Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 2nd March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- RaIDer-X.
- Dwar Praday Yojana.
- EKAM Fest” in New Delhi.
- Themes for International Women’s Day 2020.
- National Security Guard (NSG) Regional Hub.
- LaCONES:
- Water Crisis in the Himalayan Region.
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species.
- India and Armenia signed deals on DRDO built “Swathi” weapon locating radars.
- National Sports Development Fund.
- Inner line permit.
- USA-Taliban Peace Deal.
- Other important current affairs.
1.RaIDer-X:

RaIDer-X, a new explosive detection device, was unveiled at the National Workshop on Explosive Detection (NWED-2020) in Pune.
- RaIDer-X has been co-developed by High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL) Pune and Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. HEMRL Pune is a premier laboratory of DRDO.
- RaIDer-X has the capability to detect explosives from a stand-off distance.
- The data library can be built in the system to expand its capability to detect a number of explosives in pure form as well as with the contaminants.
- Bulk explosive in a concealed condition can also be detected by the device.
2.Dwar Praday Yojana:

Dwar Praday Yojana (Door Delivery System) is a pilot project that was started in Indore by the Government of Madhya Pradesh.
- Applicants living within the boundaries of the Indore Municipal Corporation (IMC) get five types of documents — domicile certificate, income certificate, birth certificate, death certificate and copy of Khasra-Khatauni (a land ownership document) delivered at their home within 24 hours of applying online.
- The administration has engaged a local courier agency, which delivers the documents after collecting them from public service centres.
- The central idea is to improve the government’s service delivery mechanism.
3.EKAM Fest” in New Delhi.:

Union Minister of Social Justice & Empowerment inaugurated the week-long Exhibition-cum-Fair “EKAM Fest” in New Delhi.
- EKAM Fest is being organised by National Handicapped Finance Development Corporation (NHFDC) under M/o Social Justice & Empowerment.
- The word Ekam stands for Entrepreneurship, Knowledge, Awareness, Marketing. The word also represents the inclusiveness, oneness and unity.
- Ekam Fest aims to promote Craftsmanship & Products of Divyang/Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) Artisans And Entrepreneurs.
- The new initiatives of NHFDC will be showcased in the Fest.
A few are highlighted below:
- NHFDC Swavalamban Kendra (NSK): NHFDC has taken an initiative to establish PwD owned micro skill training Centers throughout the country for skill training of PwDs.
- These NSKs will have the capacity to provide quality skill training to around 120 PwDs per year NSK.
- Safe Cabs in Delhi and Indore: NHFDC has made an arrangement with Sakha Cabs where the PwD owned commercial vehicles will be driven by the Women drivers to provide safe taxi option for the women, children and senior citizen commuters. Such Safe cabs are already in operation at New Delhi and Indore Airport.
About National Handicapped Finance Development Corporation (NHFDC)
- NHFDC is an Apex corporation under the aegis of Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment and is working since 1997.
- It is registered as a company, not for profit and provides financial assistance to the Divyangjan/Persons with Disabilities for their economic rehabilitation and provides the number of skill development programmes to empower them to grow & sustain their enterprises.
4.Themes for International Women’s Day 2020:

The Ministries of Women and Child Development with other ministries have launched a campaign from 1st-7th March to celebrate International Women’s Day (IWD) 8th March 2020.
- The campaign has a theme for all the days beginning from 1st March 2020.
- The themes that are being observed include:
- Education,
- Health and nutrition,
- Empowerment of women,
- Skills & entrepreneurship,
- Participation in sports,
- Rural women agriculture,
- Urban women.
5.National Security Guard (NSG) Regional Hub:

Union Home Minister inaugurated the National Security Guard (NSG) Regional Hub campus at Kolkata.
- This latest NSG complex has become a model regional hub of the NSG, which will help in honing the professional acumen of the NSG commandos and also contribute significantly in capacity building of the first responders, the Police forces of the States.
- The area of responsibility of this Hub comprises of West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand & the entire North East.
- The Kolkata hub is the fourth to have permanent infrastructure after Mumbai, Chennai and Hyderabad.
About National Security Guard (NSG):
- NSG which comprises of Indian Army and CAPFs has multi-dimensional responsibility of countering terrorist attacks/hijack attempts and also providing proximate security.
- Parent agency: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- It was raised in 1984, following Operation Blue Star and the assassination of Indira Gandhi.
- It has been formed under the National Security Guard Act, 1986.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs website, it is one of the 7 Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF).
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
6.LaCONES:

According to a top scientist at the Laboratory for Conservation of Endangered Species (LaCONES), introduction of cheetahs in India will be a big challenge as India first have to adopt International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) protocol to introduce wild animals in the country.
- LaCONES is an acronym for The Laboratory for the Conservation of Endangered Species.
- It is a dedicated Laboratory of CSIR’s Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) in Hyderabad.
- Objective: To use modern biotechnologies for the conservation of endangered wildlife (It supports both the measures of conservation i.e. in situ and ex-situ measures).
- CCMB-LaCONES is the only laboratory in India that has developed methods for collection and cryopreservation of semen and oocytes from wildlife and successfully reproducing endangered blackbuck, spotted deer and Nicobar pigeons.
- Through this work, it has established the Genetic Resource Bank for Indian wildlife.
- Project LaCONES was established in 1998
- The laboratory was itself established in 2007. It is India’s only dedicated laboratory for conservation of endangered species.
7.Water Crisis in the Himalayan Region:
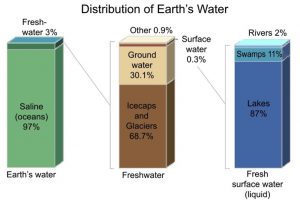
Recently, several towns were surveyed in the Himalayan region of Bangladesh, Nepal, India and Pakistan to understand the challenges of the water crisis in urban areas of these regions.
- Eight towns in the Himalayan region of Bangladesh, Nepal, India and Pakistan were nearly 20%-70% deficient in their water supply.
- The places surveyed are extremely dependent on springs (ranging between 50% and 100%) for their water, and three-fourths were in urban areas.
- Rural areas have typically garnered much of the attention in terms of development and issues surrounding urban environments have been sidelined.
- Factors responsible:
- Unplanned urbanisation
- Climate change
- Across the region, the encroachment and degradation of natural water bodies (springs, ponds, lakes, canals, and rivers) and the growing disappearance of traditional water systems (stone spouts, wells, and local water tanks) are evident.
- Although only 3% of the total Hindu Kush Himalayan population lives in larger cities and 8% in smaller towns, projections show that over 50% of the population will be living in cities by 2050, placing stress on water availability.
- Under current trends, the demand-supply gap may double by 2050.
8.Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species :

With new additions to the wildlife list put out by the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), scientists say that the total number of migratory fauna from India comes to 457 species. Birds comprise 83% (380 species) of this figure.
- The new additions are the Asian elephant, great Indian bustard, Bengal florican, oceanic white-tip shark, urial and smooth hammerhead shark.
- Globally, more than 650 species are listed under the CMS appendices and India, with over 450 species, plays a very important role in their conservation.
Migratory Birds:
- The bird family Muscicapidae has the highest number of migratory species.
- The next highest group of migratory birds is raptors or birds of prey, such as eagles, owls, vultures and kites which are from the family Accipitridae.
- The country has three flyways (flight paths used by birds): the Central Asian flyway, East Asian flyway and East Asian–Australasian Flyway.
- Another group of birds that migrate in large numbers are waders or shorebirds.
- In India, their migratory species number 41, followed by ducks (38) belonging to the family Anatidae.
Migratory Mammals:
- The estimate of 44 migratory mammal species in India has risen to 46 after COP 13.
- The Asian elephant was added to Appendix I and the urial to Appendix II.
- The largest group of mammals is definitely bats belonging to the family Vespertilionidae.
- Dolphins are the second-highest group of mammals with nine migratory species of dolphins listed.
Migratory Fish:
- The total number of migratory fish species from India under CMS now stands at 24.
- The oceanic white-tip shark and smooth hammerhead shark are the new additions to the list.
Migratory Reptiles:
- Seven reptiles, which include five species of turtles and the Indian gharial and saltwater crocodile, are among the CMS species found in India. There was no addition to the reptiles list.
9. India and Armenia signed deals on DRDO built “Swathi” weapon locating radars:

India bagged a deal to supply 4 indigenously built radars (capable of locating weapons) to Armenia. The deal was worth 40 million USD.
- India and Armenia signed deals on DRDO built “Swathi” weapon locating radars.
- Armenia has decided to go with Indian built radars after testing Russian and Poland made systems.
- Armenia also claims that Indian made systems were more reliable as compared to the other two.
Swathi Radar:
- The Radar is capable of handling multiple weapons at different locations.
- Currently, the Indian army is also using the same radar along the line of control to trace the source of an attack of the Pakistan army.
The Deal will help India achieve its Rs 35,000 crores of defence exports very soon.
10.National Sports Development Fund:
Under CSR initiative, Security Printing & Minting Corporation of India (SPMCIL) contributes Rs 1 crore towards the National Sports Development Fund.
- NSDF: Established in 1998 under the Charitable Endowments Act 1890 and notified by Government of India in November 1998.
- Purpose of creation is to impart momentum and flexibility in assisting the cause of sports.
- Role of the Fund is supplementary to the overall policy and activities of the Department of Sports in achieving excellence in sports.
11.Inner line permit:

Tribal organisations in Meghalaya have been demanding the ILP system for restricting the entry of outsiders into the State. These demands have turned into violent protests across the state in the past few days.
Inner line permit:
- It is a document required by non- natives to visit or stay in a state that is protected under the ILP system.
- At present, four Northeastern states are covered, namely, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Nagaland.
- Both the duration of stay and the areas allowed to be accessed for any non-native are determined by the ILP.
- The ILP is issued by the concerned state government and can be availed both by applying online or in person.
The Inner Line Permit is an extension of the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act 1873.
- The Britishers framed regulations restricting entry in certain designated areas.
- This was done to protect the Crown’s interest in certain states by preventing “British subjects” (Indians) from trading within these regions.
- In 1950, the term ‘British subjects’ was replaced with ‘Citizens of India’. Today, all non-natives require the permit.
- This was done to protect the indigenous tribal communities of these states from exploitation.
12.USA-Taliban Peace Deal:

The United States has signed a historic deal with Taliban insurgents that could pave the way for ending the 18-year-war in Afghanistan.
- The deal was signed in Doha (Qatar) and thus termed as Doha Agreement.
- India has welcomed the signing of the U.S.-Taliban peace deal by accepting an invitation to attend the meeting for the same in Doha.
Key Elements of the Deal:
- The agreement set out a course for the next 14 months.
- Comprehensive Ceasefire between the Afghan Government and Taliban.
- Timeline for the withdrawal of all foreign forces from Afghanistan will be carried out, provided the Taliban adhere to their security guarantees and ceasefire.
- The prevention of the use of Afghanistan by any group or individual against the security of the United States and its allies.
- The facilitation of an intra-Afghan dialogue.
- The participants of intra-Afghan negotiations will discuss the date and modalities of a permanent and comprehensive ceasefire, including agreement over the future political roadmap of Afghanistan.
- In turn, the Taliban has demanded the release of 5000 fighters from Afghan-run jails.
Other important current affairs:
1. Maj Gen Madhuri Kanitkar was elevated to the rank of Lieutenant General, becoming the third woman officer in the Army and first paediatrician from the armed forces to hold the rank.
- Lt Gen Kanitkar took charge as Deputy Chief, Integrated Defence Staff (DCIDS), Medical (under Chief of Defence Staff), in New Delhi.
- Lt Gen Kanitkar has served for 37 years. She and husband Rajiv, also a Lt Gen, will be the first couple in the armed forces to hold this rank.
- She is the first trained paediatric nephrologist in the armed forces and is also a member of the Prime Minister’s scientific and technical advisory board.
- Lt Gen Punita Arora was the first woman officer to hold the rank. Padmavathy Bandopadhyay is the first woman Air Marshal of Indian Air Force, and the second woman officer in the armed forces to be promoted to a three-star officer rank.
2.Araku Utsav 2020:
- The two-day festival Araku Utsav 2020 is being held at Araku Valley in Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh.
- It is being organized by the Andhra Pradesh Government.
- The aim of organising this festival was to spread the tribal tradition and culture to other regions.
- Such events would also put Araku – often referred to as Ooty of Andhra – on a global map.
3. Scotland may become the first country in the world to end ‘period poverty’ by making sanitary products free for all.
- The Scottish Parliament passed the Period Products (Free Provision) (Scotland), Bill.
- Referring to “period dignity”, the legislation aims to develop a universal system in Scotland, which will provide free sanitary products for “anyone who needs them”.
- As of now, in Scotland, the provision of free sanitary products is already available in schools, universities and colleges.
- The Bill has only passed the first hurdle to become a law. It still needs to be considered by a parliamentary committee, following which it will require approval from the parliament. It will finally need the Royal Assent of the Queen.
- What is ‘period poverty’: Some circumstances make menstruation a “difficult experience” for women.
- These include homelessness, coercive, controlling and violent relationships and health conditions such as endometriosis. Some trans people may also experience difficulties in accessing sanitary products.
4. Zero Discrimination Day was observed globally.
- The day was observed to challenge discrimination and inequality faced by women and girls.
- It aims to protect the rights of women and promote their empowerment and gender equality.
- Theme: Zero Discrimination against Women and Girls
5. The Indian Meteorological Department has announced that months of March, April and May are to be warmer than normal. The heatwaves are to prevail over the heatwave zones of India
- The Core Heat Wave zone of India includes Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh. Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Telangana.
- In India, heat waves are experienced from March to July
- According to the World Meteorological Organization, a Heat Wave occurs when the daily maximum temperature of 5 consecutive days exceeds average maximum temperature by 5 degrees Celsius.
- During a heatwave, the weather is excessively hot and also highly humid. Heat Waves usually occur in oceanic countries.
6. The Asian Development Bank is to provide 4 million USD to member countries in Asia and Pacific to contain COVID-19, the Corona Virus.
- The fund is being allocated for buying emergency supplies, assessing health systems, improve resilience and respond to animal-human disease outbreaks.
8. Corona Virus: WHO increases Global threat; US postpones ASEAN; Geneva International Motor Show Cancelled
- The COVID-19 (Corona Virus), that began in China has now spread to more than 45 countries.
- Outside China, South Korea has the highest number of COVID-19 victims.
- On February 29, 2020, the World Health Organization increased the global risk of COVID-19.
- This was because the endemic has now spread to sub-Saharan Africa and has plunged financial markets. WHO also says that more than 20 vaccines for the virus are under development globally.
- India has banned travel to China and Iran. Several airlines have restricted their flights to Hong Kong and Singapore.
9.Eurasian Otter:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Protection: CITES: Appendix I, Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II.
- Habitat: Found throughout Europe and in Asia.
- In India, the species is distributed in the Himalayan foothills, southern Western Ghats and the central Indian landscape.
- Spotted in Chilika lake.




