorization and 27% reservation is a monolithic entity.
3.Credit Guarantee Scheme for Sub-ordinate Debt (CGSSD) :

The scheme was announced by the Finance Minister as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- It is also called a “Distressed Assets Fund–Sub-ordinate Debt for MSMEs”.
- It is a scheme for the distressed MSME sector.
- The scheme seeks to extend support to the promoter(s) of the operational MSMEs which are stressed and have become NPAs as on 30th April 2020.
- As per the Scheme, guarantee cover worth Rs. 20,000 crores will be provided to the promoters who can take debt from the banks to further invest in their stressed MSMEs as equity.
- The scheme will be operationalized through the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for MSEs (CGTMSE).
- Promoter(s) of the MSMEs will be given credit equal to 15% of their stake (equity plus debt) or Rs. 75 lakh whichever is lower.
- Promoter(s) in turn will infuse this amount in the MSME unit as equity and thereby enhance the liquidity and maintain the debt-equity ratio.
- 90% guarantee coverage for this sub-debt will be given under the Scheme and 10% would come from the concerned promoters.
- There will be a moratorium of 7 years on payment of principal whereas the maximum tenor for repayment will be 10 years.
4.Global Education Monitoring Report 2020: UNESCO:

Recently, the Global Education Monitoring Report, 2020 was released by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- It highlighted that Covid-19 had worsened the inequalities in education systems worldwide.
Global Findings:
- During the height of school closures in April 2020, almost 91% of students around the world were out of school.
- About 40% of low and lower middle income countries have not supported learners at risk of exclusion during this crisis, such as the poor, linguistic minorities and learners with disabilities.
- Education systems responded with distance learning solutions, all of which offered less or more imperfect substitutes for classroom instruction.
- Poorer countries opted for radio and television (TV) lessons, 55% of low-income, 73% of lower-middle-income, and 93% of upper-middle-income countries adopted for online learning platforms for primary and secondary education.
- 17% of low and middle-income countries are planning to recruit more teachers, 22% to increase class time, and 68% to introduce remedial classes when schools reopen to combat the situation.
- India has used a mix of all three systems (radio, TV and online platforms) for educational continuity.
5. Seabed 2030 Project.:

Recently, it was announced that mapping of nearly one-fifth of the world’s ocean floor had been finished under the Seabed 2030 Project.
Seabed 2030 Project:
- Seabed 2030 is a collaborative project between the Nippon Foundation of Japan and the General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO).
- It was launched at the United Nations Ocean Conference in June 2017 and is aligned with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14 to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources.
- The United Nations Ocean Conference intended to be a game-changer in reversing the decline in the health of the ocean for people, planet, and prosperity.
- The project aims to bring together all available bathymetric data to produce the definitive map of the world ocean floor by 2030 and make it available to all.
- Bathymetry is the measurement of the shape and depth of the ocean floor.
- In the past, satellites and planes carrying altimeter instruments have been able to provide large swathes of data about the ocean floor.
- However, the Seabed 2030 Project aims to obtain higher quality information that has a minimum resolution of 100 meters at all spots, using equipment such as deepwater hull-mounted sonar systems, and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs).
- Importance of the Study of the Ocean Floor: It helps in understanding several natural phenomena, including ocean circulation, tides, and biological hotspots.
- Provides key inputs for navigation, forecasting disasters, exploration for oil and gas projects, building offshore wind turbines, fishing resources, and for laying cables and pipelines.
- Ensure a better understanding of climate change.
Climate change has impacted the flow of ocean currents and has led to sea-level rise.
6.Pakistan to remain on FATF grey list:

Pakistan is likely to remain on the grey list of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) for failing to comply with the global terrorist-financing watchdog’s deadline to prosecute and penalize terrorist financing in the country.
- At a FATF meeting in February, Islamabad had been told that ‘all deadlines’ had expired and if they didn’t prosecute and penalize terrorist financing by June, the watchdog would take action.
- At the Paris plenary too, the FATF had expressed serious concerns over Pakistan’s failure to complete its 27-point action plan in line with the agreed timelines – which ended in September 2019.
- With Pakistan’s continuation in the ‘Grey List’, it will be difficult for the country to get financial aid from the IMF, the World Bank, the ADB, and the European Union.
- This will further enhance problems for the nation which is in a precarious economic situation.
- Also, there is every possibility that the global body may put the country in the ‘Black List’.
About FATF:
- It is an inter-governmental body established in 1989 on the initiative of the G7.
- Its Secretariat is located at the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) headquarters in Paris.
- Member Countries: There is 39 member of FATF, representing most financial centers around the world. This includes 2 regional organizations- GCC and EC. The FATF Plenary is the decision making body of the FATF. It meets three times per year.
Blacklist and grey list:
- Black List: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put in the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities. The FATF revises the blacklist regularly, adding or deleting entries.
- Grey List: Countries that are considered safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list. This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
7.Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY):

The government has approved a 2% interest subsidy scheme for Shishu loan account holders under the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY).
- The Scheme will help small businesses tide over difficulties created by the lockdown following the Covid-19 outbreak.
- PMMY is a scheme launched by the government in 2015 for providing loans up to Rs. 10 lakh to the non-corporate, non-farm small/micro-enterprises.
- MUDRA, which stands for Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd., is a financial institution set up by the Government to provide funding to the non-corporate small business sector through various last-mile financial institutions like Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs).
- MUDRA does not lend directly to micro-entrepreneurs/individuals.
- Under the aegis of PMMY, MUDRA has created three products i.e. ‘Shishu’, ‘Kishore’, and ‘Tarun’ as per the stage of growth and funding needs of the beneficiary micro unit.
- Shishu: covering loans up to Rs. 50,000.
- Kishore: Covering loans above Rs. 50,000 and up to Rs. 5 lakh
- Tarun: covering loans above Rs. 5 lakh and up to Rs. 10 lakh
- Loans under this scheme are collateral-free loans.
Other important current affairs:
1. To protect depositors, the Centre has decided to bring all urban and multi-State cooperative banks under the supervision of the RBI. The Union Cabinet approved an ordinance to this effect.
- RBI’s powers on scheduled banks would be hence applicable to cooperative banks as well.
- The urban cooperatives and multi-State cooperative banks are 1,540 in number and have a depositor base of 8.6 crores who have saved ₹4.84 lakh crore
- Currently, these banks come under dual regulation of the RBI and the Registrar of Co-operative Societies.
- The move to bring this urban and multi-State coop. banks under the supervision of the RBI comes after several instances of fraud and serious financial irregularities, including the major scam at the Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank last year. In September, the RBI was forced to supersede the PMC Bank’s board and impose strict restrictions.
2. Union Health Minister launched the ‘eBloodServices’ mobile App developed under the guidance of the Indian Red Cross Society. The Health Minister is also the Chairman of the Indian Red Cross Society.
- This application is developed by the E-Raktkosh team of Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (CDAC) under the Digital India scheme launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2015.
- Through this App, four units of blood can be requisitioned at a time and the blood bank will wait for as long as 12 hours for the person to collect it. This app makes it easy for those in need to request for Blood units.
4.NITI Aayog, in partnership with Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), Centre for Social and Behavioural Change (CSBC), Ashoka University, and the Ministries of Health and WCD, launched a behavior change campaign called ‘Navigating the New Normal’, and its website.
- The campaign focusses on COVID-safe behaviors, especially wearing masks, during the ‘Unlock’ phase of the ongoing pandemic.
- Developed under the guidance of Empowered Group 6, constituted by the Government of India and chaired by CEO, NITI Aayog, the campaign has two parts.
- The first is a web portal, containing resources informed by behavioral science and the use of nudge and social norms theory, related to COVID-safe behavioral norms during the ongoing Unlock phase.
- The second is a media campaign focused on the wearing of masks.
5. Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the creation of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- This is part of reforms aimed at giving a boost to private sector participation in the entire range of space activities.
- It will act as a single-point interface between Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), and everyone who wants to participate in space-related activities, or use India’s space resources.
- It will also hand-hold, promote, and guide the private industries in space activities through encouraging policies and a friendly regulatory environment.
- Indian National Space Promotion Board: It would be set up to strengthen the Department of Space and for the promotion of the private space entrepreneurs or non-government space entrepreneurs,
- The overall idea is to let ISRO concentrate on essential activities like research and development, planetary exploration, and strategic use of space while freeing itself from ancillary or routine work which could easily be done by private industry.
- The main objective of NSIL is to scale up industry participation in Indian space programs in comparison to IN-SPACe which gives emphasis on the participation of the private sector.
6. A research team at the Indian Institute of Science in Bengaluru has developed nanozymes that destroy the cell membrane of bacteria by directly targeting its phospholipids.
- Nanozymes are nanomaterials that can disintegrate the cell membranes of a range of diseases causing bacteria.
- The nanomaterial developed in IISc is tested on several potentially pathogenic bacteria causing typhoid, gastroenteritis, dysentery, cholera, and pneumonia.
- It was found that the nanozyme stopped growth and killed the microbes.
- Nanozymes developed by them can replace the antibiotics that have become ineffective as several bacteria have developed resistance to them by producing their own enzymes.




