What Is Flood Plain Zoning?
The Ministry of Jal Shakti has informed the Rajya Sabha that the states of Manipur, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand and erstwhile State of Jammu & Kashmir had enacted the National Floodplains Zoning Policy.
- However, delineation and demarcation of flood plains is yet to be undertaken.
- Earlier, the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) presented a report on preparedness and response to floods in the Kerala assembly.
- The report pointed out that the state is yet to enact flood plain zoning legislation, 45 years after the Union Government circulated to all states a model draft bill for flood plain zoning legislation.
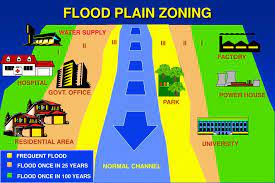
- Flood Plain Zoning has been recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
- The basic concept of flood plain zoning is to regulate land use in the flood plains to restrict the damage caused by floods.
- It aims at determining the locations and the extent of areas for developmental activities in such a fashion that the damage is reduced to a minimum.
- It envisages laying down limitations on development of both the unprotected as well as protected areas.
- In the unprotected areas, boundaries of areas in which developmental activities will be banned, are to be established to prevent indiscriminate growth.
- In the protected areas, only such developmental activities can be allowed, which will not involve heavy damage in case the protective measures fail.
- Zoning cannot remedy existing situations, although, it will definitely help in minimising flood damage in new developments.
- Flood plain zoning is not only necessary in the case of floods by rivers but it is also useful in reducing the damage caused by drainage congestion particularly in urban areas.
- Model Bill for Flood Plain Zoning clauses about flood zoning authorities, surveys and delineation of flood plain area, notification of limits of flood plains, prohibition of the use of the flood plains, compensation and most importantly removing obstructions to ensure free flow of water.
- It seeks to replace dwellings in low-lying areas by parks and playgrounds as absence of human settlement in those areas would cut down loss of lives and property.




