Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:25th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc.
Contents:
- National Forensic Sciences University Bill, 2020
- Parliamentary standing committees
- (MPLADS)
- Kurzarbeit scheme
- Cess Fund for Welfare of Construction Workers.:
- The Invest India Business Immunity Platform
- Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS):
- Bio-Safety Levels
- Other important current affairs
1. National Forensic Sciences University Bill, 2020:

Minister for Home Affairs introduced the National Forensic Sciences University Bill, 2020 in the Lok Sabha.
- The bill seeks to establish a National Forensic Sciences University as an institution of national importance by upgrading the Gujarat Forensic Sciences University in Gandhinagar.
- The proposed National Forensic Sciences University will promote studies and research in forensic science in conjunction with applied behavioral science studies, law, criminology and other allied areas for strengthening the criminal justice system in the country.
2. All meetings of parliamentary standing committees have been deferred indefinitely because of the lockdown to curb the spread of COVID-19.:

Committee reports are usually exhaustive and provide authentic information on matters related to governance.
Bills that are referred to committees are returned to the House with significant value addition. However, Parliament is not bound by the recommendations of committees.
Types of committees:
- ‘Standing’ committees: Their existence is uninterrupted and usually reconstituted on an annual basis. Some standing committees are departmentally related.
- ‘Select’ committees formed for a specific purpose, for instance, to deliberate on a particular bill. Once the Bill is disposed of, that select committee ceases to exist.
- Finance committees are considered to be particularly powerful. The three financial committees are the Public Accounts Committee, the Estimates Committee and the Committee on Public Undertakings.
About parliamentary committees:
- Parliament is the embodiment of the people’s will. Committees are an instrument of Parliament for its own effective functioning.
- Members of Parliament may have great acumen but they would require the assistance of experts in dealing with such situations. It is through committees that such expertise is drawn into lawmaking.
- Executive accountability to the legislature is enforced through questions in Parliament also, which are answered by ministers.
- However, department standing committees go one step further and hear from senior officials of the government in a closed setting, allowing for more detailed discussions.
- This mechanism also enables parliamentarians to understand the executive processes closely.
3. Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) guidelines.:

The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has made amendments to the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) guidelines.
- MPs are to recommend every year, works costing at least 15 percent of the MPLADS entitlement for the year for areas inhabited by Scheduled Caste population and 7.5 percent for areas inhabited by the S.T. population.
- In order to encourage trusts and societies for the betterment of tribal people, a ceiling of Rs. 75 lakh is stipulated for building assets by trusts and societies subject to conditions prescribed in the scheme guidelines.
- The amendments allow Members of Parliament (MPs) to recommend funds for the purchase of medical testing and screening equipment for government hospitals and setting up of other related facilities in their respective constituencies, to contain COVID-19.
- The government has permitted the one-time use of funds from MPLADS.
- Expenditure under this one-time dispensation will be restricted to the end of the financial year 2020-21 and no expenditure, under any circumstances, shall be allowed to make/roll over into the next financial year 2021-22.
- Apart from this, fieldwork of large-scale sample surveys has been suspended by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
About the MPLAD scheme:
- It was launched in December 1993, to provide a mechanism for the Members of Parliament to recommend works of developmental nature for creation of durable community assets and for provision of basic facilities including community infrastructure, based on locally felt needs.
- The MPLADS is a Plan Scheme fully funded by the Government of India.
- The annual MPLADS fund entitlement per MP constituency is Rs. 5 crores.
4.Kurzarbeit scheme:

Amid the all-round disruption caused to the economy by the novel coronavirus outbreak, various governments have unveiled various measures to address such concerns, and one of the most talked-about is Germany’s Kurzarbeit scheme.
- Kurzarbeit is German for “short-work”. The policy provides for a short-time work allowance, called kurzarbeitgeld, which partially compensates for lost earnings during uncertain economic situations.
- The policy was rolled out during the 2008 economic crisis while its origins date back as far as the early 20th century, before and after World War I.
- When companies face a loss of earnings due to unforeseen economic situations, they often need to cut back on their working hours or send some of their employees home.
- The Kurzarbeit scheme aims to address workers who are impacted by a loss of income due to shortened work hours during such times. They can apply for short-term work benefits under the scheme, with the government stepping in to pay employees a part of their lost income.
- This helps the companies retain their employees instead of laying them off, and allows the latter to sustain themselves for a period of up to 12 months.
5. Cess Fund for Welfare of Construction Workers.:

Recently, the Ministry of Labour & Employment has issued an advisory to all States/UTs to use the Cess Fund for Welfare of Construction Workers.
- The advisory comes under Section 60 of the Building and Other Construction Workers (BOCW) Act, 1996.
- The Act regulates the employment and conditions of service of building and other construction workers.
- It provides for their safety, health and welfare measures and for other matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- All-State Governments/UTs have been advised to transfer funds from the Cess Fund to the account of construction workers through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- The amount to be granted to construction workers may be decided by the respective state governments and Union territories.
- The financial assistance at this point in time would help to mitigate the financial crisis of construction workers to some extent and boost their morale to deal with COVID-19.
About the Cess Fund:
- The BOCW Cess Act, 1996, provides for the levy and collection of cess at 1-2 % of the cost of construction, as the Central Government may notify.
- The cess has been levied at the rate of 1% of the cost of construction, as notified by the Central government in its official gazette.
- The cess is collected by the State governments and UTs.
- It is utilized for the welfare of building and other construction workers by the respective State Building and Other Construction Workers Welfare Boards.
- Cess is a form of tax levied over and above the base tax liability of a taxpayer.
6. The Invest India Business Immunity Platform.:

Invest India, India’s national Investment Promotion & Facilitation Agency, under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has launched The Invest India Business Immunity Platform.
- The platform, hosted on the Invest India website, is designed as a comprehensive resource to help businesses and investors get real-time updates on India’s active response to Coronavirus.
- The Business Immunity Platform (BIP) is the active platform for business issue redressal, operating 24/7, with a team of dedicated sector experts and responding to queries at the earliest. features of BIP are:
- It keeps a regular track of developments with respect to the coronavirus.
- Provides the latest information on various central and state government initiatives, and answers and resolves queries through emails and on WhatsApp.
- Includes frequently asked questions on important aspects like locations of COVID-19 testing and other location-specific information.
- Maps and highlights the response mechanism put in place by leading Indian companies such as sanitation of staff vehicles, disabling biometric attendance systems, usage of video-conferencing and teleconferencing, developing online solutions and other unique initiatives.
- This platform also provides the ability to join the dots to find matching suppliers with required supplies and for innovators, startups, and MSMEs to showcase their solutions.
7. Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS):

Recently, the Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS) has allowed Defence veterans with lifestyle diseases on long treatment to purchase the required medicines for the month of April at once to contain the spread of COVID-19.
- ECHS is a flagship Scheme of the Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare, Ministry of Defence.
- It was launched with effect from April 2003.
- Aim: To provide quality healthcare for Ex-servicemen (Army, Navy and Air Force) pensioners and their dependents.
- Under the scheme allopathic and AYUSH medicare is provided through a network of ECHS Polyclinics, AYUSH hospitals spread across the country.
- Services Provided: ECHS Polyclinics are designed to provide ‘OutPatient Care’ which includes consultation, essential investigation and provision of medicines.
8.Bio-Safety Levels:
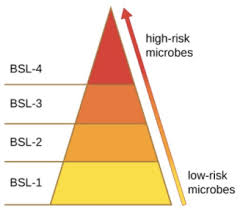
The National Centre for Disease Control provides four levels of Bio-Safety to be followed in India.
- Bio-Safety is the principle used to contain the spread of pathogens and toxins.
- India follows Bio-Safety Levels as prescribed by the World Health Organization.
- The monitoring and implementing agency of these bio-safety levels is done by the National Centre for Disease control.
Bio-Safety Levels:
There are four Bio-Safety levels:
- BSL-1 that are basic teaching laboratories.
- BSL-2 offering diagnostic services
- BSL-3 offers high containment special diagnostic services.
- BSL-4 are those laboratories that handle dangerous pathogens.
The COVID-19 has been put under the BSL-4 level.
Other important current affairs:
1. The International Olympic Committee and the Tokyo 2020 Organising Committee have decided to postpone the Tokyo 2020 Summer Games to the summer of 2021 due to the coronavirus pandemic.
2. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has made a series of announcements to ease the burden of companies during the COVID-19 outbreak. Increase in the threshold for initiation of corporate insolvency from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1 crore.
3. Hantavirus: Case of hantavirus in the Yunnan province of China. The hantaviruses are a family of viruses spread mainly by rodents. A person can get infected if he/she comes in contact with a rodent that carries the virus.
It remains unclear whether human-to-human transmission of the virus is possible.
4. In the wake of the coronavirus outbreak, the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) has made an appeal to people to wash their hands after touching or counting currency.
5. The President of India has greeted the people on the eve of Chaitra Shukla Pratipada, Ugadi, Gudi Padova, Cheti Chand, Navreh and Sajibu Cheiraoba. These festivals of the spring season mark the beginning of the traditional new year in India.
6. The Union Cabinet chaired by PM Modi approved MoU signed between India and Germany. The MoU was signed between the Ministry of Railways and DB Engineering and Consulting GMBH of Germany. The Memorandum will facilitate technological cooperation in the Railway sector.
7. A new district in Tamil Nadu is going to be formed after bifurcating the Nagappattinam district. The new district will be headquartered at Mayiladuthurai, in the heart of the Delta region.
8. The government has announced a complete lockdown of the entire country for 21 days to fight COVID-19.
All road, rail, and air services will remain suspended during the lockdown. However, freight movement will continue to carry essential commodities across the country.
9. The scientists of the Agharkar Research Institute (Pune), operating under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) have developed biofortified high-quality wheat. The new variety is MACS 4028
10. 11 people were killed in a terror attack that targeted a “Dharmashala” in Kabul. The Dharamshala is reported to have a sizeable number of Hindu and Sikh minorities. The Islamic State Organization has claimed to take responsibility for the attack.
11. International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and the Transatlantic Slave Trade is observed every year on 25 March to honor and remember those who suffered and died at the hands of the brutal slavery system. International Day also aims to raise awareness about the dangers of racism and prejudice today. Theme 2020: ‘Confronting Slavery’s Legacy of Racism Together’.
12. The E-Commerce Giants Flipkart and Amazon has temporarily stopped their services in India following lockdown in the country.
13. The Saudi Arabian King Salman is to chair the G20 summit on Corona Virus through a video conference. The Summit is to be held on March 26, 2020. The summit becomes significant as several international organizations are to participate in the summit. India is a member of G20.
14. Indian-origin American author Ruchika Tomar is named as the winner of the annual PEN/Hemingway Award 2020 for her 1st novel (debut)” A Prayer for Travelers”.
15. The government banned the export of anti-malarial drug hydroxychloroquine and formulations made from it in the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak. It is aimed at ensuring sufficient availability of medicine in the domestic market. ICMR recommended the use of hydroxychloroquine for treating healthcare workers handling suspected or confirmed coronavirus cases. This has been approved by the Drug Controller General of India (DGCI) for restricted use in emergency situations.
16.7.5 magnitude earthquake hit the northern Pacific. The quake was 37 miles deep and stuck the eastern Kuril Islands of Russia. The Islands are located at the tectonically unstable region called the “Ring of Fire”. The Ring of Fire is the area of the Pacific Ocean where several volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur.
17. Thermal Screening is being used at airports to check the COVID-19 virus. Thermal screening is a process that detects radiation emitted by an object with increased temperature. When a person has a fever, his temperature levels shoot up and thermal screening helps to detect them.




