Bond Yield:
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) decision to step up the purchase of Government Securities (G-Sec) under the Government Securities Acquisition Programme (G-SAP) led to the yield on the benchmark 10-year bond falling below 6%.
- In India, the yield of 10-year G-Sec is considered the benchmark and shows the overall interest rate scenario.
Bond Yield:
- Bond yield is the return an investor realizes on a bond. The mathematical formula for calculating yield is the annual coupon rate divided by the current market price of the bond
- Bond: Is an instrument to borrow money. A bond could be issued by a country’s government or by a company to raise funds.
- Coupon Rate: It is the rate of interest paid by bond issuers on the bond’s face value.
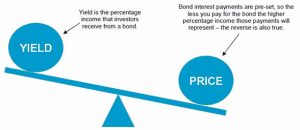
Effect of General Movement of Bond Yields:
- Movements in yields depend on trends in interest rates, it can result in capital gains or losses for investors.
- A rise in bond yields in the market will bring the price of the bond down.
- A drop in bond yield would benefit the investor as the price of the bond will rise, generating capital gains.
Reason for Decreasing Bond Yields:
- Due to economic uncertainty caused by Covid-19.
- In April 2021, the RBI launched G-SAP which has caused a decrease in G-sec yields which has continued since then




