Deadly Nipah virus’ transmission from animals to humans:
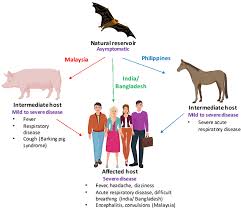
Health experts and physicians have raised concerns about the deadly Nipah virus’ transmission from animals to humans in Kerala.
- The Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus that can spread from animals to humans, as well as through contaminated food or direct human-to-human transmission.
- Nipah virus encephalitis is caused by an RNA (ribonucleic acid) virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae, genus Henipavirus, and is closely related to the Hendra virus.
- NiV was first identified in domestic animals such as pigs, dogs, cats, goats, horses, and sheep.
- The virus is transmitted by fruit bats of the genus Pteropus and is present in their urine, feces, saliva, and birthing fluids.
- NiV causes encephalitic syndrome in humans, with symptoms like fever, headache, drowsiness, confusion, and coma, often leading to death.
- The fatality rate is 40% to 75%.
- Diagnosis is done via real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from body fluids. No vaccines exist for humans or animals.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has designated Nipah as a priority disease.




