Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 8th September 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Forex Reserves:
- RBI’S Plan:
- The report on ‘Household Social Consumption: Education in India as part of 75th round of National Sample Survey – from July 2017 to June 2018’ has been released.:
- Business Reform Action Plan (BRAP) ranking of states:
- Meetings of the SCO defence ministers and foreign ministers were recently held in Russia.:
- Assam Rifles:
- Chushul:
- Other important current affairs
1.Forex Reserves:

As per the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data, India’s foreign exchange (forex) reserves touched a record high of USD 541.431 billion in the week ended 28th August 2020.
Forex Reserves:
- Foreign exchange reserves are assets denominated in a foreign currency that is held on reserve by a central bank. These may include foreign currencies, bonds, treasury bills, and other government securities.
- Objectives Behind Holding Forex Reserves:
- Supporting and maintaining confidence in the policies for monetary and exchange rate management
Provides the capacity to intervene in support of the national or union currency. - Limits external vulnerability by maintaining foreign currency liquidity to absorb shocks during times of crisis or when access to borrowing is curtailed.
- Supporting and maintaining confidence in the policies for monetary and exchange rate management
Forex Reserves in India: Forex reserves are external assets accumulated by India and controlled by the RBI in the form of:
- Gold
- SDRs (special drawing rights of the International Monetary Fund – IMF)
- Foreign currency assets (capital inflows to the capital markets, Foreign Direct Investment and external commercial borrowings)
- Reserve Position with IMF
Forex Reserves Storage: The RBI Act, 1934 provides the legal framework for the deployment of reserves in different foreign currency assets and gold within the broad parameters of currencies, instruments, and issuers.
Reasons for High Forex Reserves:
- The rise in investment by foreign portfolio investors and increased foreign direct investments (FDIs).
- The sharp jump in reserves started with the Finance Ministry’s announcement in 2019, cutting corporate tax rates.
- Fall in crude oil prices has brought down the oil import bill, saving precious foreign exchange.
- Dollar outflow from overseas remittances and foreign travels have fallen steeply.
2.RBI’S Plan:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) specified five financial ratios and sector-specific thresholds for resolution of COVID-19-related stressed assets in 26 sectors, including auto components, aviation, and tourism.
- The circular issued by the Reserve Bank for resolution of the stressed assets is based on the recommendations of the K.V. Kamath Committee, which submitted its report on the 4th of September.
- The 26 sectors specified by the RBI include automobiles, power, tourism, cement, chemicals, gems and jewelry, logistics, mining, manufacturing, real estate, and shipping among others.
- Five financial metrics need to be taken into account while deciding on a recast plan:
- total outstanding liabilities/ adjusted tangible net worth,
- total debt/Ebitda,
- current ratio,
- debt service coverage ratio, and
- average debt service coverage ratio.
- For each of these parameters, RBI has prescribed either a floor or a ceiling.
- The committee sets 180 days to implement the plan and makes an inter-creditor agreement (ICA) mandatory.
- The tenure of a loan may be extended by a maximum of two years, with or without a moratorium, the panel has said.
- The resolution process shall be treated as invoked once lenders representing 75% by value and 60% by number agree to invoke the same.
3. The report on ‘Household Social Consumption: Education in India as part of the 75th round of National Sample Survey – from July 2017 to June 2018’ has been released.:

It is based on the National Statistical Office (NSO) survey and provides for state-wise detail of literacy rate among the persons aged seven years and above.
- The report comes before the International Literacy Day which is celebrated on 8th September every year.
Key Points
- Data Analysis: India’s Overall Literacy Rate is 77.7%.
- Urban Areas: 87.7%.
- Rural areas: 73.5%.
- Male Literacy Rate: 84.7%.
- Female Literacy Rate: 70.3%.
- The male literacy rate is higher than the female literacy rate among all states with a considerable gap in the worst-performing states.
- Best Performers: Kerala > Delhi > Uttarakhand > Himachal Pradesh > Assam.
- Worst Performers: Andhra Pradesh < Rajasthan < Bihar < Telangana < Uttar Pradesh.
- Digital Literacy:
- 23% of urban households and 4% of rural households possess computers.
- Among persons age 15-29 years, nearly 56% in urban areas and 24% in rural areas were able to operate a computer.
- In the same age group, nearly 25% in rural areas and 58% in urban areas reported the use of the internet.
4.Business Reform Action Plan (BRAP) ranking of states::
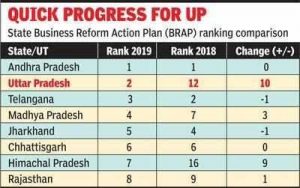
4th edition of the Business Reform Action Plan (BRAP) ranking of states announced recently by the Department of Industrial Promotion and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- The ranking of States is based on the implementation of the Business Reform Action Plan started in the year 2015.
- One “major change” in the current rankings is the government’s decision to link the state’s performance “exclusively” to user feedback.
- The five-ten states under the State Reform Action Plan 2019 are:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Telangana
- Madhya Pradesh
- Jharkhand
BRAP:
- The Business Reform Action Plan 2018-19 includes 180 reform points covering 12 business regulatory areas such as Access to Information, Single Window System, Labour, Environment, etc.
- The states ranked on BRAP Implementation: For larger objective of attracting investments and increasing Ease of Doing Business in each State was sought to be achieved by introducing an element of healthy competition through a system of ranking states based on their performance in the implementation of Business Reform Action Plan.
5. Meetings of the SCO defense ministers and foreign ministers were recently held in Russia.:

Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO):
- It is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- Its creation was announced on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai (China) by the Republic of Kazakhstan, the People’s Republic of China, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Tajikistan, and the Republic of Uzbekistan.
- It was preceded by the Shanghai Five mechanism.
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Charter was signed during the St.Petersburg SCO Heads of State meeting in June 2002 and entered into force on 19 September 2003.
- The SCO’s official languages are Russian and Chinese.
- SCO’s main goals are as follows:
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states; promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology, and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas; making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security, and stability in the region; and moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
- Bodies under SCO:
- Heads of State Council (HSC) is the supreme decision-making body in the SCO. It meets once a year and adopts decisions and guidelines on all important matters of the organization.
- SCO Heads of Government Council (HGC) meets once a year to discuss the organization’s multilateral cooperation strategy and priority areas, to resolve current important economic and other cooperation issues, and also to approve the organization’s annual budget.
- Two permanent bodies — the SCO Secretariat based in Beijing and the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) based in Tashkent.
- The SCO Secretary-General and the Director of the Executive Committee of the SCO RATS are appointed by the Council of Heads of State for a term of three years.
6.Assam Rifles:

The Delhi High Court has directed the Centre to take a decision on the issue of bringing Assam Rifles out of the dual control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) and the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- A petition was filed by the Assam Rifles Ex-Servicemen Welfare Association seeking direction to the government for placing Assam Rifles under one control, preferably under the MoD.
Issue: - The administrative control of the Assam Rifles is with the MHA and the operational control of Assam Rifles rests with the MoD.
- This duality of administrative control and operational control leads to problems of coordination.
The objectives and functions of Assam Rifles are that of the military and paramilitary force and considering it anything less than that is arbitrary, unreasonable and in violation of the rights of Assam Rifles personnel. - There is a disparity in the pay scale between the Assam Rifles personnel operating alongside the Army on similar duties.
Delhi High Court’s Direction:
- The issue has been pending for nearly three years and now the Centre should resolve it within 12 weeks with cooperation from all the stakeholders.
- It noted that “The matter involves servicemen/ex-servicemen and whose interest is not only to be paramount but is proclaimed from various platforms of the Government, to be paramount”.
Centre’s Stand: - The in-principle decision, that Assam Rifles like other Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) should come under the exclusive control of MHA, appears to have already been taken but the final decision has not been made official yet.
- The Centre has asked for a period of further six months as the process has been affected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Assam Rifles
- Assam Rifles is a Central Paramilitary Force under the Central Armed Police Forces.
- It came into being in 1835, as a militia called the ‘Cachar Levy’, to primarily protect British Tea estates and their settlements against tribal raids.
- It significantly contributed to the opening of Assam region to administration and commerce and over time it came to be known as the “right arm of the civil and left arm of the military”.
7. Chushul:
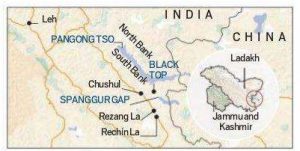
The Chushul sub-sector has come into focus in the standoff between the Indian and PLA troops of China following the movement that took place on the intervening night of August 29 and 30.
- The Chushul sub-sector lies south of Pangong Tso in eastern Ladakh. It comprises high, broken mountains and heights of Thatung, Black Top, Helmet Top, Gurung Hill, and Magger Hill besides passes such as Rezang La and Reqin La, the Spanggur Gap, and the Chushul valley.
- Situated at a height of over 13,000 feet close to the LAC, the Chushul Valley has a vital airstrip that played an important role even during the 1962 War with China.
- Chushul is one among the five Border Personnel Meeting points between the Indian Army and the People’s Liberation Army of China.
- It is here that representatives of the two armies meet for regular interactions.
- Chushul enjoys tremendous strategic and tactical importance because of its location and terrain, which make it a centre for logistics deployment. Chushul is the gateway to Leh. If China enters the Chushul, it can launch its operations for Leh.
Other important current affairs:
1. Countries across the world are celebrating International Literacy Day on September 8, 2020.
- International Literacy Day-2020 will focus on Literacy teaching and learning in the COVID-19 crisis and beyond with a focus on the role of educators and changing pedagogies.
- This day was declared International Literacy Day by UNESCO on 26th October 1966 at the 14th Session of UNESCO’s General Conference.
- It was celebrated for the first time in 1967 and its main aim is to highlight the importance of literacy to individuals, communities, and societies.
2. The DRDO successfully flight tested the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV) from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Launch Complex at Wheeler Island off the coast of Odisha.
- The HSTDV, which operates on scramjet engines that can attain the speed of around Mach 6, has been developed by the DRDO.
3. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has organized a webinar on the occasion of the first-ever International Day of Clean Air For Blue Skies.
- In December 2019, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution to observe this day on 7th September every year, starting from 2020.
- The Day aims to demonstrate the close link of air quality to other environmental/developmental challenges and raise public awareness related to air quality at all levels.
4.Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP)::
- SVEP has made impressive progress and has extended business support services and capital infusion to 153 blocks of 23 states as of August 2020.
- Around, 2,000 trained cadre of Community Resource Person-Enterprise Promotion (CRP-EP) are providing services to rural entrepreneurs and as of August 2020, around 100,000 enterprises are supported by them.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP):
- Implemented by Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana –National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM), Ministry of Rural Development, as a sub-scheme since 2016.
- The focus of the scheme: Providing self-employment opportunities with financial assistance and training in business management and soft skills while creating local community cadres for promotion of enterprises.
- Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India (EDII), Ahmedabad is the technical support partner of SVEP.
- SVEP promotes both individual and group enterprises, set-up and promotes enterprises majorly on manufacturing, trading and service sectors.
5. The National Immunogenicity & Biologics Evaluation Center (NIBEC) for assessing clinical immunogenicity of viral vaccines was inaugurated virtually recently.
- It has been established jointly by Bharati Vidyapeeth University through its constituent unit Interactive Research School for Health Affairs (IRSHA) and BIRAC-DBT, Government of India through National Biopharma Mission.
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC):
- It is a not-for-profit Public Sector Enterprise, set up by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) as an Interface Agency to strengthen and empower the emerging Biotech enterprise to undertake strategic research and innovation, addressing nationally relevant product development needs.
6. Researchers have found that the concentration of near-surface ozone in this region is low compared to the other urban locations in India.
- Tropospheric or ground-level ozone:
- It is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC).
- It usually increases when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, and other sources chemically react in the presence of sunlight, impacting human health.
- Low ozone in Brahmaputra Valley:
- This site is well influenced by local sources such as adjacent major national highway. During the daylight hours, the site is in or nearly in a photo-stationary state, indicating a low impact of organic species on the ozone concentrations.
- Concern about ground-level ozone:
- Ozone at ground level is a harmful air pollutant, because of its effects on people and the environment, and it is the main ingredient in “smog.”
- Elevated ground-level ozone exposures affect agricultural crops and trees, especially slow-growing crops and long-lived trees.
- The main health concern of exposure to ambient ground-level ozone is its effect on the respiratory system, especially on lung function.
7. Sir David Attenborough has been conferred with Indira Gandhi Peace Prize for 2019 at a virtual ceremony.
- The Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development is an annual prestigious award named after former prime minister Indira Gandhi.
- It is conferred every year by Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust since 1986.
- It consists of a citation and a monetary award of Rs. 25 lakh.
- The award recognizes creative efforts by individuals/organizations working towards:
- Creating new international economic order,
- Promoting international peace & development,
Ensuring that scientific discoveries are used for the larger good of humanity and enlarging the scope of freedom.
- David Attenborough
- Sir David is an English broadcaster and natural historian.
- He is best known for writing and presenting the BBC Natural History Unit.
- The nine natural history documentary series forming the Life collection that together constitutes a comprehensive survey of animal and plant life on Earth.
- He has worked to make aware about the need to- preserve and protect the biodiversity of the planet, to live in a sustainable and harmonious way with all life.
8. The Yanomami tribe has launched a global campaign to expel 20,000 gold miners from their land amid the coronavirus pandemic.
- The Yanomami live in the rainforests and mountains of northern Brazil and southern Venezuela, and are, according to Survival International, the largest relatively isolated tribe in South America.
- Guarani, Kaingang, Pataxó, Hã Hã Hãe, Tupinambá, Yanomami, Tikuna and Akuntsu are popular tribes of the Amazon basin. Amazon is a river of South America and its basin is the largest tropical rainforest in the world.
- Survival International is an international human rights advocacy based in London (UK), which campaigns for the rights of indigenous and tribal peoples around the world.
- The tribe numbers around 38,000 today, and its members live in the contiguous forested territory of around 9.6 million hectares in Brazil and 8.2 million hectares in Venezuela.
- They live in large, circular houses called yanos or shabonos, some of which can hold up to 400 people.
- The Yanomami consider all people to be equal and do not have a chief. Instead, all decisions are based on consensus after long discussions and debates.
- They are speakers of a Xirianá language.
9. The first World Solar Technology Summit (WSTS) is being organized by the International Solar Alliance (ISA) on 8th September 2020.
- The Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), as the convenor of ISA Global Leadership Task Force on Innovation, is working with ISA in organizing the summit.
- More than 26000 participants from 149 countries have registered to join the virtual Summit which is expected to bring the spotlight on accelerating affordable and sustainable clean green energy.
- The summit will witness the announcement of three agreements between ISA and International Institute of Refrigeration, a second with Global Green Growth Institute and the third agreement with National Thermal Power Corporation.
- A tripartite agreement between India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, the World Bank and the International Solar Alliance is also set to be inked.
- ISA’s technology journal, Solar Compass 360 will also be launched during the summit.
10. Prime Minister Narendra Modi shall inaugurate the Patrika Gate in Jaipur on the 8th September 2020.
- Patrika Gate derives its name from newspaper and media company-Rajasthan Patrika.
- The gate is built on Jawahar Circle near Sanganer International Airport. It is on the southern end of JLN Marg which connects Ramniwas Garden on the north side and Jaipur International Airport on the Southern end.
- The facade is inspired by the traditional architecture and features Jharokhas, Pols, Pavilions, and Chhatris.
- The idea of building this gate is linked with the old city gates of Jaipur walled city. When Maharajah Sawai Jai Singh II founded Jaipur in 1727 AD, he secured the perimeter with a wall and eight gates.




