Today Current Affairs: 28th March 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
What Is Institutional Delivery?
It has been a decade-and-a-half since India started incentivising institutional deliveries to ensure safe childbirths. But health indicators for mothers and infants have not improved as much as the number of such deliveries.
- Institutional Delivery means giving birth to a child in a medical institution under the overall supervision of trained and competent health personnel.
- It also signifies an availability of amenities to handle the situation and save the life of the mother and child.
- The share of India’s institutional deliveries increased to 88.6% in 2019-2021 (National Family Health Survey 5 (NFHS-5) from 40.8 % in 2005-06 (NFHS 3).
- The nine targeted states Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Assam recorded a similar uptick during the period, ranging from 50-64 % points.
- Madhya Pradesh led the way with a 64.5 % point growth.
- These states account for nearly half of India’s population, over 60% of maternal deaths, 70% of infant deaths and 12% of global maternal deaths.
- Maternal mortality ratio (MMR), infant mortality rate and neonatal mortality rate (NMR), have not improved at the same pace as institutional births.
- The nine focus states continue to have the highest MMR, a majority of which are well beyond India’s national average of 103.
- Healthcare delivery and service utilisation are very different in two groups of India’s states those performing better than the national average and those lagging behind.
- The country as a whole may be able to meet the United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goal of reducing MMR to 70 by 2030, but the lagging states will continue to perform poorly unless given an impetus.
What Is Bucharest Nine?
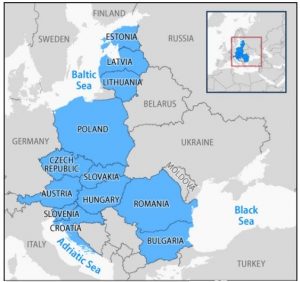
The Bucharest Nine (B 9) rejected the Russian claim about the eastward “expansion” of North-Atlantic Treaty Alliance organisation (NATO).
- They underlined that NATO is not an organisation that “expanded” to the east”, rather, these countries as the independent European states that decided on our own to go west.
- The B 9 is a group of nine NATO countries in Eastern Europe that became part of the US-led military alliance after the end of the Cold War.
- The B 9 or Bucharest Format, often abbreviated as the B9, was founded on November 4, 2015.
- It takes its name from Bucharest, the capital of Romania.
- B9, it is also regarded as the “voice of the Eastern Flank” in the NATO alliance.
- The group was created on the initiative of Klaus Iohannis, who has been President of Romania and Andrzej Duda, who became President of Poland in August 2015, at the High-Level Meeting of the States from Central and Eastern Europe in Bucharest.
- The members of B9 are Romania and Poland, Hungary, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and the three Baltic republics of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- B9 offers a platform for deepening the dialogue and consultation among the participant allied states across the members of NATO.
- All nine countries were once closely associated with the now dissolved Soviet Union, but later chose the path of democracy.
- All members of the B9 are part of the European Union (EU) and NATO.
- The B9 countries have been critical of Russia’s aggression against Ukraine since 2014, when the war in the Donbas started and Russia annexed the Crimean peninsula.
Earth Hour 2022:

Earth Hour was observed on March 26, 2022 (Saturday) from 8:30 to 9:30 PM.
- It is the world’s largest grassroots movement for the environment where people around the globe unite to take a stand against climate change by turning off non-essential lights for one hour.
- Starting out as a symbolic lights-out event in Sydney in 2007, it has come to be observed every year on the last Saturday of March in more than 180 countries uniting millions of people in the effort to decarbonise the planet both collectively and individually.
- The “theme for this year’s global event was “Shape our Future”, highlighting our collective responsibility towards the environment.
Extension Of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana:

The Union Cabinet extended the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY) by another six months till September 2022.
- The scheme was originally introduced in April 2020 a month into the first lockdown during the initial onset of the COVID pandemic.
- This will be the sixth phase of PM-GKAY. The Phase-V of the scheme was to end in March 2022.
- The government has spent approximately ₹2.6 lakh crore so far and another ₹80,000 crore will be spent over the next six months till September 2022, taking the total expenditure under PM-GKAY to nearly ₹3.4 lakh crore.
- The ration card portability has also helped in extending the schemes to the migrant workers.
- The benefit of free ration can be availed through portability by any migrant labourer or beneficiary under One Nation One Ration Card plan from nearly five lakh ration shops across the country.
- So far, over 61 crore portability transactions have benefitted the beneficiaries away from their homes.”
Export Preparedness Index 2021:

NITI Aayog, in collaboration with the Institute of Competitiveness, has released the second edition of the Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2021.
- The first Index was launched in August 2020.
- The Export Preparedness Index is a comprehensive analysis of India’s export achievements.
- It aims to identify the fundamental areas critical for subnational export promotion.
- The coastal states have been adjudged as the best performers in the index.
- The index ranked states on four key parameters – policy; business ecosystem; export ecosystem; export performance.
- The index also took into consideration 11 sub-pillars — export promotion policy; institutional framework; business environment; infrastructure; transport connectivity; access to finance; export infrastructure; trade support; R&D infrastructure; export diversification; and growth orientation.
Performance of various states:
- Gujarat has topped NITI Aayog’s Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2021 for the second consecutive time.
- Maharashtra has been ranked second and Karnataka has been ranked third.
Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Bill:

The bill will be tabled in the Parliament.
- It aims to merge the Capital’s three municipal corporations — South, North and East — ten years after the trifurcation of the civic body.
- In 2011, the state government had proposed the trifurcation for better efficiency.
Constitutional Provisions related to Municipal Corporations:
- In the Constitution of India, no provision was made for the establishment of local self-government, except the incorporation of Article 40 in the Directive Principles of State Policy.
- The 74th Amendment Act, 1992 has inserted a new Part IX-A into the Constitution which deals with the administration of Municipalities and Nagar Palikas.
- It consists of Article 243P to 243ZG.
- It also added a new twelfth schedule to the Constitution.
- The 12th schedule consists of 18 items.
Challenge To The Constitutional Validity Of PM-CARES Fund:

The Supreme Court has refused to entertain an appeal challenging an Allahabad High Court order which rejected a challenge to the constitutional validity of the PM-CARES Fund.
- The High Court had dismissed the PIL which challenged the validity of the PM-CARES Fund and the Prime Minister National Relief Fund in the backdrop of the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- The petitioner had contended that the fund was established without statutory backing and was kept beyond the scrutiny of the RTI Act.
- PM CARES has been under a cloud of suspicion ever since it was announced, with opposition parties demanding transparency over the handling of the funds.
About PM-CARES:
- The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations (PM-CARES) Fund was set up to accept donations and provide relief during the Covid-19 pandemic, and other similar emergencies.
PM-CARES Fund:
- PM-CARES was set up as a public charitable trust with the trust deed registered on March 27, 2020.
- It can avail donations from the foreign contribution and donations to fund can also avail 100% tax exemption.
- PM-CARES is different from the Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund (PMNRF).
- rime Minister is the ex-officio Chairman of the PM CARES Fund and Minister of Defence, Minister of Home Affairs and Minister of Finance, Government of India are ex-officio Trustees of the Fund.
- In 2021, the Delhi High Court was informed that the PM CARES Fund is not a Government of India fund and that the amount collected by it does not go to the Consolidated Fund of India.
Wildlife Conservation Bond:

The world’s first wildlife bond has been issued by the World Bank, raising USD 150 million that will partly be used for the conservation of South Africa’s black rhinos.
- The Wildlife Conservation Bond is the world’s first-of-its-kind financial instrument that is outcome-based to conserve black rhino populations.
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development of the World Bank has announced that the returns paid by the five-year bond will be determined by the rate of population growth of animals in two reserves of South Africa, the Great Fish River Nature Reserve and the Addo Elephant National Park.
- If this program is successful it could be expanded for the protection of black rhinos in Kenya along with other wildlife species like tigers, lions, orangutans, and gorillas.
- Similar bonds have earlier been issued to finance various outcomes from marine projects in Seychelles to the education of girls in rural India.
- Globally, there are five species of rhino.
- Most of the rhinoceros are concentrated in South Africa with most of them being white rhinos.
- The number of Black rhinos has dropped significantly from 65000 in 1970 to around 2600.
- These animals are found in three other countries of Africa.
- They weigh as much as 1.4 tons and are much smaller as compared to the white rhinos.
- The issuer, instead of paying a coupon, will be making contributions towards the conservation of the animals.
- The buyers will be receiving a payment from the Global Environment Facility which will be based on targets that are pre-set for the growth of the animals’ population.
Polar Science And Cryosphere Research Scheme:

The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), an autonomous institute that falls under the ambit of the Ministry of Earth Sciences has successfully implemented the Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER) scheme which comprises of Indian Arctic program, the Antarctic program, Cryosphere, and Climate program, and Southern Ocean
- It has successfully executed the 39th and 40th Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica.
- The 41st Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica is currently ongoing.
- Under this scheme 10 sediment cores have been collected from lakes to reconstruct the climate of the past that is associated with the dynamics of the ice-sheet.
- Various geophysical and glaciological measurements have been carried out in the coastal Dronning Maud Land with the objective to understand patterns of snow accumulation and the glaciochemical process contribution.
- In the lakes of Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica, studies were conducted to understand the biogeochemical process in the supraglacial environments.
- At the Bharati and Maitri stations, clear-air atmospheric observatories which contain automatic weather stations, sensors to measure greenhouse gas and aerosol concentrations have been established.
- Ice core analyses were also conducted to understand the long-term climate variability over Antarctica and dissolved organic carbon pathways.
- Hydrophone system, as well as IndARC mooring system, was successfully deployed in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard.
- In the Arctic Svalbard archipelago, coastal cruises were done to conduct microbial and biogeochemical research.
- Using Arctic regional atmospheric model with Chemistry module, Arctic Regional Ocean Model, and Global sea-ice simulations several modeling initiatives were started.
- The continuation of this scheme has also been approved for the 221-26 period.
INS Valsura Has Been Awarded The Prestigious President’s Colour:

The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Valsura has been awarded the prestigious President’s Colour by President Ram Nath Kovind.
- To mark this occasion, a guard of honour of 150-men was presented to the President and a ceremonial parade was held.
About President’s Colour Award:
- It is the highest award or honour that can be bestowed upon any of India’s military units.
- This award is also called ′Nishaan′ as it is an emblem that will be worn by the bestowed units’ officers on their left-hand sleeve of the uniform.
- This awards presentation acts as an acknowledgment of the receiving unit’s meritorious service.
- Although the practice of carrying the President’s Colour Award into battle has ceased, the custom of receiving, holding, and parading it is still practiced in the Armed Forces.
- This award can be bestowed on a military unit as a sign of recognition of exceptional service rendered to the country, both during war and peace.
About INS Valsura:
- In 1942 INS Valsura was established. It is one of Indian Navy’s premier training establishment.
- INS Valsura has been entrusted with the responsibility of training the sailors and officers who are part of the Indian Navy, and Coast Guard.
- Foreign countries having a friendly relationship with India are also trained here. Training is imparted on electronics, electrical, information technology, and weapon systems.
Indian Antarctic Bill 2022:

A Draft legislation has been approved by India’s Union Cabinet to provide a regulatory framework for research activities of India in Antarctica and also to protect the continent’s environment.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences has piloted the Indian Antarctica Bill.
- This bill is expected to help fulfill the nation’s obligations under the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources of 1982, the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, and 1998s Treaty of the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic.
- This bill is going to be introduced in the Budget Session of the Parliament which is ongoing.
- India’s Antarctic program began in the year 1981 and since then 40 scientific expeditions have been completed.
- India has also built three bases on the continent.
- As of now, India has two fully functioning base stations in Antarctica named Maitri which was established in 1988, and Bharati which was established in 2012. Another one named Dakshin Gangotri was established in 1983 but it is not functional currently.
Air Traffic Management System:
The Airports Authority of India (AAI), under its R&D initiative, has signed an agreement with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) to jointly develop indigenous Air Traffic Management System.
- Under this Agreement, BEL and AAI will jointly develop Civil Air Traffic Management System (ATMS) with Advanced-Surface Movement Guidance and Control System (ASMGCS), a complex ground surveillance system that manages air traffic at airports and in Indian Civil Airspace for safe operation of flights from take-off to landing.
- Air traffic management and control primarily involves the control of traffic in and around airports, airport terminals and airspace.
- Air traffic controllers that work from Air Traffic Control (ATC) towers are responsible for ensuring a safe distance between all aircraft, both in the air and on the ground, to prevent accidents.
- Air traffic controllers prevent collisions and maintain an orderly flow of air traffic
- It will help in leveraging the complementary strengths and capabilities of BEL and AAI and enabling both to address airport modernization opportunities.
- It will ensure safety, maintain separation between multiple aircraft, and efficient management of operations at the airport and Indian airspace.
- It aims to upgrade its ANS (Air Navigation Services) Infrastructure in systematic, efficient and cost-effective manner and in compliance with the ‘Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ missions of the Government of India.
- It will reduce AAI’s foreign dependency for procurement of ANS infrastructure.




