Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 11th June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Gairsain
- Revenue deficit grant
- Asiatic lions
- International Religious Freedom Report 2019
- Rights issue
- Border Adjustment Tax
- Genetically Modified Seeds
- Other important current affairs:
1.Gairsain :
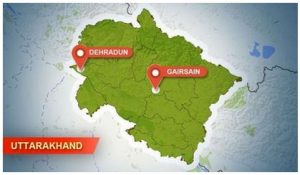
Gairsain in Chamoli district has been formally declared as the summer capital of Uttarakhand. A notification was issued after the state governor gave her assent to the move.
- The development came three months after Chief Minister Trivendra Singh Rawat Chief Minister Trivendra Singh Rawat had announced making Gairsain the summer capital, besides Dehradun, during the budget session of the assembly on March 4.
- Now, with the announcement of Gairsain as the summer capital, there is a lack of clarity on the status of Dehradun.
- Gairsain is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Chamoli district, Uttarakhand. Gairsain is situated at the eastern edge of the Dudhatoli mountain range.
- Uttarakhand was carved out as a separate state from Uttar Pradesh in 2000.
- Statehood activists had long contended that Gairsain, a tehsil in Chamoli district, was best suited to be the capital of the mountainous state as it was a hilly region falling on the border of Kumaon and Garhwal regions.
- But it was Dehradun, located in the plains, that served as the temporary capital.
- The state Assembly is located in Dehradun, but sessions are held in Gairsain as well.
2.Revenue deficit grant:

The Finance Ministry has released Rs 6,195.08 crore revenue deficit grant to 14 states as the third equated monthly installment to enhance their resources during the Covid-19 crisis.
- The government on May 11, 2020, had released Rs 6,195.08 crore to 14 states as the second equated monthly installment of the Post Devolution Revenue Deficit Grant as recommended by the 15th Finance Commission. This would provide them additional resources during the Corona crisis.
- The 15th Finance Commission used the following criteria while determining the share of states:
- 45% for the income distance.
- 15% for the population in 2011
- 15% for the area
- 10% for forest and ecology
- 12.5% for demographic performance, and
- 2.5% for tax effort.
- For 2020-21, the Commission has recommended a total devolution of Rs 8,55,176 crore to the states, which is 41% of the divisible pool of taxes. This is 1% lower than the percentage recommended by the 14th Finance Commission.
- The Terms of Reference of the Finance Commission require it to recommend grants-in-aid to the States.
- These grants include (i) revenue deficit grants, (ii) grants to local bodies, and (iii) disaster management grants.
3. Asiatic lions :

According to June 5, 2020 census, the number of Asiatic lions have now risen by 29% over five years to an estimated 674 in the Gir forest region and other revenue areas of coastal Saurashtra. During 2015, their population was 523 lions. Geographically, the distribution area is up by 36%.
- Scientific Name: Panthera Leo Persica.
- Common Name: Asiatic lion, Indian Lion.
- Status: Listed in Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972, in Appendix I of CITES and as Endangered on IUCN Red List.
- Asiatic lions are slightly smaller than African lions. The most striking morphological character is a longitudinal fold of skin running along the belly of Asiatic Lions.
- At present Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary in Gujarat is the only abode of the Asiatic lion. They live in a compact tract of dry deciduous forest and open grassy scrublands in southwestern part of Saurashtra region of Gujarat.
4.International Religious Freedom Report 2019:

Recently, the US State Department has released its annual International Religious Freedom (IRF) Report 2019, which is a survey of the state of religious freedom across the world.
- It published a report i.e. the country report for India to highlight the issue of religious freedom in the country.
Earlier, the US Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF report) downgraded India’s religious freedom to the lowest grade — in the ‘Country of Particular Concern (CPC)’ category. - The IRF report listed countries for positive developments in religious freedom and negative examples.
- Nicaragua, Nigeria, and China were cited as negative examples.
- It stated that in China, state-sponsored repression against all religions continues to intensify because of the Chinese Communist Party.
- India is not cited in either list.
The Country Report for India:
- It highlighted the developments that took place in 2019 i.e. the status of Jammu and Kashmir, the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), and the National Register of Citizens (NRC).
- It discussed in detail about mob lynchings, anti-conversion laws, cow vigilantism, and related issues.
- Taking note of the alleged attacks and discrimination against religious and ethnic minorities in India, the report emphasized the need to ensure full protection to minorities in the country as guaranteed under the Constitution.
- It also outlines the U.S. engagement with India on these issues.
The Indian government has rejected the report by asserting that there is no locus standi for a foreign government to comment on the state of its citizens’ constitutionally protected rights.
- It also emphasized that the report did not talk about religious freedom given to various communities in India.
5.Rights issue :

Many companies including Reliance Industries Limited, Mahindra finance, Tata Power, Shriram Transport Finance among others plan to raise funds (aggregating to over Rs 10,000 crore) through rights issue amidst the Covid-19 pandemic.
Rights issue:
- It is an offering of shares made to existing shareholders in proportion to their existing shareholding.
- Companies often offer shares in a rights issue at a discount on the market price.
- Rights issues are used by companies seeking to raise capital without increasing debt.
- Shareholders are not obliged to purchase shares offered in a rights issue.
- For a rights issue, there is no requirement of shareholders’ meeting and approval from the board of directors is sufficient and adequate.
- Therefore, the turnaround time for raising this capital is short and is much suited for the current situation, unlike other forms that require shareholders’ approval and may take some time to fructify.
- Thus the rights issue is a more efficient mechanism of raising capital.
- Sebi reduced the eligibility requirement of the average market capitalization of public shareholding from Rs 250 crore to Rs 100 crore for a fast track rights issuance.
- It also reduced the minimum subscription requirement from 90 per cent to 75 per cent of the issue size.
- Also, listed entities raising funds up to Rs 25 crores through a rights issue are now not required to file a draft offer document with SEBI.
6.Border Adjustment Tax:

Recently, a NITI Aayog member has favoured imposing a Border Adjustment Tax (BAT) on imports to provide a level-playing field to domestic industries.
- This suggestion comes in the backdrop of the USA-China trade tensions (trade war) which are expected to rise even further post-Covid-19.
- BAT is a duty that is proposed to be imposed on imported goods in addition to the customs levy that gets charged at the port of entry.
- BAT is a fiscal measure that imposes a charge on goods or services in accordance with the destination principle of taxation.
- Under this principle, government taxes products based on the location of their sale to the final consumer rather than on the location of their production or origin.
- Thus, to adjust a tax “at the border,” a country:
- taxes imported products and domestically produced products sold on its market on the same basis and at the same rate; and
- exempts from these tax products exported for sale to foreign consumers.
- Generally, BAT seeks to promote “equal conditions of the competition” for foreign and domestic companies supplying products or services within a taxing jurisdiction.
- The World Trade Organisation (WTO) rules allow for the adjustment of certain types of internal taxes at the border under certain conditions.
- The main conditions are:
- The tax must be applied equally to imports and “like” domestic products.
- The tax must be “borne” by a product and not be “direct”.
- A permitted border tax adjustment must not subsidize exports.
7.Genetically Modified Seeds:

In the current Kharif season, farmers would undertake mass sowing of GM seeds for maize, soybean, mustard brinjal, and herbicide-tolerant (Ht) cotton, although these are not approved.
- So, in this regard, Shetkari Sanghatana — a farmers’ union— has announced fresh plans in its agitation for use of genetically modified seeds.
- The Sanghatana has announced that this year they are going to undertake large-scale sowing of unapproved GM crops like maize, Ht Bt cotton, soybean, and brinjal across Maharashtra.
- Farmers who plant such variants will put up boards on their fields proclaiming the GM nature of their crop.
- This action will draw attention to the need for the introduction of the latest technology in the fields.
Genetically modified seeds:
- Genetic engineering aims to transcend the genus barrier by introducing an alien gene in the seeds to get the desired effects. The alien gene could be from a plant, an animal, or even a soil bacterium.
- Bt cotton, the only GM crop that is allowed in India, has two alien genes from the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) that allows the crop to develop a protein toxic to the common pest pink bollworm.
- Ht Bt cotton is derived with the insertion of an additional gene, from another soil bacterium, which allows the plant to resist the common herbicide glyphosate.
- In Bt brinjal, a gene allows the plant to resist attacks of fruit and shoot borer.
- In DMH-11 mustard, genetic modification allows cross-pollination in a crop that self-pollinates in nature.
Legal position of genetically modified crops in India:
- In India, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is the apex body that allows for the commercial release of GM crops.
- The use of the unapproved GM variant can attract a jail term of 5 years and a fine of Rs 1 lakh under the Environmental Protection Act,1989.
Other important current affairs:
1. The Kerala government has approved the proposed Athirapally Hydro Electric Project (AHEP) on the Chalakudy river in Thrissur district of the state.
- There are already five dams for power and one for irrigation and it will be the seventh along the 145 km course of the Chalakudy river.
- Chalakudy River originates in the Anamalai region of Tamil Nadu and is joined by its major tributaries Parambikulam, Kuriyarkutti, Sholayar, Karapara and Anakayam in Kerala.
- The river flows through Palakkad, Thrissur and Ernakulam districts of Kerala.
2. Under operation named Desert Chase, Rajasthan Police arrested two civil defence employees in Jaipur based on Military Intelligence (MI) inputs that they had been passing on sensitive information to Pakistan’s spy agency ISI.
- Operation Desert Chase was the name of the Anti-espionage operation started by Military Intelligence (MI) in early 2019.
- It successfully culminated in June 2020 with the arrest of two men. Both were arrested under relevant sections of the Official Secrets Act, 1923.
- The Directorate of Military Intelligence (M.I.) is the Intelligence arm of the Indian Army. The agency was set up in 1941 and is based at Sena Bhavan in Delhi. M.I.
3. The skirmishes and the standoff between Indian and Chinese troops at Naku La in Sikkim last month, in an area of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) has brought back the focus onto the historical Sikkim-Tibet Convention of 1890.
- Experts say, as per this convention, Naku la belongs to India. Besides, Prior to Sikkim’s merger with India in 1975, China has officially accepted this demarcation.
- 1890 convention: The treaty was formalized between Britain and the Chinese kingdom.
- It was signed at Calcutta Convention in 1890. Of the eight Articles mentioned in the treaty, Article 1 is of critical significance.
- As per Article (1), it was agreed that the boundary of Sikkim and Tibet shall be the crest of the mountain range separating the waters flowing into the Sikkim Teesta and its affluents, from the waters flowing into the Tibetan Mochu and northwards into other rivers of Tibet.
- The line commences at Mount Gipmochi, on the Bhutan frontier, and follows the above-mentioned water-parting to the point where it meets Nepal territory. However, Tibet refused to recognise the validity of Convention of 1890 and further refused to carry into effect the provisions of the said Convention.
- In 1904, a treaty known as a Convention between Great Britain and Tibet was signed at Lhasa.
- As per the Convention, Tibet agreed to respect the Convention of 1890 and to recognise the frontier between Sikkim and Tibet, as defined in Article (1) of the said Convention.
- On April 27, 1906, a treaty was signed between Great Britain and China at Peking, which confirmed the Convention of 1904 between Great Britain and Tibet.
4.RBI has released draft Frameworks for ‘Sale of Loan Exposures’ and ‘Securitisation of Standard Assets’.
- These draft guidelines are applicable to all Scheduled Commercial Banks (excluding Regional Rural Banks); All India Financial Institutions (NABARD, NHB, EXIM Bank, and SIDBI); and, all Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) including Housing Finance Companies (HFCs).
- The guidelines attempt to align the regulatory framework with the Basel guidelines on securitisation that have come into force effective January 1, 2018.
- The revisions also take into account the recommendations of the Committee on Development of Housing Finance Securitisation Market in India (Chair: Dr Harsh Vardhan) and the Task Force on the Development of Secondary Market for Corporate Loans (Chair: Shri T.N. Manoharan), which were set up by the RBI in May 2019.
5. The World Accreditation Day (WAD) was celebrated on 9th June by the Quality Council of India (QCI) to highlight as well as to promote the role of accreditation in trade & economy.
- The theme for WAD 2020 was “Accreditation: Improving Food Safety”.
- Accreditation is a formal, independent verification that a program or institution meets established quality standards in terms of testing, inspection, or certification.
- It is an important tool to improve the quality of products and services in the field of health, education, food as well as other areas.
- It also promotes the adoption of quality standards relating to Quality Management Systems, Food Safety Management Systems, and Product Certification.
- Overall, it helps in realizing the objective of improving the quality competitiveness of Indian products and services.
6. Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR) have recorded at least 14 earthquakes of low or medium intensity since April 2020.
- As per the 2002 map by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), India is divided into four seismic zones – viz. Zone II, III, IV and V – based on seismicity, earthquakes occurred in the past and tectonic setup of the region.
- Delhi falls in Zone IV, which makes it vulnerable to earthquakes. Delhi does not lie on a plate boundary. It is located on a single plate, and the seismic activity is generated by internal deformities.
7.Daulat Beg Oldie::
- The construction of the 255-km long Darbuk-Shyokh-Daulat Beg Oldie (DSDBO) all-weather road is said to be the immediate reason behind the standoff between the Indian Army and a Chinese Army along LAC.
- Built by BRO, the road runs almost parallel to the LAC and connects Leh to DBO.DBO is the northernmost corner of Indian territory in Ladakh, in the area better known in Army parlance as Sub-Sector North.
- It has the world’s highest airstrip, originally built during the 1962 war but abandoned until 2008, when the Indian Air Force (IAF) revived it as one of its many Advanced Landing Grounds (ALGs) along the LAC.
- DBO is less than 10 km west of the LAC at Aksai Chin.
- To the west of DBO is the region where China abuts Pakistan in the Gilgit-Baltistan area, once a part of the erstwhile Kashmir principality.
8. Central Pollution Control Board will classify railway stations under the red, orange and green categories based on the quantity of wastewater generated.
- Red: railway stations generating wastewater equal to or more than 100 Kilo Litres per Day.
- Orange: those greater than 10 KLD but less than 100 KLD.
- Green: less than 10 KLD of waste water generation.
9. A 3,000-years-old Mayan temple has been discovered in Mexico through the laser mapping technique, making it the ancient civilization’s oldest and largest monument.
- The temple site called Aquada Fenix, in Mexico, is 4,600 feet long and up to 50 feet high, making it larger than the Mayan pyramids and palaces of later periods.
- It was built between 800 BC and 1,000 BC.
- One of the most remarkable revelations from the find was the complete lack of stone sculptures related to rulers and elites, such as colossal heads and thrones, that are commonly seen in other Mayan temples.
- This suggests that the people who built it were more egalitarian than later generations of Mayans.




