Today Current Affairs: 7th August 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Plastic-Mixed Handmade Paper:

Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) has secured Patent registration for its innovative Plastic-mixed Handmade Paper developed to reduce plastic menace from nature.
- The plastic-mixed handmade paper (which is recyclable and eco-friendly) was developed under Project REPLAN (REducing PLAstic from Nature).
- The project was launched in September 2018 as part of KVIC’s commitment to Swachh Bharat Abhiyaan.
- It aims to make carry bags by mixing processed and treated plastic waste with cotton fibre rags in the ratio 20:80.
- This is the first of its kind project in India, where plastic waste is de-structured, degraded, diluted and used with paper pulp while making handmade paper and thus reduces plastic waste from nature.
- The invention is aligned with the Prime Minister’s call for fighting the menace of single-use plastic.
- The production of waste-plastic mixed handmade paper is likely to serve the twin objectives:
- Protecting the environment
- Creating sustainable employment
- The technology developed by KVIC uses both high & low density waste polythene that not only adds extra strength to the paper but also reduces the cost by up to 34%.
- KVIC has developed products such as carry bags, envelopes, files/folders, etc. using plastic mixed handmade paper.
E-Prisons Project:
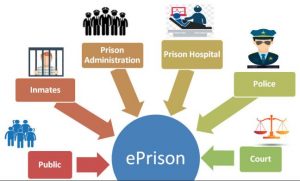
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has provided financial assistance of Rs. 99.49 crores to the States and Union Territories (UTs) for the E-Prisons Project.
- Also, acting on the request of the MHA, NIMHANS, an Institute of National Importance, has recently issued a set of guidelines on the management of mental health issues of the prisoners and prison staff.
- This project aims at computerization of the functioning of prisons in the country. It has been operationalised in all States and Union Territories.
- e-Prisons data has been integrated with the Police and Court system under the Inter-operable Criminal Justice System.
- ePrisons application suite has been developed by National Informatics Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY).
- It has 3 components:
- e-Prison Management Information System (MIS): It is used at the prisons for their day to day regular activities.
- National Prisons Information Portal: It is a citizen centric portal showing statistical data of various prisons in the country.
- Kara Bazaar: Portal for showcasing and selling the products manufactured in various prisons of the country by inmates.
Inter-operable Criminal Justice System:
- It is a common platform for information exchange and analytics of all the pillars of the criminal justice system comprising Police, Forensics, Prosecution, Courts, Prisons.
- Purpose: To reduce errors and time taken in sharing of necessary information between the pillars, which often lead to larger challenges like longer duration of trials, poorer convictions, transit losses of documents etc.
- Some other critical benefits arising out of the ICJS ecosystem are usable analytics products like the National Database on Sexual Offenders (NDSO) to identify & track repeat and habitual sexual offenders.
MK Bhan Fellowship-Young Researcher Fellowship Programme (MKB-YRFP):

The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India, announced the results of the First MK Bhan Fellowship-Young Researcher Fellowship Programme (MKB-YRFP), which was instituted to honour eminent scientist and Former Secretary of the DBT.
- The Department established the MK Bhan Fellowship-Young Researcher Fellowship Programme (MKB-YRFP) with an aim to encourage young bright researchers below 35 years of age to continue their research in the country after Ph.D. in any branch of Life Sciences/ Biotechnology/allied areas.
- The scheme offers an independent research grant for three years to the young Post-Doctoral Fellows to enable them to emerge as future leaders and take up cutting edge research focused on issues of national relevance.
- This Fellowship, entails a monthly emolument of Rs 75,000.
- Maharaj Kishan Bhan (1947 – 2020) was an Indian pediatrician and clinical scientist.
- He was known for developing Rota Viral Vaccine in collaboration with Bharat Biotech International.
- He was positioned as Secretary, Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, until 2012.
The Mekedatu Project:

Tamil Nadu has protested against Karnataka’s move to build a reservoir on river Cauvery at Mekedatu. However, the Karnataka Government has asserted that there is no “compromise” on the Mekedatu project and the state wants to undertake the project.
- Meanwhile, the Centre has said the project required the approval of the Cauvery Water Management Authority’s (CWMA).
- The Detail Project Report (DPR) sent by Karnataka was tabled in the CWMA several times for approval, but the discussion on this issue could not take place due to a lack of consensus among party states Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Also, as per the Cauvery Water Dispute Tribunal‘s final award, which was modified by the Supreme Court, acceptance of CWMA would be a prerequisite for consideration of the DPR by the Jal Shakti Ministry.
- Since the project was proposed across an inter-state river, it required approval of lower riparian state(s) as per the interstate water dispute act.
- Mekedatu is a multipurpose (drinking and power) project.
- It involves building a balancing reservoir, near Kanakapura in Ramanagara district in Karnataka.
- The project once completed is aimed at ensuring drinking water to Bengaluru and neighboring areas (4.75 TMC) and also can generate 400 MW power.
- The estimated cost of the project is Rs 9,000 crore.
- Tamil Nadu is against this project becausenIt says, the CWDT and the SC have found that the existing storage facilities available in the Cauvery basin were adequate for storing and distributing water so Karnataka’s proposal is ex-facie (on the face of it) untenable and should be rejected outright.
- It has also held that the reservoir is not just for drinking water alone, but to increase the extent of irrigation, which is in clear violation of the Cauvery Water Disputes Award.
The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

The Rajya Sabha has passed the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021. The Bill amends the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
Highlights of the Bill:
- The Bill removes the Abor tribe from the list of identified STs in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It replaces certain STs with other tribes. This includes Tai Khamti, Mishmi-Kaman (Miju Mishmi), Idu (Mishmi) and Taraon (Digaru Mishmi).
- The Constitution empowers the President to specify the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in various states and union territories.
- Further, it permits Parliament to modify this list of notified STs.
Samagra Shiksha Scheme 2.0:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the school education programme Samagra Shiksha Scheme 2.0 till the 2025-26 financial year.
- It has been upgraded to align it with the Sustainable Development Goal for Education and the new National Education Policy launched in 2020.
About Samagra Shiksha Scheme:
- It is an integrated scheme for school education covering the entire gamut from pre-school to class XII.
- It aims to deliver inclusive, equitable, and affordable school education.
- It subsumes the three Schemes of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) and Teacher Education (TE).
- The scheme covers 1.16 million schools, over 156 million students and 5.7 million Teachers of Govt. and Aided schools (from pre-primary to senior secondary level).
- It is being implemented as a centrally sponsored scheme. It involves a 60:40 split in funding between the Centre and most States. It was launched by the Ministry of Education in 2018.
About Samagra Shiksha Scheme 2.0:
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- In order to enhance the direct outreach of the scheme, all child-centric interventions will be provided directly to the students through DBT mode on an IT-based platform over a period of time.
- This DBT would include RTE (Right to Education) entitlements such as textbooks, uniforms and transport allowance.
On NEP Recommendations:
- Encouraging Indian languages:
- It has a new component for appointment of language teachers, which includes salaries, and training costs as well as bilingual books and teaching learning material as recommended in NEP.
- Pre-primary Education:
- It will now include funding to support pre-primary sections at government schools, i.e. for teaching and learning materials, indigenous toys and games and play-based activities.
- Master trainers for pre-primary teachers and anganwadi workers will be supported under the scheme.
- NIPUN Bharat Initiative:
- Under this initiative, an annual provision of Rs. 500 per child for learning materials, Rs. 150 per teacher for manuals and resources and Rs. 10-20 lakh per district will be given for assessment for foundational literacy and numeracy.
- On Digital Initiatives:
- There is a provision for ICT labs and smart classrooms, including support for digital boards, virtual classrooms and DTH channels which have become more important in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- For out-of-school children:
- It includes a provision to support out of school children from age 16 to 19 with funding of Rs. 2000 per grade to complete their education via open schooling.
- There will also be a greater focus on skills and vocational education, both for students in school and dropouts.
Jammu And Kashmir (J&K) Completing Two Years As Union Territory:
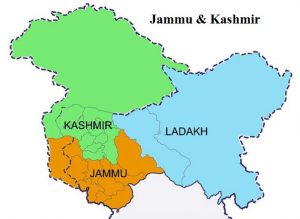
The Forum for Human Rights in J&K (FHRJK) released its report a day ahead of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) completing two years as Union Territory.
- The report raised concerns about the militancy that continues to remain a major challenge in J&K.
- FHRJK is an independent body co-chaired by former Supreme Court judge Justice Madan B. Lokur and former Kashmir interlocutor Radha Kumar.
- On 5 August 2019, the government of India revoked the special constitutional status of the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370 of the Constitution, and abrogated Article 35A.
- Article 35A had allowed J&K to define who its ‘permanent residents’ are and what rights and privileges are attached to such residency.
- The former state was bifurcated into the Union Territories of Ladakh (without a legislature) and Jammu-Kashmir (with a legislature).
Concurrently, the Indian government imposed a near-total telecommunications lockdown in the region, detained political leaders and dissidents, and enforced Section 144 of the Indian Penal Code to prevent violent unrest.
Findings from the Report:
- The reports raised concerns regarding human rights abuses, arbitrary detentions, prohibition on assembly and censorship on local media houses in J&K.
- The government has taken several positive steps, but they fell short of expectations.
- It also held that the counter-insurgency concerns continue to be given priority over public, civilian and human security.
Retrospective Tax Law Of 2012:

The Government of India took the first step towards doing away with the contentious retrospective tax law of 2012, which was used to raise large tax demands on foreign investors such as Vodafone and Cairn Energy, and blamed for vitiating India’s investment climate.
- Union Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister introduced the Taxation Laws (Amendment) Bill in the Lok Sabha on Thursday to nullify the relevant retrospective tax clauses that were introduced in 2012 to bring past indirect transfer of Indian assets under the ambit of taxation.
- As per the proposed changes, any tax demand made on transactions that took place before May 2012 shall be dropped, and any taxes already collected shall be repaid, albeit without interest.
- To be eligible, the concerned taxpayers would have to drop all pending cases against the government and promise not to make any demands for damages or costs.
- Former Finance Minister, the late Pranab Mukherjee, had introduced the retrospective taxation power after the Supreme Court held that Vodafone could not be taxed for a 2007 transaction involving its purchase of a 67% stake in Hutchison Whampoa for $11 billion.
Tunisia:

After ten years of democracy and multiple leaders struggling to keep up with it, Tunisia faces its biggest turmoil as President Kais Saied suspended Prime Minister Hichem Mechichi and Parliament over a week ago.
- The President stated that the move was taken amidst the economic trouble the country has been facing for years and the government’s mishandling of the coronavirus pandemic.
- Tunisia, which was supposed to be a hope of democracy in the Arab world, has seen leader after leader come with little to no relief to the citizens of the country.
- Tunisia is the northernmost country in Africa.
- It is a part of the Maghreb region of North Africa, and is bordered by Algeria, Libya and the Mediterranean Sea.
- It contains the eastern end of the Atlas Mountains and the northern reaches of the Sahara desert.
- Tunisia is home to Africa’s northernmost point, Cape Angela.
- Its capital and largest city is Tunis.
- Tunisia’s democratic history/Arab Spring
- In January 2011, Tunisia erupted into protests against the authoritarian government of Zine al-Abedine Ben Ali after a fruit seller, who was harassed by the police, killed himself.
- The demonstrations were so widespread that Tunisian authorities were overwhelmed. This led to Ali fleeing to Saudi Arabia.
- The unrest spread across the middle east — protests in Egypt, Bahrain, Yemen, Iran and Algeria; civil wars in Libya and Syria and all middle eastern countries facing protests. This unrest was termed as “Arab Spring”.
- Tunisia was a country where democracy came out as a solution to the protests. In October 2011, Tunisia held its first democratic elections.




