Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 5th August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- The grand temple at Rama Janmabhoomi in Ayodhya will follow the Nagara style of temple architecture:
- Three capitals for Andhra Pradesh::
- One Nation-One Ration Card:
- .Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme:
- Other important current affairs:
1. The grand temple at Rama Janmabhoomi in Ayodhya will follow the Nagara style of temple architecture:

The Nagara style of temple architecture is found in northern India.
- In the Nagara style, the temple is generally constructed on an upraised platform called jagati.
- Mandapasare present in front of the Garbhagriha. These are adorned with the Shikhara, the tallest one being above the Garbhagriha.
- Nagara style doesn’t usually have elaborate boundary walls or gateways.
- Generally, there is no water tank in the temple premises and the pradakshina patha is covered.
- The garbhagriha is always located directly under the tallest tower.
- The basic form of a Hindu temple contains the following architectural elements:
- Garbhagriha– the small room where the principal deity/deities of the temple reside
- Mandapa– the portico or hall at the entrance of the temple generally designed to house a large number of people
- Shikhara– the mountain like spire which can have different shapes from pyramidal to curvilinear
- Vahana– the mount or vehicle of the main deity placed generally in line of sight from Garbhagriha
- Nagara school is further subdivided into different schools based on regions like Odisha, Khajuraho, Solanki, etc.
2. Three capitals for Andhra Pradesh::
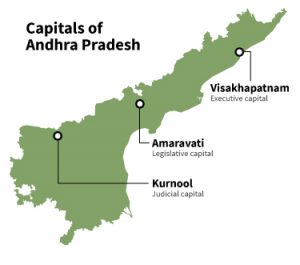
The Andhra Pradesh high court has stayed the notifications issued by the YSR Congress government on the formation of three capitals for the state till August 14.
- Various petitions were filed opposing the three capitals move and demanding a stay on the two new acts.
In response, the Court has granted a stay on the implementation of the gazette notifications and asked the state government to file a counter within 10 days. - Andhra Pradesh Assembly, in January 2020, passed The Andhra Pradesh Decentralisation and Equal Development of All Regions Bill, 2020.
- On July 31 the state government notified the AP Decentralisation and Inclusive Development of All Regions Act, 2020, and the AP Capital Region Development Authority (Repeal) Act, 2020.
- This law paves the way for three capitals for the state.
- Amaravati– legislative capital.
- Visakhapatnam– executive capital.
- Kurnool– judicial capital.
- The government says it is against building one mega capital while neglecting other parts of the state.
- Three capitals ensure equal development of different regions of the state.
- Decentralization has been the central theme in recommendations of all major committees that were set up to suggest a suitable location for the capital of Andhra Pradesh.
- These include Justice B N Srikrishna Committee, K Sivaramakrishnan Committee, G N Rao Committee, etc.
- Coordination and logistics fear: Coordinating between seats of legislature and executive in separate cities will be easier said than done, and with the government offering no specifics of a plan, officers and common people alike fear a logistics nightmare.
- Time and costs of travel: Executive capital Visakhapatnam is 700 km from judicial capital Kurnool, and 400 km from legislative capital Amaravati. The Amaravati-Kurnool distance is 370 km. The time and costs of travel will be significant.
3.One Nation-One Ration Card:

Recently, Manipur, Nagaland, and Uttarakhand, along with the Union Territory (UT) of Jammu and Kashmir have been integrated with the One Nation-One Ration Card (ONORC) Scheme.
- Now a total of 24 States/UTs are connected under the ONORC scheme.
- The remaining states/UTs are targeted to be integrated into the scheme by March 2021.
The ONORC Scheme:
- It was started as inter-State portability of ration cards in 2019.
- It allows the migratory National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013 beneficiaries to lift their entitled quota of food grains from any Fair Price Shop (FPS) of their choice anywhere in the country.
- This can be done by using their existing ration card with Aadhaar based authentication.
- With 24 States/UTs connected under the scheme, about 65 crore beneficiaries, comprising 80% of the total beneficiaries covered under the NFSA, can now get their subsidized ration from anywhere in these 24 states and union territories.
- It will bring more transparency and efficiency in the distribution of foodgrains.
- It will improve the mechanism to identify fake/duplicate ration cards and provide the option to Public distribution system (PDS) beneficiaries to lift their entitled foodgrains from the Fair Price Shops of their choice at the national level.
- The scheme will ensure the food security of migrant laborers who move to other states to seek better job opportunities.
- This will help achieve the target set under Sustainable Developmental Goals (SDG) 2 of ending hunger by 2030.
- Also, it will address the poor state of hunger in India, as highlighted by the Global Hunger Index, where India has been ranked 102 out of 117 countries in 2019.
4.Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme:

Recently, the government has expanded its Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) to cover loans given to larger firms as well as to self-employed people and professionals who have taken loans for business purposes.
- ECLGS was rolled out in May 2020 as part of the Centre’s Aatmanirbhar package in response to the Covid-19 crisis. The objective was to support small businesses struggling to meet their operational liabilities due to the imposition of a nationwide lockdown.
- The ECLGS provides for the Guaranteed Emergency Credit Line (GECL) facility.
- The GECL is a loan for which 100% guarantee is provided by the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company (NCGTC) to Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) – banks, financial institutions and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- The loans are extended in the form of additional working capital term loan facility in case of banks and additional term loan facility in case of NBFCs to eligible Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)/business enterprises and interested Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) borrowers.
- First-time borrowers and Non-Performing Asset (NPA) accounts cannot raise funds under the scheme.
- The tenor of loans provided under the GECL facility is four years from the date of disbursement.
- A moratorium period of one year on the principal amount is provided.
- Interest rates of banks and financial institutions have been capped at 9.25% per annum, while NBFCs can lend at a maximum of 14% per annum.
- The Scheme is applicable to all loans sanctioned under the GECL facility during the period from, 23rd May 2020 to 31st October 2020, or till an amount of Rs. 3 lakh crore is sanctioned under GECL, whichever is earlier.
- Enterprises with a turnover up to Rs. 250 crore with outstanding loans up to Rs. 50 crore (as on 29th February 2020).
- The earlier limit was Rs. 100 crore and Rs 25 crore, respectively.
- Credit under GECL is provided up to 20% of the borrower’s total outstanding credit up to Rs. 25 crore.
- The expansion of the limits has increased the maximum amount of loans that can be availed under the Scheme to Rs. 10 crores (20% of 50 crores) from Rs. 5 crores (20% of 25 crores).
- Individual beneficiaries including both professionals such as doctors, lawyers and chartered accountants, as well as self-employed people such as vendors or taxi drivers.
- The changes in the ECLGS scheme are likely to make an additional Rs 1 lakh crore eligible.
- Till now, a total of around Rs. 1.37 lakh crore has been sanctioned under the scheme by member lending institutions to around 40 lakh accounts, of which around Rs 87,000 crore has been disbursed.
Other important current affairs:
1. Union Agriculture Minister launched the National Cooperative Development Corporation’s YouTube channel, ‘Sahakar Cooptube NCDC India’, to encourage farmers and the youth to take benefit of cooperatives.
- He also released videos on the formation and registration of cooperatives for 18 states in Hindi and regional languages. The videos will be aired on the news channel.
- The guidance videos in different languages covering 18 states would also strengthen and deepen the major initiatives of our government to promote and form 10,000 farmer-producer organizations (FPOs).
- More states will be added to the collection of guidance videos on the Sahakar Cooptube NCDC India channel on YouTube in due course of time.
2. Union Minister for MSME has approved a unique employment generation program proposed by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) to make India Aatmanirbhar in Agarbatti production.
- The program named as “Khadi Agarbatti Aatmanirbhar Mission” aims at creating employment for unemployed and migrant workers in different parts of the country while increasing domestic Agarbatti production substantially. The pilot project will be launched soon.
- The scheme is designed by KVIC on PPP mode. Under the scheme, KVIC will provide Automatic Agarbatti making machines and powder mixing machines to the artisans through the successful private Agarbatti manufacturers who will sign the agreement as business partners.
- KVIC will provide a 25% subsidy on the cost of the machines and will recover the remaining 75% of the cost from the artisans in easy installments every month.
- The business partner will provide the raw material to the artisans for making Agarbatti and will pay them wages on a job work basis.
- Cost of artisans’ training will be shared between KVIC and the private business partner wherein KVIC will bear 75% of the cost while 25% will be paid by the business partner.
3. As the Barakah Nuclear Plant’s 1st Unit got operational, UAE became the first country in the Arab World to produce nuclear energy.
- The Barakah nuclear power plant in the United Arab Emirates’ first nuclear power station, the first nuclear power station in the Arabian Peninsula, and the first commercial nuclear power station in the Arab World.
- It is situated in the Al Dhafrah region of Abu Dhabi.
- It consists of four APR-1400 nuclear reactors (one operational, three mostly completed).
- The plant, powered by South Korean technology, hopes to produce 5.6 gigawatts of electricity and supply up to 25% of the UAE’s electricity needs.
4. Over 120 countries around the world are celebrating the week-long World Breastfeeding Week. The theme of this year is to support breastfeeding for a healthier planet and taking precautionary measures in light of the global pandemic.
- World Breastfeeding Week (WBW) is annually held from 1 to 7 August.
- Objective: To promote exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life which has huge health benefits.
- It is jointly organized by the World Alliance for Breastfeeding Action (WABA), WHO, and UNICEF.
- History: It was first celebrated in 1992 and is now annually observed in more than 100 countries.
5. The Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) has received a funding of ₹455.02 crore for the construction of new academic buildings, hostels, and research centers, among others, under the Union ministry of human resources development (MHRD)’s higher education funding agency (HEFA).
- HEFA incorporated on 31st May 2017, is a joint venture of Ministry of HRD, GOI, and Canara Bank with agreed equity participation in the ratio of 90.91% and 09.09% respectively.
- HEFA is registered under the Companies Act 2013 as a Union Govt company and as Non–deposit-takings NBFC with RBI.
- To enable India’s premier educational institutions to excel and reach the top in global rankings by financing building world-class infrastructure including R&D Infra.
6. United Nations has released its policy brief on the pandemic’s impact on education.
- More than 1.6 billion learners affected across the world by the disruption of the education system.
- Disparities increased: The pandemic has served to exacerbate existing disparities, with vulnerable populations in low-income countries taking a harder and longer hit.
- School dropouts: Almost 24 million children are at risk of not returning to school next year due to the economic fallout of COVID-19.
- Girls and young women are likely to be disproportionately affected as school closures make them more vulnerable to child marriage, early pregnancy, and gender-based violence.
- Learning losses: Even for those who do not drop out of school, learning losses could be severe, especially in the foundational years.
7. Researchers have claimed that vitamin D deficiency can negatively affect Covid-19 high-risk patients, particularly those who are diabetic, have heart conditions, pneumonia, obesity, and those who smoke.
- It is also associated with infections in the respiratory tract and lung injury.
- India has a large population suffering from vitamin D deficiency among the public irrespective of their location (urban or rural), age or gender, or whether they are poor or even rich.
- This is despite India being a tropical nation getting abundant sunshine, which is a precursor to Vitamin D formation in the body.
- According to an analysis published in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2017, the level of vitamin D in people from different states of India ranged between 3.15 nanogram/milliliter to 52.9 ng/ml, which was considerably lower than the needed level of 30-100 ng/ml.
- Vitamin D level among south Indians is 15.74–19.16 ng/ml.
- Females showed consistently lower levels than males.
8. According to a recent study published in Nature Microbiology, the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has been circulating unnoticed in bats for decades.
- Bats have been the ‘primary reservoirs’ for SARS-CoV-2, which is likely to have diverged from closely related bat viruses called the RaTG13 sarbecovirus, 40-70 years ago.
- The current study confirms an earlier Chinese study and also suggests the probable time of divergence of the two viruses.
- According to that Chinese study, SARS-CoV-2 is most closely related to RaTG13, which was isolated from a horseshoe bat in Yunnan province in 2013.
- Based on the nearly 96% genome sequence identity between SARS-CoV-2 and RaTG13, it was held that an origin in bats is probable for the Covid-19 outbreak.
- SARS-CoV-2 has not arisen from recombination of any sarbecovirus
10. The Thenzawl Golf Resort Project in Mizoram has been virtually inaugurated.
- The project was implemented under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme of the Ministry of Tourism, Government of India.
- The project was sanctioned under the Integrated Development of New Eco-Tourism under Swadesh Darshan-North East Circuit at Thenzawl and South Zote, District Serchhip and Reiek, Mizoram.
- Eco-Tourism has been broadly defined as tourism which is ecologically sustainable.
- A total amount of Rs. 92.25 crore was sanctioned for it, out of which Rs. 64.48 crore was sanctioned for various components at Thenzawl including the golf course which is designed to have facilities of international standards.
- The competitive advantage of Thenzawl Golf Course is that it will provide quality golfing experience at a fair price.
- Currently, India has more than 230 golf courses in all out of which several are of international standards and golf events held there attract domestic and international tourists.
11.Parivar Pehchan Patra (PPP):
- Launched by the Haryana government.
- PPP will provide a unique identity to complete family and it would have name of the head of the family on top.
- The name of family member will be added to the ‘Parivar Pehchan Patra’ right after his birth and after marriage of a girl her name will be transferred to the ‘Parivar Pehchan Patra’ of her in-laws.
- PPP will enable the citizens to get the benefits of various central and state government schemes at their door-step in a fair and transparent manner.
12.Beirut:
- A huge explosion recently devastated the port area of the capital Beirut
- The blast was caused by 2,750 tonnes of ammonium nitrate stored unsafely in a warehouse.
- It is the capital and largest city of Lebanon.
- Located on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon’s Mediterranean coast, Beirut is an important regional seaport.




