Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 27th July 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).:
- Maratha Quota:
- Istanbul Convention:
- Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH):
- Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) 2020
- .Assessment of Climate Change over Indian Region’:
- 100th birth anniversary of Rosalind Franklin,:
- Other important current affairs:
1. Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).:

In a significant development, the Trump administration has relaxed standards for exporting drones to friendly countries.
- Under the new policy, drones that fly at speeds below 800 km per hour are no longer subject to the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
- The move will increase the US’ national security by improving the capabilities of its partners and increase economic security by opening the expanding drones market to the US industry.
Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR):
- The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) is an informal political understanding among states that seek to limit the proliferation of missiles and missile technology.
- The regime was formed in 1987 by the G-7 industrialized countries.
- There are currently 35 countries that are members (Partners) of the MTCR. India became its member in 2016.
- While there is no formal linkage, the activities of the MTCR are consistent with the UN’s non-proliferation and export control efforts.
- The MTCR is not a treaty and does not impose any legally binding obligations on Partners (members). Rather, it is an informal political understanding.
- The MTCR has no formal secretariat. France serves as the Regime’s Point of Contact (POC) which receives and distributes all Regime documents.
2.Maratha Quota:

The Supreme Court (SC) is set to commence the final hearing on the batch of Special Leave Petitions (SLPs-Article 136) against Maratha reservation in Maharashtra on a daily basis through video-conferencing.
- The apex court will also hear a petition challenging admission to postgraduate medical and dental courses under the quota in the state.
- The SLPs challenged the Bombay High Court (HC) decision, which upheld the constitutional validity of the Maratha quota under the state’s Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC) Act, 2018.
- The SEBC Act provides for reservation of seats for admission in educational institutions in the state and for reservation of posts for appointments in public services and posts under the state.
- Maharashtra is one of the few states which have more than 50% reservation.
- Tamil Nadu, Haryana, and Telangana also exceed the reservation cap.
- Indra Sawhney’s case 1992 ruled that the total reservation for backward classes cannot go beyond the 50% mark.
- A group of aspiring medical students challenged the constitutional validity of an amendment to the SEBC Act, 2018 allowing Maratha reservation for 2019-2020 admissions to MBBS courses.
- In July 2019, the Bombay HC dismissed the petition.
- The SC refused to stay the judgment and have, time and again, refused to put an interim stay on the quota.
- Recently, the SC refused to grant interim stay on a plea by medical students, seeking a direction that the 12% quota not be made applicable for admissions in postgraduate medical and dental courses for the academic year 2020-21.
Marathas:
- It is a politically dominant community in Maharashtra comprising mainly peasants and landowners and forms nearly one-third of the population of the state.
- The majority of the Chief Ministers of the state have been from this community since the formation of the state in 1960.
- Marathas are mostly Marathi-speaking but not all Marathi-speaking people belong to the Maratha community.
- Historically, they have been identified as a ‘warrior’ caste with large land-holdings.
- While the division of land and agrarian problems over the years have led to a decline of prosperity among the middle class and lower-middle-class Marathas, the community still plays an important role in the rural economy.
3.Istanbul Convention:

Poland is to withdraw from Istanbul Convention- a treaty aimed at preventing violence against women.
- The reason behind withdrawal is that Poland thinks the Convention is harmful because it required schools to teach children about gender.
- Also, it says, the treaty tries to construct a “socio-cultural gender against the biological gender”.
Istanbul Convention:
- It is also called the Council of Europe Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence.
- The treaty is the world’s first binding instrument to prevent and tackle violence against women.
- It is the most comprehensive legal framework that exists to tackle violence against women and girls, covering domestic violence, rape, sexual assault, female genital mutilation (FGM), so-called honor-based violence, and forced marriage.
- The Convention sets minimum standards for governments to meet when tackling violence against women.
- When a government ratifies the Convention, it are legally bound to follow it.
- As of March 2019, it has been signed by 45 countries and the European Union.
- The convention was adopted by the Council of Europe Committee of Ministers on 7 April 2011.
4.Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH):

81 projects have been approved so far under the Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing (SWAMIH) fund.
- The approval, under the SWAMIH Investment Fund I, will enable the completion of nearly 60,000 homes across India.
SWAMIH:
- In November 2019, the Union Cabinet cleared a proposal to set it up.
- SWAMIH Investment Fund has been formed to complete construction of stalled, RERA-registered affordable and mid-income category housing projects which are stuck due to paucity of funds.
- The fund was set up as a Category-II AIF (Alternate Investment Fund) debt fund registered with SEBI.
- The Investment Manager of the Fundis SBICAP Ventures, a wholly-owned subsidiary of SBI Capital Markets, which in turn is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the State Bank of India.
- The Sponsor of the Fundis the Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Government of India on behalf of the Government of India.
- AIFs created/funded under the Special Window would solicit investment into the fund from the Government and other private investors including cash-rich financial institutions, sovereign wealth funds, public and private banks, domestic pension and provident funds, global pension funds, and other institutional investors.
5.Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) 2020:
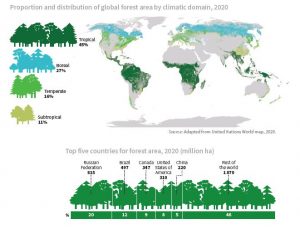
Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) 2020 was recently released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
- FAO has brought out this comprehensive assessment every five years since 1990.
This report assesses the state of forests, their conditions, and management for all member countries. - According to FRA 2020, the top 10 countries that have recorded the maximum average annual net gains in a forest area during 2010-2020 are:
- China
- Australia
- India
- Chile
- Vietnam
- Turkey
- The United States’
- France
- Italy
- Romania
Key findings:
- The Asian continent reported the highest net gain in a forest area in 2010-2020. It recorded a 1.17 million hectares (ha) per year net increase in forests in the last decade.
- South Asia sub-region reported net forest losses during 1990-2020.
- During the decade under assessment, India reported 0.38 per cent annual gain in forest, or 266,000 ha of forest increase every year at an average.
- The FRA 2020 has credited the government’s Joint Forest Management program for the significant increase in community-managed forest areas in the Asian continent.
- The forest area managed by local, tribal, and indigenous communities in India increased from zero in 1990 to about 25 million ha in 2015.
- However, the naturally regenerating forest rate is disappointing, according to the assessment. During 2010-20, the rate of increase in naturally regenerating forest was just 0.38 percent.
- India reported maximum employment in the forestry sector in the world. Globally, 12.5 million people were employed in the forestry sector. Out of this, India accounted for 6.23 million, or nearly 50 percent.
6.Assessment of Climate Change over Indian Region’:

The first ‘Assessment of Climate Change over Indian Region’ was recently released by the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Report:
- Temperature: By the end of the 21st century, the average temperature over India is projected to rise by 4.4°C, relative to the average temperature during 1976-2005.
- Heatwaves: In the coming decades, the average duration of heatwaves during April-June is projected to double, and their frequency to rise by 3 to 4 times compared to 1976-2005.
- Monsoon: The coming decades are projected to witness a considerable rise in the mean, extreme and inter-annual variability of rainfall associated with the monsoon.
- Floods: Flood risks are higher over the east coast, West Bengal, eastern Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Konkan and cities like Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata. The Himalayan flood basins are projected to greater floods, due to the faster glacial and snow melting.
- Droughts: Eastern India could face two more droughts per decade compared to what was experienced during 1976-2005, while the Southern Peninsula is projected to experience one or two droughts fewer.
- Sea level: In an extreme climate scenario, a risk of inundation looms over Andhra Pradesh and Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta basins. By 2030, some 340 million coastal residents of the North Indian Ocean and its islands would be exposed to coastal hazards.
- Tropical cyclones: Storms in the Arabian Sea are gaining more strength and the trend is projected to continue. The number of extremely severe cyclonic storms formed in the Arabian Sea has increased in the last 20 years.
- Himalaya snow cover: By the end of the century, the Hindukush Himalayas are projected to be warmer by 2.6-4.6°C.
7.100th birth anniversary of Rosalind Franklin,

The 100th birth anniversary of Rosalind Franklin, a leading virologist of her time was observed recently.
- Rosalind Franklin (1920 – 1958) was an English chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA, RNA, viruses, coal, and graphite.
- She is best known for her work on the X-ray diffraction images of DNA, particularly Photo 51, which led to the discovery of the DNA double helix for which James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962.
- She would have ideally been awarded a Nobel Prize in Chemistry, but the Nobel Committee generally did not make posthumous nominations.
- Photo 51 is an X-ray diffraction image of a paracrystalline gel composed of DNA fiber taken by Raymond Gosling, working under the supervision of Rosalind Franklin in May 1952.
- The image was tagged “photo 51” because it was the 51st diffraction photograph that Franklin and Gosling had taken. It was critical evidence in identifying the structure of DNA.
Other important current affairs:
1. Recently, HIL (India) Limited supplied 20 Metric tonnes of DDT to South Africa for their Malaria control program.
- HIL (India) Limited is a PSU under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- It is the sole manufacturer of DDT globally.
- The company was incorporated in the year 1954 to manufacture and supply DDT to the Government of India’s Ministry of Health for the malaria control program.
- The Company is also exporting the product to many African countries.
- Spraying of insecticides inside the human habitats i.e. Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS) has proven to be an effective mosquito control tool. World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends DDT as one of the efficient IRS chemicals to curb malaria mosquito menace.
- Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound.
2. Last week, the Supreme Court of India suo motu registered a case of contempt against lawyer Prashant Bhushan.
- He stands accused of Criminal contempt.
- The court registered the proceedings after a petition was moved citing two tweets Bhushan had published over the last two months.
- In the tweets, the lawyer had commented on Chief Justice of India SA Bobde and about the general functioning of the court under the last four chief justices.
- The court said it found the tweets prima facie contempt.
- The contempt of court law is one of the most controversial elements in the Indian legal context.
- While the basic idea of contempt law is to punish those who do not respect the orders of the courts, in the Indian context, contempt is also used to punish speech that lowers the dignity of the court and interferes with the administration of justice.
- Contempt of court can be of two kinds:
- Civil, that is the willful disobedience of a court order or judgment or willful breach of an undertaking given to a court.
- Criminal, that is written or spoken words or any act that scandalizes the court or lowers its authority or prejudices or interferes with the due course of a judicial proceeding or interferes/obstructs the administration of justice.
- Article 129 and 215 of the Constitution of India empowers the Supreme Court and High Court respectively to punish people for their respective contempt.
- Section 10 of The Contempt of Courts Act of 1971 defines the power of the High Court to punish contempts of its subordinate courts.
3.Kargil Vijay Diwas(26th july)
- The day commemorates the success of “Operation Vijay” launched by the Indian Army to recapture the Indian territories from Pakistani intruders in the Kargil-Drass sector in 1999.
- The Kargil war took place despite the two nations signing the Shimla Agreement that stated that no armed conflict shall take place on the said boundary.
- The Indian and Pakistani armies fought the Kargil War in May-July 1999 in Kargil and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC).
- Safed Sagar, the Indian Air Force’s operation, was a major part of the Kargil war.
4. Researchers have found that the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 changes its form after it attaches itself to a human cell, folding in on itself and assuming a rigid hairpin shape. The researchers believe the knowledge can help in vaccine development.
- It is a protein that protrudes from the surface of a coronavirus, like the spikes of a crown or corona — hence the name ‘coronavirus’.
- In the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, it is the spike protein that initiates the process of infection in a human cell.
- It attaches itself to a human enzyme, called the ACE2 receptor, before going on to enter the cell and make multiple copies of itself.
5. The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has launched the India-Russia Joint Technology Assessment and Accelerated Commercialization Programme.
- The program has been launched by DST in partnership with the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) and Foundation for Assistance to Small Innovative Enterprises (FASIE) of the Russian Federation. On behalf of DST, FICCI will implement the program in India.
- The program will connect Indian, and Russian Science & Technology (S&T) led SMEs and Start-ups for joint R&D for technology development and for cross-country technology adaptation.
- The program will run through two annual cycles with up to five projects to be funded under each cycle. Projects are being sought on leading S&T focus areas.
- Over a period of two years, the DST will fund up to INR 15 Crores to ten Indian SMEs/Start-ups and FASIE will provide similar funding to the Russian projects.
6. Ministry of Shipping has decided to waive waterway usage charges with immediate effect to promote inland waterways.
- The charges are waived initially for three years. Water usage charge was applicable on the use of all the national waterways by vessels.
- Currently, only 2% of the total cargo traffic moves through waterways.
- The decision of waiving waterway charges will attract the industries to use the national waterways for their logistical needs.
- The decision is estimated to increase the inland waterway traffic movement to 110MMT in 2022-23 from 72MMTin 2019-20
7. India has collaborated with the Israeli defense companies under the new liberalized Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) regime in defense manufacturing.
- Earlier, the government has increased the limit for FDI in defense through the automatic route from 49% to 74%.
- FDI is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country.
- Recently, the Defence Ministry has given emergency powers to the Armed Forces to procure weapons systems up to Rs. 300 crore on an urgent basis without any further clearances to cut short the procurement cycle.
- Therefore, Indian Armed Forces are undertaking a series of emergency defense purchases amid ongoing tensions with China on the border.
- The Army has decided to order launchers, Spike Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM), and additional Heron Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), from Israel through the emergency procurement route.
8. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has issued a warning that a huge “Asteroid 2020 ND” will move past Earth on 24th July.
- The asteroid, about 170 meters-long, will be as close as 0.034 Astronomical Unit (AU- Astronomical Unit is the distance between the Earth and the Sun and is roughly 150 million km) to the Earth, and is traveling at a speed of 48,000 kilometers per hour.
- It is a Near-Earth Object (NEO) and its distance from Earth has placed it in the Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHA) category.
- Potentially Hazardous Asteroids:
- It means that an asteroid has the potential to make threatening close approaches to the Earth.
- Specifically, all asteroids with a Minimum Orbit Intersection Distance (MOID) of 0.05 AU (which is about 7,480,000 Km) or less and an Absolute Magnitude (H) of 22.0 (about 150 mt in diameter) or less are considered PHAs.
- MOID is a method for calculating the minimum distance between two almost overlapping elliptical orbits.
The absolute magnitude is a measure of the star’s luminosity i.e. the total amount of energy radiated by the star every second.
9. Hurricane Hanna has made landfall (the point at which a hurricane reaches land) in Texas with life-threatening storm surge and strong winds.
- Tropical cyclones are called hurricanes in the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- It has reached wind speeds of up to 90 mph and is expected to produce heavy rains across portions of southern Texas and northeastern Mexico, which will result in flash flooding and isolated minor to moderate river flooding.
- It has been categorized as a Category 1 storm on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).
- This year, an “above-normal” hurricane season is expected in the USA.
- One reason for this is the warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the tropical Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, along with weaker tropical Atlantic trade winds and an enhanced west African monsoon.
10. The government has announced that Haryana will host the fourth edition of the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG).
- The 2021 Khelo India Youth Games are scheduled to take place after the 2021 Tokyo Olympics and will be held in Panchkula (Haryana).
- The 2021 Tokyo Olympics are set to open on 23rd July.
- In 2020, for the first time, the Olympics were postponed following the Covid-19 outbreak.
- Usually, the KIYG takes place in January of every year.
- KIYG is a part of the revamped national program for the development of sports ‘Khelo India’ which was approved by the Union Cabinet in 2017.
- The 2020 edition of KIYG was held in Guwahati (Assam).
- The Khelo India Scheme aims to encourage sports all over the country, thus allowing the population to harness the power of sports through its cross-cutting influence, namely holistic development of children & youth, community development, social integration, gender equality, healthy lifestyle, national pride and economic opportunities related to sports development.
- Under the Scheme, talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels are provided annual financial assistance of Rs. 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
- Khelo India App, developed by the Sports Authority of India (SAI), aims to create awareness about sports and fitness in the country.
- SAI is under the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
11. Recently, the Bombay High Court said that the Nag river has become extremely polluted due to industrialization and urbanization.
- Nagpur city derives its name from the Nag river which passes through the city.
- The Nag river originates from the Ambazari Lake in west Nagpur.
- Major Tributaries – Pili river.
- Endpoint – confluence with Kanhan River.




