Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 10th August 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Delhi State Legal Services Authority (DSLSA) recently organized the e-lok Adalat:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently announced a list of 101 items that the Defence Ministry will stop importing.:
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands to be Maritime and Startup Hub:
- 8th Aug 2020, India completed 78 years of Quit India Movement also known as August Kranti.:
- Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG).:
- Indus Water Treaty (IWT)::
- Other important current affairs:
1. Delhi State Legal Services Authority (DSLSA) recently organized the e-lok Adalat:

In a first of its kind in the country, the Delhi State Legal Services Authority (DSLSA) recently organized the e-lok Adalat to facilitate mediation between the parties, who are willing to get their matters settled amicably, in all the District Courts Complexes of Delhi.
- In the e-Lok Adalat, an online link would be sent by SAMA (an Online Dispute Resolution platform recognized by the Department of Justice for resolving disputes through video conferencing) to the concerned parties and a judge would preside over the mediation process.
- Following the settlement, an OTP would be sent to them and on the confirmation, the dispute would be settled.
- 77 Benches were constituted wherein a total of 5838 cases were disposed of pertaining to various categories in which settlement amount was approx Rs 46.28 crores.
Lok Adalat:
- Lok Adalat is one of the alternative dispute redressal mechanisms, it is a forum where disputes/cases pending in the court of law or at the pre-litigation stage are settled/ compromised amicably.
- The Lok Adalats are formed to fulfill the promise given by the preamble of the Indian Constitution– securing Justice – social, economic, and political of every citizen of India.
- Article 39A of the Constitution provides for free legal aid to the deprived and weaker sections of the society and to promote justice on the base of equal opportunity.
- Articles 14 and 22(1) of the Constitution also make it compulsory for the State to guarantee equality before the law.
- Under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 Lok Adalats have been given statutory status.
- The decision made by the Lok Adalats is considered to be a verdict of a civil court and is ultimate and binding on all parties.
- There is no provision for an appeal against the verdict made by Lok Adalat.
- But, they are free to initiate litigation by approaching the court of appropriate jurisdiction by filing a case by following the required procedure, in the exercise of their right to litigate.
2. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently announced a list of 101 items that the Defence Ministry will stop importing.:

It essentially means that the Armed Forces—Army, Navy and Air Force—will only procure all of these 101 items from domestic manufacturers.
- The manufacturers could be private sector players or defense Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs).
- The list of 101 embargoed items comprises of some high technology weapon systems like artillery guns, assault rifles, corvettes, sonar systems, transport aircraft, LCHs, radars, and many other items to fulfill the needs of the defense Services.
- The list also includes wheeled Armoured Fighting Vehicles (AFVs) with indicative import embargo date of December 2021, of which the Army is expected to contract almost 200 at an approximate cost of over ₹5,000 crores.
- The embargo on imports is planned to be progressively implemented between 2020 to 2024.
- The Government also intends to reach a turnover of $25 billion through indigenously manufactured defence products and also expects to export products worth $5 billion.
- The government has also decided that in any government contract over ₹200 crores, no foreign company can participate in the tendering process.
- This year ₹52,000 crore items are to be bought only from Indian companies.
- MoD has also bifurcated the capital procurement budget for 2020-21 between domestic and foreign capital procurement routes.
3.Andaman and Nicobar Islands to be Maritime and Startup Hub:

The Prime Minister has declared that the Andaman and Nicobar islands will be developed as a “maritime and startup hub”.
- A transshipment hub has been proposed in the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- A transhipment is when cargo or a container is moved from one vessel to another while in transit to its final destination.
- It will be built in South Bay, Great Nicobar Island, to provide Indian shippers with an alternative to the Colombo (Sri Lanka), Singapore and Port Klang (Malaysia) transhipment ports.
- 12 islands of the archipelago have been selected for high-impact projects with an emphasis on boosting trade of sea-based, organic and coconut-based products of the region.
- A submarine cable project has been launched in the islands to make it digitally independent.
2300 Km of submarine optical fibres cable (OFC) have been laid down - The fibre will connect chennai and port blair and seven other islands- Swaraj Deep (Havelock), Long island etc.
- The connectivity project was funded by the Centre through the Universal Service Obligation Fund under the Ministry of Communications.
- It was executed by Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) and Telecommunications Consultants India Limited (TCIL) was the technical consultant.
- In addition, Port Blair airport is to be expanded and some of the islands will be also connected with seaplanes.
Submarine Communications cable:
- It is a cable laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea.
- The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed.
- There are two types of Submarine fibre cables: unrepeatered and repeatered.
- Unrepeatered cables are preferred in short cable routes because it does not require repeaters, lowering costs; however, their maximum transmission distance is limited.
4.8th Aug 2020, India completed 78 years of Quit India Movement also known as August Kranti.:

Taking inspiration from the Quit India Movement, the Prime Minister gave a call for the revival of its spirit of the Quit India Movement by coining a new slogan karenge aur karake rahenge in place of Gandhi’s slogan of karo ya maro (Do or Die).
- The aim of this slogan is to achieve the goal of building a “New India” by 2022.
About:
- On 8th August 1942, Mahatma Gandhi gave a clarion call to end the British rule and launched the Quit India Movement at the session of the All-India Congress Committee in Mumbai.
- Gandhiji gave the call “Do or Die” in his speech delivered at the Gowalia Tank Maidan, now popularly known as August Kranti Maidan.
- Aruna Asaf Ali popularly known as the ‘Grand Old Lady’ of the Independence Movement is known for hoisting the Indian flag at the Gowalia Tank Maidan in Mumbai during the Quit India Movement.
- The slogan ‘Quit India’ was coined by Yusuf Meherally, a socialist and trade unionist who also served as Mayor of Mumbai.
- Meherally had also coined the slogan “Simon Go Back”.
Causes:
- The immediate cause of the movement was the collapse of the Cripps Mission.
- The British assumption of unconditional support from India to the British in World War II was not taken well by the Indian National Congress.
- The anti-British sentiments and demand for full independence had gained popularity among Indian masses.
- The two decades of the mass movement which were being conducted on a much more radical tone under the leadership of the various associated and affiliated bodies of the Congress, like All India Kisan Sabha, Forward Bloc, etc. had already prepared the ground for the movement.
- There were militant outbursts happening at several places in the country which got channelized with the Quit India Movement.
- The economy was also in shatters as a result of World War II.
- The demand was to end the British rule in India with immediate effect to get the cooperation of Indians in World War-II against fascism.
- There was a demand to form a provisional government after the withdrawal of the Britishers.
Phases: The movement had three phases
- First Phase urban revolt, marked by strikes, boycott, and picketing, which were quickly suppressed.
- There were strikes and demonstrations all over the country and workers provided support by not working in the factories.
- Gandhiji was soon imprisoned at Aga Khan Palace in Pune and almost all leaders were arrested.
- In the second phase, the focus shifted to the countryside, which witnessed a major peasant rebellion, marked by the destruction of communication systems, such as railway tracks and stations, telegraph wires and poles, attacks on government buildings or any other visible symbol of colonial authority.
- The last phase witnessed the formation of national governments or parallel governments isolated pockets (Ballia, Tamluk, Satara etc.)
- Spontaneous Violence: The movement saw violence at some places which was not premeditated.
- Future Leaders: Underground activities were taken by leaders that included Ram Manohar Lohia, J.P. Narayan,
- Aruna Asaf Ali, Biju Patnaik, Sucheta Kriplani, etc which later emerged as prominent leaders.
- Women Participation: Women took active participation in the movement. Female leaders like Usha Mehta helped set up an underground radio station which led to the awakening about the movement.
- Muslim League, the Communist Party of India and the Hindu Mahasabha did not support the movement. The Indian bureaucracy also did not support the movement.
- The League was not in favor of the British leaving India without partitioning the country first.
- The Communist party supported the British since they were allied with the Soviet Union.
- The Hindu Mahasabha openly opposed the call for the Quit India Movement and boycotted it officially under the apprehension that the movement would create internal disorder and will endanger internal security during the war.
- Meanwhile, Subhas Chandra Bose organized the Indian National Army and the Azad Hind government from outside the country.
- As C Rajagopalachari was not in favor of complete independence, he resigned from the INC.
5. Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG).:

Girish Chandra Murmu has been appointed the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG).
- He has replaced Rajiv Mehrishi and will have a tenure up to 20th November 2024.
Constitutional Body: Article 148 provides for an independent office of the CAG. It is the supreme audit institution of India.
- Other Provisions Related to CAG include Articles 149-151 (Duties & Powers, Form of Accounts of the Union and the States and Audit Reports), Article 279 (calculation of net proceeds, etc.) and Third Schedule (Oath or Affirmation) and Sixth Schedule (Administration of Tribal Areas in the States of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram).
- Head of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department – created in 1753.
- Guardian of the public purse and controls the entire financial system of the country at both the levels–the Centre and the state.
- One of the bulwarks of the democratic system of government in India.
- The others being the Supreme Court, the Election Commission, and the Union Public Service Commission.
- The accountability of the executive (i.e. Council of Ministers) to the Parliament in the sphere of financial administration is secured through audit reports of the CAG.
- Appointment: Appointed by the President of India by a warrant under his hand and seal.
- Tenure: A period of six years or upto the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- Removal: CAG can be removed by the President on the same grounds and in the same manner as a judge of the Supreme Court. He does not hold his office till the pleasure of the President.
- In other words, he can be removed by the President on the basis of a resolution passed to that effect by both the Houses of Parliament with special majority, either on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity
Duties & Powers as also under the CAG’s (Duties, Powers and Conditions of Service) Act, 1971:
- Audits the accounts related to all expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India, consolidated fund of each state, and consolidated fund of each union territory having a Legislative Assembly.
- Audits all expenditures from the Contingency Fund of India and the Public Account of India as well as the contingency fund of each state and the public account of each state.
- Audits profit and loss accounts, balance sheets and other subsidiary accounts kept by any department of the Central Government and state governments.
6.Indus Water Treaty (IWT)::
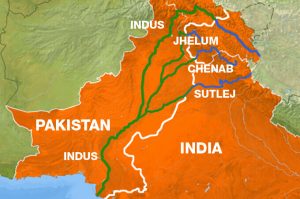
India has refused a request by Pakistan to hold a meeting on issues around the Indus Water Treaty (IWT) at the Attari check post near the India-Pakistan border.
- In March India had suggested a virtual conference but Pakistan had insisted on a physical meeting.
- But, India said because of restrictions on movement in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, traveling to the border for a meeting isn’t advisable.
- The practice at the IWT meetings is that they are led by Indus Water Commissioners from both countries and a range of issues on the construction of dams and hydropower projects concerning the Indus river system are discussed.
- The last such meeting between the two countries was in October in Islamabad, and, as per the agreement in the Indus Water Treaty (IWT), a meeting was to be scheduled in India before March 31.
The dispute which is going on:
- Evolving a procedure to solve differences in technical aspects governing the construction of the Ratle run-of-the-river (RoR) project on the Chenab in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- India has called for the appointment of a ‘neutral’ party while Pakistan favors a Court of Arbitration to agree upon a final resolution on the design parameters of this hydropower project.
Indus Water Treaty:
- It is a Water-Distribution Treaty, signed in Karachi in 1960, between India (Pm Jawaharlal Nehru) and Pakistan (President Ayub Khan), brokered by the World Bank.
- Under the treaty, India has control over the water flowing in the eastern rivers– Beas, Ravi, and Sutlej.
- Pakistan has control over the western rivers– Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum.
- As per the treaty, the water commissioners of Pakistan and India are required to meet twice a year and arrange technical visits to projects’ sites and critical river head works.
- Both sides share details of the water flow and the quantum of water being used under the treaty.
- The treaty sets out a mechanism for cooperation and information exchange between the two countries regarding their use of the rivers.
Other important current affairs:
1.MATHERAN
- After a long gap of 125 years, scientists have found 140 rare species of butterflies, including 77 new ones, in Matheran.
- The last time butterflies have codified in this eco-sensitive zone was in 1894, when a researcher identified 78 species.
- Matheran is a hill station and a municipal council in Karjat Tahsil in the Raigad district, Maharashtra. It is located on the Western Ghats range.
- Matheran is part of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region.
- Matheran, which means “forest on the forehead” (of the mountains) is an eco-sensitive region, declared by the Union Ministry of Environment.
2. After the all India handicrafts and handloom boards, the ministry of textiles has disbanded another advisory body — the All India Powerloom Board.
- The All India Powerloom Board was first constituted as an advisory board in 1981. It was reconstituted for a period of two years in 2013.
- It had representatives of central and state governments, Powerloom Federation and was headed by the Union minister of textiles.
- The decision to disband the boards follows an assessment that they failed to impact policy-making and became vehicles of “political patronage”
3.IIT Kanpur has developed indigenous seed balls named BEEG (Bio -compost Enriched Eco-friendly Globule) which will help people and farmers in plantation with safety in Corona times and will also provide employment to people.
- The BEEG is developed in collaboration with Agnys Waste Management Private Limited (start-up at IIT Kanpur).
- The Seed Balls are comprised of indigenous variety of seeds, compost, and clay. There is no need for digging pits for planting saplings .
- These seed balls are to be thrown at aimed places and they will germinate when come into contact with water.
- BEEG is enriched with the right ingredients and seeds to germinate early, and are the best way to utilise Monsoon and plant as many trees as possible without risking lives by social gathering during Covid 19.
4. Educationist Professor Pradeep Kumar Joshi has been appointed as the chairman of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
- Joshi is currently a member in the Commission.
- He will succeed Arvind Saxena.
- Article-316– Appointment and term of office of members:
- The Chairman and other members of a Public Service Commission shall be appointed, in the case of the Union Commission or a Joint Commission, by the President, and in the case of a State Commission, by the Governor of the State.
- A member of a Public Service Commission shall hold office for a term of six years from the date on which he enters upon his office or until he attains, in the case of the Union Commission, the age of sixty-five years, and in the case of a State Commission or a Joint Commission, the age of sixty-two years, whichever is earlier.
5. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) has sent a letter to the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) backing an extension of its arms embargo on Iran, just two months before it is set to expire.
- Gulf Cooperation Council
- It is a political and economic alliance of countries in the Arabian Peninsula.
- It was established in 1981 to foster socioeconomic, security, and cultural cooperation.
- Members: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- All these member countries of the GCC come under the Persian Gulf Region.
- The GCC has alleged that Iran had not ceased or desisted from armed interventions in neighboring countries, directly and through organizations and movements armed and trained by Iran.
- The UN, the USA and other armament experts have accused Iran of providing arms to Yemen’s Houthi rebels.
- Iran allegedly arms Hezbollah fighters in Lebanon and Syria and also provides weapons to Shiite militias in Iraq and terrorist groups in Bahrain, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia.
- The letter also mentioned Iran’s shootdown of a Ukrainian passenger plane and its navy accidentally killing 19 sailors in a missile strike during an exercise.
- Iran also is suspected of launching an attack on Saudi Arabia’s oil industry in September 2019
6. Union Health Minister presided over a review meeting with States/UTs on the “eSanjeevani” and “eSanjeevaniOPD” platforms.
- In a short span of time since November 2019, teleconsultation by eSanjeevani and eSanjeevaniOPD have been implemented by 23 States (which covers 75% of the population) and other States are in the process of rolling it out.
- eSanjeevani, the Tele-Medicine platform rolled out by the Health Ministry, has completed more than 1,50,000 teleconsultations enabling the patient to doctor consultations from the confines of their home, as well as doctor to doctor consultations.
- This eSanjeevani platform has enabled two types of telemedicine services viz. Doctor-to-Doctor (eSanjeevani) and Patient-to-Doctor (eSanjeevani OPD) Tele-consultations. The former is being implemented under the Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centre (AB-HWCs) program.
7. More than 38,000 Indians became Australian citizens in 2019-2020, a 60% increase from the previous year and the largest diaspora group to be granted the country’s citizenship.
- Out of the over 2,00,000 people who became Australian citizens in 2019-2020, 38,209 were Indians, the highest number on record, followed by 25,011 Britishers, 14,764 Chinese, and 8,821 Pakistanis.
- As per the Australian Bureau of Statistics’ 2016 census, 6,19,164 people in Australia declared that they were of ethnic Indian ancestry. This comprises 2.8% of the Australian population.
- Among those, 5,92,000 were born in India.
8. India will take part in the Russian Kavkaz 2020 strategic command-post exercise next month. A small tri-service contingent will take part in the exercise to be held in Astrakhan.
- The Kavkaz 2020 – also referred to as Caucasus-2020 – is an exercise aimed at assessing the ability of the armed forces to ensure military security in Russia’s southwest.
- The invitees also include China and Pakistan, apart from other member-states of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.




